Civil War
... secede from the Union and viewed them as outlaws not citizens of another country • Southern leaders – put loyalty to their home state above everything else and fought for the protection * See Key Leaders of their homes and property chart provided by the teacher (some did not support secession) ...
... secede from the Union and viewed them as outlaws not citizens of another country • Southern leaders – put loyalty to their home state above everything else and fought for the protection * See Key Leaders of their homes and property chart provided by the teacher (some did not support secession) ...
Civil War Maps
... • Label each state (abbreviation) and the year that each Confederate state seceded from the Union. • Label (•) the following battle sites: Ft. Sumter, Antietam, Gettysburg, and Chattanooga -- Include the year of each battle! • Label the Mississippi River and Atlantic Ocean. • Label the Anaconda plan ...
... • Label each state (abbreviation) and the year that each Confederate state seceded from the Union. • Label (•) the following battle sites: Ft. Sumter, Antietam, Gettysburg, and Chattanooga -- Include the year of each battle! • Label the Mississippi River and Atlantic Ocean. • Label the Anaconda plan ...
Military Leadership in the Civil War
... together at West Point When the war broke out, many of the officers had to choose which side to work for. ...
... together at West Point When the war broke out, many of the officers had to choose which side to work for. ...
Civil War Review Sheet
... Identify and Put in Chronological Order the Following Civil War Events: End of Siege at Vicksburg Battle of Gettysburg Secession of South Carolina Surrender at Appomattox Court House Battle of 2nd Bull Run End of Peninsular Campaign Battle of the Merrimac v. Monitor ...
... Identify and Put in Chronological Order the Following Civil War Events: End of Siege at Vicksburg Battle of Gettysburg Secession of South Carolina Surrender at Appomattox Court House Battle of 2nd Bull Run End of Peninsular Campaign Battle of the Merrimac v. Monitor ...
Chapter 11 Section 2
... the union army in the east after Gen. McDowell’s defeat at the first Battle of Bull Run. Goal is to capture the CSA capital. McClellan develops the peninsula campaign: a plan to assemble troops near Yorktown, VA and march them up a peninsula where the James and York rivers meet up to Richmond. Thi ...
... the union army in the east after Gen. McDowell’s defeat at the first Battle of Bull Run. Goal is to capture the CSA capital. McClellan develops the peninsula campaign: a plan to assemble troops near Yorktown, VA and march them up a peninsula where the James and York rivers meet up to Richmond. Thi ...
Chapter 16:2 Early Years of the War
... leader is going to lead his 1200 troopers in a circle around the Union forces that are advancing under McClellan. McClellan will be surrounded before he even knows what happened to him! Scene Setter: The meeting of the Union and Rebel forces became known as the Seven Days Battle. The Union Army was ...
... leader is going to lead his 1200 troopers in a circle around the Union forces that are advancing under McClellan. McClellan will be surrounded before he even knows what happened to him! Scene Setter: The meeting of the Union and Rebel forces became known as the Seven Days Battle. The Union Army was ...
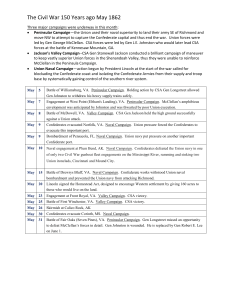
The Civil War 150 Years ago May 1862
... The Civil War 150 Years ago May 1862 Three major campaigns were underway in this month: Peninsular Campaign—the Union used their naval superiority to land their army SE of Richmond and move NW to attempt to capture the Confederate capital and thus end the war. Union forces were led by Gen George M ...
... The Civil War 150 Years ago May 1862 Three major campaigns were underway in this month: Peninsular Campaign—the Union used their naval superiority to land their army SE of Richmond and move NW to attempt to capture the Confederate capital and thus end the war. Union forces were led by Gen George M ...
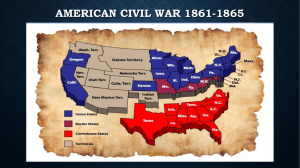
American Civil War
... 27. Who developed the Union plan for winning the Civil War? 28. What was this general’s nickname? ...
... 27. Who developed the Union plan for winning the Civil War? 28. What was this general’s nickname? ...
Read More - Battle of Westport
... crossing was the scene of two successive battles on October 22 and 23, 1864 — the first a Confederate victory and the second a Union victory. A total of approximately 11,000 troops clashed on October 22 and 23, 1864 over the Hallowed Ground at Byram’s Ford. On October 22, the notorious Kansan Col. C ...
... crossing was the scene of two successive battles on October 22 and 23, 1864 — the first a Confederate victory and the second a Union victory. A total of approximately 11,000 troops clashed on October 22 and 23, 1864 over the Hallowed Ground at Byram’s Ford. On October 22, the notorious Kansan Col. C ...
Beginning on page 500, answer these questions: What questions
... 1. What questions faced the United States at the end of the Civil War? - What rights will African Americans have? Will the slave holders be punished? How could the war torn nation be brought back together? 2. Where did most of the fighting during the Civil War take place? – The South 3. What was tor ...
... 1. What questions faced the United States at the end of the Civil War? - What rights will African Americans have? Will the slave holders be punished? How could the war torn nation be brought back together? 2. Where did most of the fighting during the Civil War take place? – The South 3. What was tor ...
2017 CHAP 19
... 3. Why did James Buchanan not act more forcefully against Southern secession? 4. Who were the candidates for president for the 1860 election, where did each get his support, and what were the results of ...
... 3. Why did James Buchanan not act more forcefully against Southern secession? 4. Who were the candidates for president for the 1860 election, where did each get his support, and what were the results of ...
Social Studies Glossary
... Battle of Vicksburg – Battle fought in Vicksburg, MS. The Union, led by Ulysses S. Grant defeated the Confederate forces. Grant’s win gave control of the Mississippi R. to the North and won him a promotion from President Lincoln to lead the Union Army. Battle of Gettysburg – battle in southern Penns ...
... Battle of Vicksburg – Battle fought in Vicksburg, MS. The Union, led by Ulysses S. Grant defeated the Confederate forces. Grant’s win gave control of the Mississippi R. to the North and won him a promotion from President Lincoln to lead the Union Army. Battle of Gettysburg – battle in southern Penns ...
Chapter 11 The Civil War Essential Question What were the
... 3. What battle was Stonewall Jackson killed in? Chancellorsville 4. In just three days of battle in Gettysburg, how many men were lost on both sides? Over 50,000 5. Why was it so important for Grant to take Vicksburg? The Union would control the MS River and split the Confederacy in half. 6. What i ...
... 3. What battle was Stonewall Jackson killed in? Chancellorsville 4. In just three days of battle in Gettysburg, how many men were lost on both sides? Over 50,000 5. Why was it so important for Grant to take Vicksburg? The Union would control the MS River and split the Confederacy in half. 6. What i ...
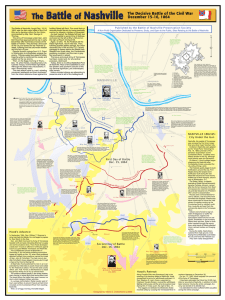
Battle of Nashville Preservation Society, Inc.
... Hood’s Advance In September 1864, Gen. William T. Sherman’s army marched into Atlanta, Ga. and began to prepare for their March to the Sea. Gen. John Bell Hood and his Army of Tennessee headed north and west, disrupting Sherman’s supply and communications lines. Then Hood developed a bold plan--moun ...
... Hood’s Advance In September 1864, Gen. William T. Sherman’s army marched into Atlanta, Ga. and began to prepare for their March to the Sea. Gen. John Bell Hood and his Army of Tennessee headed north and west, disrupting Sherman’s supply and communications lines. Then Hood developed a bold plan--moun ...
Chapter 21 Focus Questions: Essay question: What was the relative
... What did Lincoln hope the Union would capture after a victory at Bull Run? How was the South’s victory at the First Bull Run harmful to its cause and helpful to the northern cause? Describe George B. McClellan – what was his major fault? After assuming command of the Army of Potomac, General McClell ...
... What did Lincoln hope the Union would capture after a victory at Bull Run? How was the South’s victory at the First Bull Run harmful to its cause and helpful to the northern cause? Describe George B. McClellan – what was his major fault? After assuming command of the Army of Potomac, General McClell ...
Civil War Battle Chart
... a strong thrust down the Mississippi Valley with a large force, o and the establishment of a line of strong Federal positions there would isolate the disorganized Confederate nation ...
... a strong thrust down the Mississippi Valley with a large force, o and the establishment of a line of strong Federal positions there would isolate the disorganized Confederate nation ...
US history unit 4
... • Successful Union general in West; put in charge of all Union troops • Defeated South, accepted General Lee’s surrender at Appomattox ...
... • Successful Union general in West; put in charge of all Union troops • Defeated South, accepted General Lee’s surrender at Appomattox ...
The Battle of Perryville and Stones River
... of Wilson Creek, Perryville, and the First Battle of Franklin. Braxton Bragg (March 22, 1817 – September 27, 1876) was a career United States Army officer, and then a general in the Confederate States Army—a principal commander in the Western Theater of the American Civil War and later the military ...
... of Wilson Creek, Perryville, and the First Battle of Franklin. Braxton Bragg (March 22, 1817 – September 27, 1876) was a career United States Army officer, and then a general in the Confederate States Army—a principal commander in the Western Theater of the American Civil War and later the military ...
Chapter 16 Review
... Who won the first battle of Bull Run? What did the loss at Bull Run convince Lincoln he helped? During the summer of 1861, on June 16th General Lee a set of attacks against the union, what was this event called? What is another name for the second battle of Bull Run? What did the union learn from th ...
... Who won the first battle of Bull Run? What did the loss at Bull Run convince Lincoln he helped? During the summer of 1861, on June 16th General Lee a set of attacks against the union, what was this event called? What is another name for the second battle of Bull Run? What did the union learn from th ...
American civil war 1861-1865 First battle of bull run (manassas)
... McClellan; South – Robert E. Lee - North = Peninsular campaign Union come in from ship between York and James Rivers - Long Union operation to mount attack on city - Too long to attack – failed to take city ...
... McClellan; South – Robert E. Lee - North = Peninsular campaign Union come in from ship between York and James Rivers - Long Union operation to mount attack on city - Too long to attack – failed to take city ...
The War That Divided A Nation - Vernon Independent School
... the more than 2,000 land engagements of the Civil War, Gettysburg ranks supreme. Although the Battle of Gettysburg did not end the war, nor did it attain any major war aim for the North or the South, it remains the great battle of the war. Here at Gettysburg on July 1, 2, and 3, 1863, more men actua ...
... the more than 2,000 land engagements of the Civil War, Gettysburg ranks supreme. Although the Battle of Gettysburg did not end the war, nor did it attain any major war aim for the North or the South, it remains the great battle of the war. Here at Gettysburg on July 1, 2, and 3, 1863, more men actua ...
Ch. 13 Reading Guide
... 7. Which state’s strategic position near Washington, D.C., made it vital for the Union cause? A) West Virginia B) Virginia C) Delaware D) Pennsylvania E) Maryland 8. In 1861, President Lincoln suspended the right of habeas corpus in Maryland for the purpose of A) gaining support for passage of the ...
... 7. Which state’s strategic position near Washington, D.C., made it vital for the Union cause? A) West Virginia B) Virginia C) Delaware D) Pennsylvania E) Maryland 8. In 1861, President Lincoln suspended the right of habeas corpus in Maryland for the purpose of A) gaining support for passage of the ...