Solutions to Homework 2, Introduction to Differential Equations
... The equation is not exact. We seek an integrating factor that depends on one variable only. Let us recall that this is possible if either ∂M ∂y ...
... The equation is not exact. We seek an integrating factor that depends on one variable only. Let us recall that this is possible if either ∂M ∂y ...
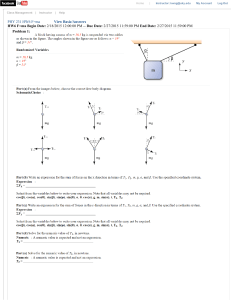
PHY 231 HW6 F=ma View Basic/Answers HW6 F=ma Begin Date: 2
... over the pulley within the crane? (Assume that the tension in each segment of the rope is the same.) Correct Algorithm: x = 5 Choice Info: ...
... over the pulley within the crane? (Assume that the tension in each segment of the rope is the same.) Correct Algorithm: x = 5 Choice Info: ...
Solutions to Assignment 2.
... (d) The best possible running time for any version of quicksort would be achieved when the median is picked for the pivot every time, but this is still only Ω(n lg n) since the array is divided in half every time and the recursion handles both halves. Thus any scheme for picking the pivot, such as t ...
... (d) The best possible running time for any version of quicksort would be achieved when the median is picked for the pivot every time, but this is still only Ω(n lg n) since the array is divided in half every time and the recursion handles both halves. Thus any scheme for picking the pivot, such as t ...
MATH 307: Problem Set #3 Solutions
... (a) Find approximate values of the solution of the given value problem in the interval [0, 0.5] with ∆t = 0.100 using Euler’s method. Record your results as a table of values in your writeup. (b) Find approximate values of the solution of the given value problem in the interval [0, 0.5] with ∆t = 0. ...
... (a) Find approximate values of the solution of the given value problem in the interval [0, 0.5] with ∆t = 0.100 using Euler’s method. Record your results as a table of values in your writeup. (b) Find approximate values of the solution of the given value problem in the interval [0, 0.5] with ∆t = 0. ...
Decision Support Systems (DSS)
... • finds the best solution out of many combinations of possibilities • E.g. find the appropriate number of products a factory should produce to meet a profit goal, given certain constraints and assumptions. E.g. • E.g. of a problem constraint: there is a limit on the number of working hours per day ( ...
... • finds the best solution out of many combinations of possibilities • E.g. find the appropriate number of products a factory should produce to meet a profit goal, given certain constraints and assumptions. E.g. • E.g. of a problem constraint: there is a limit on the number of working hours per day ( ...
Week 16
... One possible way to determine the number of candies in each bag is to divide. We calculate the quotient and remainder when we take the number of candies of each type and divide by the number of friends at the party. Number of gooey bears per bag: 60 ÷ 12 = 5 remainder 0. Number of fluffy peaches per ...
... One possible way to determine the number of candies in each bag is to divide. We calculate the quotient and remainder when we take the number of candies of each type and divide by the number of friends at the party. Number of gooey bears per bag: 60 ÷ 12 = 5 remainder 0. Number of fluffy peaches per ...
Brainstorming - Climate Change Connection
... ◦ A board, large sheets of paper, or something that can be seen easily by all, and some large marker pens to write on it; and ◦ A facilitator. Someone who’s task is to draw out the suggestions from the participants, not to impose her or his own opinions, while still using leadership skills to mainta ...
... ◦ A board, large sheets of paper, or something that can be seen easily by all, and some large marker pens to write on it; and ◦ A facilitator. Someone who’s task is to draw out the suggestions from the participants, not to impose her or his own opinions, while still using leadership skills to mainta ...
Problem Set #5
... round-robin tournament, the total number of wins by all teams equals the total number of losses – do you see why? Once you do, determine the total number of wins if n teams are involved. Problem 2: As a follow-up to Problem 1, can you show that for any roundrobin tournament, the sum of the squares o ...
... round-robin tournament, the total number of wins by all teams equals the total number of losses – do you see why? Once you do, determine the total number of wins if n teams are involved. Problem 2: As a follow-up to Problem 1, can you show that for any roundrobin tournament, the sum of the squares o ...
2.MD Task 4a - K-2 Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks
... 2.OA.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing, with unknowns in all positions, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represe ...
... 2.OA.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing, with unknowns in all positions, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represe ...
Approaching P=NP: Can Soap Bubbles Solve The Steiner Tree
... • Generation of random vertices, appropriate mesh for OpenFOAM • Solution of STP (where nodes are the random vertices) by GeoSteiner '96 • OpenFOAM computation of soap action on vertices • Comparison of exact solution with soap ...
... • Generation of random vertices, appropriate mesh for OpenFOAM • Solution of STP (where nodes are the random vertices) by GeoSteiner '96 • OpenFOAM computation of soap action on vertices • Comparison of exact solution with soap ...
Complete Characterization of Near-Optimal Sequences for the Two
... In a two-machine flow shop scheduling problem, the set of approximate sequences ( i.e. , solutions within a factor 1+ of the optimal) can be mapped to the vertices of a permutation lattice. We introduce two approaches, based on properties derived from the analysis of permutation lattices, for charac ...
... In a two-machine flow shop scheduling problem, the set of approximate sequences ( i.e. , solutions within a factor 1+ of the optimal) can be mapped to the vertices of a permutation lattice. We introduce two approaches, based on properties derived from the analysis of permutation lattices, for charac ...
Comparative Computer Results of a New Complementary Pivot
... This paper reports the development of a new algorithm for solving the general constrained optimization problem (that of optimizing an objective function subject to both equality and inequality constraints). The approach is based on the complementary pivoting algorithms that have been developed to so ...
... This paper reports the development of a new algorithm for solving the general constrained optimization problem (that of optimizing an objective function subject to both equality and inequality constraints). The approach is based on the complementary pivoting algorithms that have been developed to so ...
Intro Optimization - University of Utah Economics
... We will deal with easy to solve utility and production functions which yield solutions having anticipated SOC’s. The probability of your having to calculate the signs of the principal minors for a problem on the final exam is P(m) with 0 ≤ P(m) ≤ 0.1 ...
... We will deal with easy to solve utility and production functions which yield solutions having anticipated SOC’s. The probability of your having to calculate the signs of the principal minors for a problem on the final exam is P(m) with 0 ≤ P(m) ≤ 0.1 ...
Problem 1: (Harmonic numbers) Let Hn be the n harmonic number
... Let G = (V,E) be a connected undirected graph. A bridge is an edge e ∈ E such that removing e disconnects the graph, i.e. breaks the graph into at least two connected components. Give an O(|E|) time algorithm to find all bridge edges of G. Hint: use DFS. Problem 3: (Fast Multiplication) Analyze the ...
... Let G = (V,E) be a connected undirected graph. A bridge is an edge e ∈ E such that removing e disconnects the graph, i.e. breaks the graph into at least two connected components. Give an O(|E|) time algorithm to find all bridge edges of G. Hint: use DFS. Problem 3: (Fast Multiplication) Analyze the ...
OC #1: Example
... Whatever topic you choose, the examples must be concrete and specific. Name names in this essay. ...
... Whatever topic you choose, the examples must be concrete and specific. Name names in this essay. ...
Problem Set 1
... one can compose with projection on the i’th component to get a coordinate function xi : U → R. Then a basis for the tangent vectors at p ∈ M will be ...
... one can compose with projection on the i’th component to get a coordinate function xi : U → R. Then a basis for the tangent vectors at p ∈ M will be ...
2.MD Task 4c - K-2 Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks
... 2.MD.5 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve word problems involving lengths that are given in the same units, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem. 2.OA.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step wor ...
... 2.MD.5 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve word problems involving lengths that are given in the same units, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem. 2.OA.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step wor ...
Honors Algebra 2 and Trig
... 2. The height of an object thrown in the air is modeled by the equation h(t) = 16t2 + 48t + 6 where h represents the height of the object, in feet, and t represents the time, in seconds, since the object was thrown. During what interval of time will the object be at least 26 feet high? ...
... 2. The height of an object thrown in the air is modeled by the equation h(t) = 16t2 + 48t + 6 where h represents the height of the object, in feet, and t represents the time, in seconds, since the object was thrown. During what interval of time will the object be at least 26 feet high? ...
Solving sudoku as an Integer Programming problem
... Solving sudoku as an Integer Programming problem ⊡ A standard way to solve sudoku is by applying recursion, an algorithm where the solution depends on solutions to smaller instances of the reference problem. One checks all the combinations (for every cell it considers all integers between 1 and 9) a ...
... Solving sudoku as an Integer Programming problem ⊡ A standard way to solve sudoku is by applying recursion, an algorithm where the solution depends on solutions to smaller instances of the reference problem. One checks all the combinations (for every cell it considers all integers between 1 and 9) a ...
Topology/Geometry Jan 2016
... that there is an open neighborhood U ⊆ N of (0, 1, 0) such that for each point n ∈ U the tangent space Tn N ⊆ Tn R3 is equal to the span of X(n) and Y (n). (2) Compute the Lie bracket [X, Y ]. (3) Let D be the set of vector fields that can be written in the form f X + gY for some functions f, g ∈ C ...
... that there is an open neighborhood U ⊆ N of (0, 1, 0) such that for each point n ∈ U the tangent space Tn N ⊆ Tn R3 is equal to the span of X(n) and Y (n). (2) Compute the Lie bracket [X, Y ]. (3) Let D be the set of vector fields that can be written in the form f X + gY for some functions f, g ∈ C ...
Binomial identities
... The Rules. There are way too many problems to consider in one session. Pick a few problems you like and play around with them. Don’t spend time on a problem that you already know how to solve. The Hints. Work in groups. Try small cases. Do examples. Look for patterns. Use lots of paper. Talk it over ...
... The Rules. There are way too many problems to consider in one session. Pick a few problems you like and play around with them. Don’t spend time on a problem that you already know how to solve. The Hints. Work in groups. Try small cases. Do examples. Look for patterns. Use lots of paper. Talk it over ...
Data Representation Methods
... Permutation Problems • Solution requires you to find a permutation of n elements. • The permutation must satisfy some constraints and possibly optimize some objective function. • Examples. TSP. n-queens. Each queen must be placed in a different row and different column. Let queen i be the que ...
... Permutation Problems • Solution requires you to find a permutation of n elements. • The permutation must satisfy some constraints and possibly optimize some objective function. • Examples. TSP. n-queens. Each queen must be placed in a different row and different column. Let queen i be the que ...