Faces of the Civil War
... Barton was able to convince the United States government that the American Red Cross was a necessity in the event that another war broke out or a natural disaster occurred. ...
... Barton was able to convince the United States government that the American Red Cross was a necessity in the event that another war broke out or a natural disaster occurred. ...
April 1865 - Haiku Learning
... Ever since the founding of the republican experiment in 1776, the United States was still very much a fragile entity, and each generation was fearful of its prospects for survival. They knew that most republics throughout history had been overthrown by revolution, or had collapsed into dictatorship ...
... Ever since the founding of the republican experiment in 1776, the United States was still very much a fragile entity, and each generation was fearful of its prospects for survival. They knew that most republics throughout history had been overthrown by revolution, or had collapsed into dictatorship ...
background - dehushistory
... 11,000 additional Confederate troops had been packed into freight cars and sped to the scene. (This was the first time in history that troops were moved by train.) When McDowell finally attacked on July 21, he faced a force nearly the size of his own army. But beyond the Confederate lines lay the ro ...
... 11,000 additional Confederate troops had been packed into freight cars and sped to the scene. (This was the first time in history that troops were moved by train.) When McDowell finally attacked on July 21, he faced a force nearly the size of his own army. But beyond the Confederate lines lay the ro ...
The War in Louisiana The War in Louisiana
... cotton the southerners could supply. Often, the cotton was exchanged for essential supplies. The Union planned to seize the cotton from the Red River Valley and then take Shreveport. To prepare for this assault, federal troops moved north along Bayou Teche. Along the way, the Union army seized horse ...
... cotton the southerners could supply. Often, the cotton was exchanged for essential supplies. The Union planned to seize the cotton from the Red River Valley and then take Shreveport. To prepare for this assault, federal troops moved north along Bayou Teche. Along the way, the Union army seized horse ...
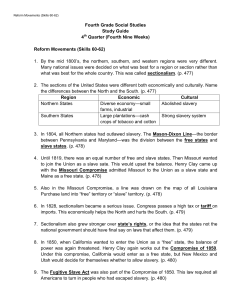
Fourth Grade Social Studies Study Guide 4 Quarter (Fourth Nine
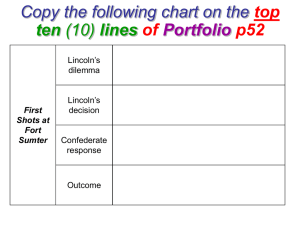
... 30. After Southern states formed the Confederacy, they took over federal or government owned property in their states. Fort Sumter in South Carolina was being held by the Union when the Confederacy attacked it on April 12, 1861. (p. 492) 31. President Lincoln called for Americans to join the Union A ...
... 30. After Southern states formed the Confederacy, they took over federal or government owned property in their states. Fort Sumter in South Carolina was being held by the Union when the Confederacy attacked it on April 12, 1861. (p. 492) 31. President Lincoln called for Americans to join the Union A ...
Ch_8_1
... Conditions in the North and the South were very different. In 1860, the U.S. population was about 31 million. Of that number, 22 million lived in the North. Only 9 million lived in the South, 3.5 million of whom were slaves. That left about 6 million whites, a number that included women, children, t ...
... Conditions in the North and the South were very different. In 1860, the U.S. population was about 31 million. Of that number, 22 million lived in the North. Only 9 million lived in the South, 3.5 million of whom were slaves. That left about 6 million whites, a number that included women, children, t ...
civilwar-reconstruction test
... 10. The ____ stated that everyone born or naturalized in the United States was a ciGzen and was enGtled to equal protecGon of the law. 11. AKer President Johnson tried to fire his Secretary of War ...
... 10. The ____ stated that everyone born or naturalized in the United States was a ciGzen and was enGtled to equal protecGon of the law. 11. AKer President Johnson tried to fire his Secretary of War ...
Lesson 16.1: War Erupts
... As in the North, Southern volunteers also rushed to enlist, with many fearing the war would be over before they could join the fight. ...
... As in the North, Southern volunteers also rushed to enlist, with many fearing the war would be over before they could join the fight. ...
ch16s1
... had 3 parts • 1. The Union should blockade Southern ports (keep them from getting supplies or exporting cotton) • 2. The Anaconda PlanGain control of the entire Mississippi River (Split the Confederacy in two) • 3. Capture Richmond, Virginia, the Confederate capital ...
... had 3 parts • 1. The Union should blockade Southern ports (keep them from getting supplies or exporting cotton) • 2. The Anaconda PlanGain control of the entire Mississippi River (Split the Confederacy in two) • 3. Capture Richmond, Virginia, the Confederate capital ...
Civil War - Outline #4 – Chapters 16-17
... victory on Northern soil would be a great blow to the North’s morale.Unfortunately for Lee, Union General McClellan found out his plans when a careless Confederate general had left Lee’s plans behind at an abandoned ...
... victory on Northern soil would be a great blow to the North’s morale.Unfortunately for Lee, Union General McClellan found out his plans when a careless Confederate general had left Lee’s plans behind at an abandoned ...
Texas and the Civil War
... The War Draws to a Close • General John Bell Hood of Texas was unable to stop Sherman • Sherman completed his March to the Sea in December 1864 • Grant was pursuing Lee • In April 1865, Union forces surrounded Lee’s army near the town of Appomattox Courthouse, VA. • Lee met with Grant on April 9 a ...
... The War Draws to a Close • General John Bell Hood of Texas was unable to stop Sherman • Sherman completed his March to the Sea in December 1864 • Grant was pursuing Lee • In April 1865, Union forces surrounded Lee’s army near the town of Appomattox Courthouse, VA. • Lee met with Grant on April 9 a ...
1 Standard 8.80 Lesson
... upon the governors and states of the Union to furnish him with 75,000 soldiers, he asked for an enlistment of only 90 days. When the Confederacy moved its capital to Richmond, Virginia, 100 miles from Washington, everyone expected a decisive battle to take place on the ground between the two cities. ...
... upon the governors and states of the Union to furnish him with 75,000 soldiers, he asked for an enlistment of only 90 days. When the Confederacy moved its capital to Richmond, Virginia, 100 miles from Washington, everyone expected a decisive battle to take place on the ground between the two cities. ...
Civil War in Louisa County
... “To the loss in the destruction of the bridges over rivers, public stores of all kinds, horses and mules captured, and those brought out by escaped slaves, there must be added the money value of some 450 negroes, who came out of the country with the various parties. Several thousand more would have ...
... “To the loss in the destruction of the bridges over rivers, public stores of all kinds, horses and mules captured, and those brought out by escaped slaves, there must be added the money value of some 450 negroes, who came out of the country with the various parties. Several thousand more would have ...
The Civil War power point
... The Confederate strategy during the war was an Offensive Defense Protect Southern territory from “Northern aggression” but attack into Union territory when the opportunity presents itself Drag out the war as long as possible to make the North quit Get Britain and France to join their cause because ...
... The Confederate strategy during the war was an Offensive Defense Protect Southern territory from “Northern aggression” but attack into Union territory when the opportunity presents itself Drag out the war as long as possible to make the North quit Get Britain and France to join their cause because ...
Chap14-CivilWar - AP US Government & Politics
... CSA •CSA currency inflated •Closed down newspapers relied on volunteer armies in the beginning, by 7,000% that did not support the war but soon needed conscription (draft) to supply their armies with troops ...
... CSA •CSA currency inflated •Closed down newspapers relied on volunteer armies in the beginning, by 7,000% that did not support the war but soon needed conscription (draft) to supply their armies with troops ...
CIVIL WAR UNIT EXAM Name
... ideals of liberty, equality, and democracy. He used this as ammunition to show reasons again for why they were fighting this war. Pickett’s Charge- Confederate General George Pickett led nearly 15,000 troops on a one mile march toward Cemetery Ridge on the third day of fighting during the Battle of ...
... ideals of liberty, equality, and democracy. He used this as ammunition to show reasons again for why they were fighting this war. Pickett’s Charge- Confederate General George Pickett led nearly 15,000 troops on a one mile march toward Cemetery Ridge on the third day of fighting during the Battle of ...
Questions%20for%20North%20and%20South%20Strategies
... Why did Confederate President Jefferson Davis believe that European countries would force the North to accept the South’s independence? To save their economies. List three parts of General Winfield Scott’s “Anaconda Plan”. a) Capture New Orleans and other Southern Ports b) Seize Mississippi River an ...
... Why did Confederate President Jefferson Davis believe that European countries would force the North to accept the South’s independence? To save their economies. List three parts of General Winfield Scott’s “Anaconda Plan”. a) Capture New Orleans and other Southern Ports b) Seize Mississippi River an ...
The American Civil War
... The blockade of southern ports begins in earnest when a fleet of Union ships with 15,000 men forces the surrender of rebel forts at Hilton Head, S.C., at the Battle of Port Royal. Plantation owners flee the region and leave the Union in possession of thousands of abandoned slaves. In the follow ...
... The blockade of southern ports begins in earnest when a fleet of Union ships with 15,000 men forces the surrender of rebel forts at Hilton Head, S.C., at the Battle of Port Royal. Plantation owners flee the region and leave the Union in possession of thousands of abandoned slaves. In the follow ...
The Battle Of Valverde
... Grande River and up the east side of the river to the ford at Valverde, north of Fort Craig, New Mexico, hoping to cut Federal communications between the fort and military headquarters in Santa Fe. Union Col. E.R.S. Canby left Fort Craig with more than 3,000 men to prevent the Confederates from cros ...
... Grande River and up the east side of the river to the ford at Valverde, north of Fort Craig, New Mexico, hoping to cut Federal communications between the fort and military headquarters in Santa Fe. Union Col. E.R.S. Canby left Fort Craig with more than 3,000 men to prevent the Confederates from cros ...
Technology of the Civil War - Conejo Valley Unified School District
... apart—North has to go in & fight South to get them back in. › Southern spirit = very strong. ...
... apart—North has to go in & fight South to get them back in. › Southern spirit = very strong. ...
The Civil War - Coronado High School
... • In early 1864 he brought Grant east to Virginia and made him commander of all the Union armies • Grant’s approach to ending the war was simply to outlast Lee by fighting a war of attrition • Grant cut off resources to Lee’s army, suffering heavier casualties than Lee’s forces in the battles of the ...
... • In early 1864 he brought Grant east to Virginia and made him commander of all the Union armies • Grant’s approach to ending the war was simply to outlast Lee by fighting a war of attrition • Grant cut off resources to Lee’s army, suffering heavier casualties than Lee’s forces in the battles of the ...
July 1863-1864
... • Burnside was sent to take command of the Department of Ohio in March of 1863 • He was sent to occupy the city of Knoxville on September 2, 1863 to “liberate East Tennessee” of the CSA presence- Lincoln believed that by taking East Tennessee, he would have the CSA by the throat • Jefferson Davis ha ...
... • Burnside was sent to take command of the Department of Ohio in March of 1863 • He was sent to occupy the city of Knoxville on September 2, 1863 to “liberate East Tennessee” of the CSA presence- Lincoln believed that by taking East Tennessee, he would have the CSA by the throat • Jefferson Davis ha ...