Battle of Gettysburg Article Review
... rebel casualties, and Lee was forced to withdraw his battered army toward Virginia on July 4. Battle of Gettysburg: Lee’s Invasion of the North In May 1863, Robert E. Lee’s Confederate Army of Northern Virginia had scored a smashing victory over the Army of the Potomac at Chancellorsville. Brimming ...
... rebel casualties, and Lee was forced to withdraw his battered army toward Virginia on July 4. Battle of Gettysburg: Lee’s Invasion of the North In May 1863, Robert E. Lee’s Confederate Army of Northern Virginia had scored a smashing victory over the Army of the Potomac at Chancellorsville. Brimming ...
states - Issaquah Connect
... were elated to get slaves back but angry at lack of Northern support. (Judges who sent slaves back to the South were awarded with $10 for their work; but only $5 if person in question was freed!!) ...
... were elated to get slaves back but angry at lack of Northern support. (Judges who sent slaves back to the South were awarded with $10 for their work; but only $5 if person in question was freed!!) ...
Divided Loyalties - Deer Creek High School
... was guerrilla warfare, or small military groups that attack and annoy the enemy. The most successful guerrillas were led by Colonel William Quantrill, a Confederate raider based in Kansas. One of his men was Jesse James. ...
... was guerrilla warfare, or small military groups that attack and annoy the enemy. The most successful guerrillas were led by Colonel William Quantrill, a Confederate raider based in Kansas. One of his men was Jesse James. ...
The Furnace of Civil War 1861-1865
... farmers that the war’s burdens were being shared equally – a hard sell to poor people forced to give up necessities while the planters only had to make do without luxuries The Confederate draft law itself became an issue because (1) it allowed a man with money to hire a ‘substitute’ to take his plac ...
... farmers that the war’s burdens were being shared equally – a hard sell to poor people forced to give up necessities while the planters only had to make do without luxuries The Confederate draft law itself became an issue because (1) it allowed a man with money to hire a ‘substitute’ to take his plac ...
Chapter 11: The Civil War
... a. blockade Southern ports b. divide Confederacy in two in west c. capture Richmond, Confederate capital 4. Confederate strategy: defense, invade North if opportunity arises B. Bull Run 1. first battle, near Washington; Confederate victory 2. Thomas J. Jackson called Stonewall Jackson for firm stand ...
... a. blockade Southern ports b. divide Confederacy in two in west c. capture Richmond, Confederate capital 4. Confederate strategy: defense, invade North if opportunity arises B. Bull Run 1. first battle, near Washington; Confederate victory 2. Thomas J. Jackson called Stonewall Jackson for firm stand ...
Antietam - NPS History eLibrary
... the Federals back to the heights near the bridge they had just taken. The Battle of Antietam was over. Throughout the day of September 18, the armies faced each other without further fighting. That night Lee withdrew his army to the Potomac at Blackford's Ford and crossed into Virginia. Neither side ...
... the Federals back to the heights near the bridge they had just taken. The Battle of Antietam was over. Throughout the day of September 18, the armies faced each other without further fighting. That night Lee withdrew his army to the Potomac at Blackford's Ford and crossed into Virginia. Neither side ...
Chapter 19 – Section 5 – The Tide of the War Turns In May 1863
... reached the top of the ridge. All those who reached the Union wall were captured or killed. Only about 6,500 men returned to the Confederate rear. Lee ordered Pickett to organize his division for a possible counterattack. Rain slowed Meade’s troops, allowing Lee to retreat from Gettysburg on July 4 ...
... reached the top of the ridge. All those who reached the Union wall were captured or killed. Only about 6,500 men returned to the Confederate rear. Lee ordered Pickett to organize his division for a possible counterattack. Rain slowed Meade’s troops, allowing Lee to retreat from Gettysburg on July 4 ...
Chapter 15- Secession and the Civil War (upload)
... Jefferson Davis did not adequately address problems on home front ...
... Jefferson Davis did not adequately address problems on home front ...
File
... effort to divide the Confederacy by seizing control of the Mississippi River, and major offensives into the Confederate hinterlands. The Confederacy first tried to defend all of its borders, but for most of the war Jefferson Davis and his advisers followed what often is termed a defensive-offensive ...
... effort to divide the Confederacy by seizing control of the Mississippi River, and major offensives into the Confederate hinterlands. The Confederacy first tried to defend all of its borders, but for most of the war Jefferson Davis and his advisers followed what often is termed a defensive-offensive ...
Worksheet by RJ Tarr at www.activehistory.co.uk / 1 ActiveHistory
... In the March to the Sea (Nov-Dec 1864, Atlanta) General Sherman pushed from the south across Georgia, capturing the state capital of Atlanta and leaving a path of destruction in his wake. In the Battle of Appomattox Courthouse (April 9th 1865, Virginia), General Grant surrounded the forces of Genera ...
... In the March to the Sea (Nov-Dec 1864, Atlanta) General Sherman pushed from the south across Georgia, capturing the state capital of Atlanta and leaving a path of destruction in his wake. In the Battle of Appomattox Courthouse (April 9th 1865, Virginia), General Grant surrounded the forces of Genera ...
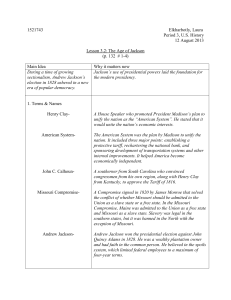
sectionalism, Andrew Jackson`s
... Wilde, 1821). He is explaining that people needed slaves in order to survive and keep their farms going. To settle the North and South’s differences, Henry Clay promoted the American System that would unify the nation’s economic interests. Andrew Jackson won the Presidential election in 1828 and was ...
... Wilde, 1821). He is explaining that people needed slaves in order to survive and keep their farms going. To settle the North and South’s differences, Henry Clay promoted the American System that would unify the nation’s economic interests. Andrew Jackson won the Presidential election in 1828 and was ...
Key Civil War Battles
... • Who: (U) Ulysses S. Grant, (C) Beauregard, Sidney Johnston • Where: Corinth, Mississippi • Why? • Goal of the West is to gain control of the Miss River • What/How: Confederates launch surprise attack • Day 1: Grant driven back • Day 2: Union recovers, defeat Confederates ...
... • Who: (U) Ulysses S. Grant, (C) Beauregard, Sidney Johnston • Where: Corinth, Mississippi • Why? • Goal of the West is to gain control of the Miss River • What/How: Confederates launch surprise attack • Day 1: Grant driven back • Day 2: Union recovers, defeat Confederates ...
THE CIVIL WAR
... •Union Strategies: blockade southern ports, split Confederate forces at Miss. River, capture Richmond: Anaconda Plan •Confederate Strategies: be on defensive, encouraged attacks, try to invade North ...
... •Union Strategies: blockade southern ports, split Confederate forces at Miss. River, capture Richmond: Anaconda Plan •Confederate Strategies: be on defensive, encouraged attacks, try to invade North ...
Chapter Twenty-One: The Furnace of Civil War
... B. George G. Meade at Gettysburg 1) Fortified a Union position at Gettysburg with 92,000 troops 2) Attacked by Lee’s 76,000 troops July 1-3, 1863 3) Failed after Pickett’s charge was turned back 4) Lincoln turned back Jefferson’s delegation at the Union line, which had been sent to negotiate peace i ...
... B. George G. Meade at Gettysburg 1) Fortified a Union position at Gettysburg with 92,000 troops 2) Attacked by Lee’s 76,000 troops July 1-3, 1863 3) Failed after Pickett’s charge was turned back 4) Lincoln turned back Jefferson’s delegation at the Union line, which had been sent to negotiate peace i ...
Anaconda Plan - OCPS TeacherPress
... Step 3 – Take Over the Confederate Capital of Richmond, Virginia Once Alabama seceded in 1861, they invited the other seceding states to join them in their capital of Montgomery, Alabama. Montgomery quickly became the acting capital of the Confederate States of America. It is here where they wrote ...
... Step 3 – Take Over the Confederate Capital of Richmond, Virginia Once Alabama seceded in 1861, they invited the other seceding states to join them in their capital of Montgomery, Alabama. Montgomery quickly became the acting capital of the Confederate States of America. It is here where they wrote ...
The Civil War - Fairview Blogs
... 2. Battle of Bull Run (Manassas, VA) July 21, 1861 – southern victory (Stonewall Jackson hero) 3. U.S. Grant fights on Miss. River in west (Fort Henry & Fort Donaldson in TN) – Union victories. Gen. Farragut seizes New Orleans ...
... 2. Battle of Bull Run (Manassas, VA) July 21, 1861 – southern victory (Stonewall Jackson hero) 3. U.S. Grant fights on Miss. River in west (Fort Henry & Fort Donaldson in TN) – Union victories. Gen. Farragut seizes New Orleans ...
final exam review.xlsx
... anti-slavery party with strong ties to the northern states a Missouri slave who sued for his freedom chief justice of Supreme Court that ruled against Scott Republican politician from Illinois who opposed Kansas-Nebraska Act an Illinois politician, rival to Lincoln, who supported Kansas-Nebraska Act ...
... anti-slavery party with strong ties to the northern states a Missouri slave who sued for his freedom chief justice of Supreme Court that ruled against Scott Republican politician from Illinois who opposed Kansas-Nebraska Act an Illinois politician, rival to Lincoln, who supported Kansas-Nebraska Act ...
5 Sparks Civil War North Vs South
... The Confederacy adopted a defensive strategy and attempted to secure alliances with more powerful countries such as Britain and France. To do that, the South needed to show it could win the war. As a result, the Confederate army attacked Union territory to draw Union troops away from the South and t ...
... The Confederacy adopted a defensive strategy and attempted to secure alliances with more powerful countries such as Britain and France. To do that, the South needed to show it could win the war. As a result, the Confederate army attacked Union territory to draw Union troops away from the South and t ...
Antietam The Civil War`s Bloodiest Day
... James H. Hillestad, Member No.6, chronicles the battle of Antietam (Sharpsburg) and the role that a nondescript cornfield would play in the final outcome. fter repelling the Army of the Potomac’s invasion of Virginia and the subsequent major Confederate victory at the Second Battle of Bull Run, Robe ...
... James H. Hillestad, Member No.6, chronicles the battle of Antietam (Sharpsburg) and the role that a nondescript cornfield would play in the final outcome. fter repelling the Army of the Potomac’s invasion of Virginia and the subsequent major Confederate victory at the Second Battle of Bull Run, Robe ...
Name Period - Humble ISD
... Describe the typical person who fought for each of the war (not only physically or what they wore) Northern Soldier Southern Soldier About half of the soldiers came from farms and had rarely traveled far from their fields. Some had never ridden a train before. Fewer than 1 million served; most of th ...
... Describe the typical person who fought for each of the war (not only physically or what they wore) Northern Soldier Southern Soldier About half of the soldiers came from farms and had rarely traveled far from their fields. Some had never ridden a train before. Fewer than 1 million served; most of th ...
unit 5: the nation breaks apart
... 2. African Americans participated in the war in a variety of ways. a. African Americans volunteered to fight. b. The War Department gave contrabands, or escaped slaves, the right to join the army in South Carolina. c. The mainly African American 54th Massachusetts Infantry was celebrated for its bra ...
... 2. African Americans participated in the war in a variety of ways. a. African Americans volunteered to fight. b. The War Department gave contrabands, or escaped slaves, the right to join the army in South Carolina. c. The mainly African American 54th Massachusetts Infantry was celebrated for its bra ...
The First Minnesota and the Battle of Gettysburg
... of withering Yankee rifle fire. The Confeder- Confederate forces crossed this field during Pickett’s Charge, aiming for ate flanks soon collapsed, but their spearUnion lines that were spread across the horizon on Cemetery Ridge. head managed to drive through the Union lines and into a clump of trees ...
... of withering Yankee rifle fire. The Confeder- Confederate forces crossed this field during Pickett’s Charge, aiming for ate flanks soon collapsed, but their spearUnion lines that were spread across the horizon on Cemetery Ridge. head managed to drive through the Union lines and into a clump of trees ...
THE CIVIL WAR - Warren County Schools
... - Four other slaveholding states might have seceded, but instead remained in the Union - The decision of Delaware, Maryland, Missouri, & Kentucky not to join the Confederacy was partly due to Union sentiment in those states & partly the result of federal policies - In Maryland, pro-secessionists att ...
... - Four other slaveholding states might have seceded, but instead remained in the Union - The decision of Delaware, Maryland, Missouri, & Kentucky not to join the Confederacy was partly due to Union sentiment in those states & partly the result of federal policies - In Maryland, pro-secessionists att ...
Chapter 15 Section 1
... often used a nearby creek or natural landform. The South often used a nearby city or structure. *Union General Irvin McDowell wanted time to train his soldiers but northern newspapers were demanding the capture of Richmond and a quick end to the war. *McDowell’s 30,000 men left DC and marched 25 mil ...
... often used a nearby creek or natural landform. The South often used a nearby city or structure. *Union General Irvin McDowell wanted time to train his soldiers but northern newspapers were demanding the capture of Richmond and a quick end to the war. *McDowell’s 30,000 men left DC and marched 25 mil ...
Battle of Wilson's Creek

The Battle of Wilson's Creek, also known as the Battle of Oak Hills, was the first major battle of the Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War. Fought on August 10, 1861, near Springfield, Missouri, between Union forces and the Missouri State Guard, it is sometimes called the ""Bull Run of the West.""Despite Missouri's neutral status at the beginning of the war, tensions escalated between Federal forces and state forces in the months leading up to the battle. In early August 1861, Confederate troops under the command of Brig. Gen. Benjamin McCulloch approached Brig. Gen. Nathaniel Lyon's Army of the West, which was camped at Springfield. On August 9, both sides formulated plans to attack the other. At about 5:00 a.m. on August 10, Lyon, in two columns commanded by himself and Col. Franz Sigel, attacked the Confederates on Wilson's Creek about 12 miles (19 km) southwest of Springfield. Confederate cavalry received the first blow and retreated from the high ground, later referred to as ""Bloody Hill,"" and infantry soon rushed up to stabilize their positions. The Confederates attacked the Union forces three times during the day but failed to break through the Union line. When General Lyon was killed during the battle and General Thomas William Sweeny wounded, Major Samuel D. Sturgis assumed command of the Union forces. Meanwhile, the Confederates had routed Sigel's column south of Skegg's Branch. Following the third Confederate attack, which ended at 11:00 a.m., the Union withdrew. When Sturgis realized that his men were exhausted and lacking ammunition, he ordered a retreat to Springfield. The Confederates were too disorganized and ill-equipped to pursue.The Confederate victory buoyed Southern sympathizers in Missouri and served as a springboard for a bold thrust north that carried Sterling Price and his Missouri State Guard as far as Lexington. In late October, a convention organized by Governor Claiborne Fox Jackson met in Neosho and passed out an ordinance of secession. Although the state remained in the Union for the remainder of the war, the Battle of Wilson's Creek effectively gave the Confederates control of southwestern Missouri. Today, the National Park Service operates Wilson's Creek National Battlefield on the site of the original conflict.