P M E S
... Overall, the largest source of mortality to sea turtles is bycatch during normal fishing operations.3,4 Most of the turtles harmed in this way are juveniles or sub-adults that are critical to the stability and recovery of marine turtle populations.5 Tens of thousands of leatherback and loggerhead t ...
... Overall, the largest source of mortality to sea turtles is bycatch during normal fishing operations.3,4 Most of the turtles harmed in this way are juveniles or sub-adults that are critical to the stability and recovery of marine turtle populations.5 Tens of thousands of leatherback and loggerhead t ...
SALCC indicator recommendations
... Number of dams mimicking natural flow provides an indicator of departures from the natural flow regime where flow is already being altered and is generally easy to monitor. A dam “mimicking natural flow” will be defined as a dam with at least one measure in it’s operation plan that is intended to im ...
... Number of dams mimicking natural flow provides an indicator of departures from the natural flow regime where flow is already being altered and is generally easy to monitor. A dam “mimicking natural flow” will be defined as a dam with at least one measure in it’s operation plan that is intended to im ...
pdf em inglês
... The predominance of L. castaneus in the present study corroborated that observed by Araújo and Santos, (2001). The greater abundance of this species, in both collection times of the present study, and the fact of corresponding to 50% of the biomass of fishes collected in the Ribeirão das Lajes reser ...
... The predominance of L. castaneus in the present study corroborated that observed by Araújo and Santos, (2001). The greater abundance of this species, in both collection times of the present study, and the fact of corresponding to 50% of the biomass of fishes collected in the Ribeirão das Lajes reser ...
Hungry Oceans: What Happens When the Prey is Gone?
... without enough energy to reproduce. Scrawny predators—dolphins, striped bass, and even whales—have turned up along coastlines around the world. Recreational fishermen are losing both their target fish—and their bait. Fishing communities are losing their livelihoods. Because we have overlooked hungry ...
... without enough energy to reproduce. Scrawny predators—dolphins, striped bass, and even whales—have turned up along coastlines around the world. Recreational fishermen are losing both their target fish—and their bait. Fishing communities are losing their livelihoods. Because we have overlooked hungry ...
j.0022-1112.2005.00934.x.doc
... total CPUE (all fishes). Depth measurements were converted to 5 semi-quantitative categories for the analyses (<20, 21–30, 31–40, 41–50 and >50 cm). This enabled the analysis of the role of depth in the variation of CPUE and fish size without assuming linear relationships, as would have been the ca ...
... total CPUE (all fishes). Depth measurements were converted to 5 semi-quantitative categories for the analyses (<20, 21–30, 31–40, 41–50 and >50 cm). This enabled the analysis of the role of depth in the variation of CPUE and fish size without assuming linear relationships, as would have been the ca ...
some features of ecosystems
... In describing a community, its biodiversity is important. However, simple taxonomic lists are inadequate because they ignore the numerical importance of each taxon. For example, most grassland communities contain ten common types of grass, at times called key grasses, which support the bulk of the l ...
... In describing a community, its biodiversity is important. However, simple taxonomic lists are inadequate because they ignore the numerical importance of each taxon. For example, most grassland communities contain ten common types of grass, at times called key grasses, which support the bulk of the l ...
Chapter 10 Notes
... Biodiversity in the United States • The United States includes a wide variety of unique ecosystems, including the Florida Everglades, the California coastal region, Hawaii, the Midwestern prairies, and the forests of the Pacific Northwest. • The United States holds unusually high numbers of species ...
... Biodiversity in the United States • The United States includes a wide variety of unique ecosystems, including the Florida Everglades, the California coastal region, Hawaii, the Midwestern prairies, and the forests of the Pacific Northwest. • The United States holds unusually high numbers of species ...
Chapter 6: Biological Resources and Biodiversity of Dutchess
... the principal cause of habitat fragmentation at present is expansion of residential land uses (see Historic Changes and Current Threats to Biodiversity section below). Interior habitat (or core habitat) and edge habitat are often considered ecologically distinct because some species avoid edges—such ...
... the principal cause of habitat fragmentation at present is expansion of residential land uses (see Historic Changes and Current Threats to Biodiversity section below). Interior habitat (or core habitat) and edge habitat are often considered ecologically distinct because some species avoid edges—such ...
Environmental context determines multi-trophic effects of consumer species loss
... The role of consumers includes both direct and indirect effects on lower trophic levels (Wootton, 1994) and recent work has yielded important insights into the direct and indirect effects of consumer species loss on ecosystem functioning and stability (O’Connor & Bruno, 2007; Griffin et al., 2008; O ...
... The role of consumers includes both direct and indirect effects on lower trophic levels (Wootton, 1994) and recent work has yielded important insights into the direct and indirect effects of consumer species loss on ecosystem functioning and stability (O’Connor & Bruno, 2007; Griffin et al., 2008; O ...
Unexpected response in community following increased fish predation
... The impact of increased fish density on the crustacean zooplankton was studied in a small, forest lake. Interestingly and contrary to our hypothesis, increased fish density resulted in an increase in biomass of large-sized cladocerans, but a decrease in biomass of smaller and dominant cladoceran spe ...
... The impact of increased fish density on the crustacean zooplankton was studied in a small, forest lake. Interestingly and contrary to our hypothesis, increased fish density resulted in an increase in biomass of large-sized cladocerans, but a decrease in biomass of smaller and dominant cladoceran spe ...
Jellyfish in the Bering Sea
... The increased biomass of medusae may be related to changes in the general circulation of the atmosphere, which helps determine sea surface temperature (SST) and annual extent of sea ice. One way of quantifying these atmospheric circulation changes is through the use of teleconnection patterns. Telec ...
... The increased biomass of medusae may be related to changes in the general circulation of the atmosphere, which helps determine sea surface temperature (SST) and annual extent of sea ice. One way of quantifying these atmospheric circulation changes is through the use of teleconnection patterns. Telec ...
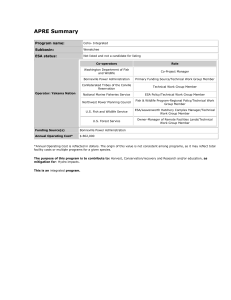
Coho- Integrated - Northwest Power and Conservation Council
... stock) is being used as initial broodstock. These fish would came as smolts from Willard or Cascade hatcheries. In 2000, 700,000 smolts came from Cascade and 400,000 from Eagle Creek, but Eagle Creek is no longer used as a source. The numbers from each hatchery are negotiated annually, but the fish ...
... stock) is being used as initial broodstock. These fish would came as smolts from Willard or Cascade hatcheries. In 2000, 700,000 smolts came from Cascade and 400,000 from Eagle Creek, but Eagle Creek is no longer used as a source. The numbers from each hatchery are negotiated annually, but the fish ...
Natural mortality and fishing mortality estimation
... of each size class survive through to the next age class (and ultimately to contribute to reproduction of a stock) • If M is very high then F may need to be relatively low (as you cannot control M) • M may limit/restrict total fishing mortality rate (F) of an age/size-class or stock if M is extremel ...
... of each size class survive through to the next age class (and ultimately to contribute to reproduction of a stock) • If M is very high then F may need to be relatively low (as you cannot control M) • M may limit/restrict total fishing mortality rate (F) of an age/size-class or stock if M is extremel ...
Do ectotherms partition thermal resources? We still do not know
... partitioning to reduce interspecific competition (Fig. 1). Imagine two lizard species (species A and B) that occupy forest habitats with sunny patches. Originally, both species have similar thermal traits (e.g., optimal and preferred body temperatures) and live on tree trunks where they defend small ...
... partitioning to reduce interspecific competition (Fig. 1). Imagine two lizard species (species A and B) that occupy forest habitats with sunny patches. Originally, both species have similar thermal traits (e.g., optimal and preferred body temperatures) and live on tree trunks where they defend small ...
Diversity among Macroalgae-Consuming Fishes on Coral Reefs: A
... small subset of taxa are capable of removing dominant macroalgae once these become established. This limited functional redundancy highlights the potential vulnerability of coral reefs to disturbance and stresses the need to assess the functional role of individual species of herbivores. However, ou ...
... small subset of taxa are capable of removing dominant macroalgae once these become established. This limited functional redundancy highlights the potential vulnerability of coral reefs to disturbance and stresses the need to assess the functional role of individual species of herbivores. However, ou ...
Functional traits, productivity and effects on nitrogen
... and ecosystem traits of a wide variety of grassland species grown under field conditions in the long term. We measured 87 traits for 33 species (32 perennial, one annual) grown in monoculture for 5 years on sandy soils, and determined the relationship among traits and their correspondence with curre ...
... and ecosystem traits of a wide variety of grassland species grown under field conditions in the long term. We measured 87 traits for 33 species (32 perennial, one annual) grown in monoculture for 5 years on sandy soils, and determined the relationship among traits and their correspondence with curre ...
Metaâ•`analysis of the effects of small mammal
... marmots, which with woodchucks were the only species above 1 kg included in our database. Based on the species identified during this phase, we conducted searches in Web of Science and Google Scholar using the terms ‘richness’, ‘diversity’ and ‘biomass’ combined with the scientific species names of ...
... marmots, which with woodchucks were the only species above 1 kg included in our database. Based on the species identified during this phase, we conducted searches in Web of Science and Google Scholar using the terms ‘richness’, ‘diversity’ and ‘biomass’ combined with the scientific species names of ...
D 56. Shachak et al. 2008. Woody sp.as landscape modulators
... landscape modulation are less developed. The concept of organisms as ecosystem engineers, which focuses on modulation processes, is relatively new and lacks a comprehensive theoretical background (Wright and Jones 2006). Ecosystem engineers are defined as “organisms that directly or indirectly modul ...
... landscape modulation are less developed. The concept of organisms as ecosystem engineers, which focuses on modulation processes, is relatively new and lacks a comprehensive theoretical background (Wright and Jones 2006). Ecosystem engineers are defined as “organisms that directly or indirectly modul ...
Evidence for the Role of Infectious Disease in Species Extinction
... three generations or 10 years, whichever is longer (not exceeding 100 years in the future) (IUCN 2004). A threat that occurred in the past, is occurring in the present, or may occur in the future is cited as ongoing (IUCN 2004). For each species account, we recorded the time frame of the threat. Bas ...
... three generations or 10 years, whichever is longer (not exceeding 100 years in the future) (IUCN 2004). A threat that occurred in the past, is occurring in the present, or may occur in the future is cited as ongoing (IUCN 2004). For each species account, we recorded the time frame of the threat. Bas ...
La biodiversité, c`est la vie - doc-developpement
... Living species ("Life") would have appeared on Earth, there are 3.6 billion years, all from originally single-celled species (bacteria or virus?). • There are between 5 and 30 million species on Earth. [11] But only 1.5 to 1.8 million plant and animal species have been described / listed scientifica ...
... Living species ("Life") would have appeared on Earth, there are 3.6 billion years, all from originally single-celled species (bacteria or virus?). • There are between 5 and 30 million species on Earth. [11] But only 1.5 to 1.8 million plant and animal species have been described / listed scientifica ...
A stoichiometric exception to the competitive exclusion principle.
... or zero. (One notable exception to this rule is Levin’s (1970) extension of the CEP, where resources were replaced with more abstract “limiting factors.” Levin’s formulation requires only that species-specific growth rates be linear ...
... or zero. (One notable exception to this rule is Levin’s (1970) extension of the CEP, where resources were replaced with more abstract “limiting factors.” Levin’s formulation requires only that species-specific growth rates be linear ...
Overexploitation

Overexploitation, also called overharvesting, refers to harvesting a renewable resource to the point of diminishing returns. Sustained overexploitation can lead to the destruction of the resource. The term applies to natural resources such as: wild medicinal plants, grazing pastures, game animals, fish stocks, forests, and water aquifers.In ecology, overexploitation describes one of the five main activities threatening global biodiversity. Ecologists use the term to describe populations that are harvested at a rate that is unsustainable, given their natural rates of mortality and capacities for reproduction. This can result in extinction at the population level and even extinction of whole species. In conservation biology the term is usually used in the context of human economic activity that involves the taking of biological resources, or organisms, in larger numbers than their populations can withstand. The term is also used and defined somewhat differently in fisheries, hydrology and natural resource management.Overexploitation can lead to resource destruction, including extinctions. However it is also possible for overexploitation to be sustainable, as discussed below in the section on fisheries. In the context of fishing, the term overfishing can be used instead of overexploitation, as can overgrazing in stock management, overlogging in forest management, overdrafting in aquifer management, and endangered species in species monitoring. Overexploitation is not an activity limited to humans. Introduced predators and herbivores, for example, can overexploit native flora and fauna.