Global Warming
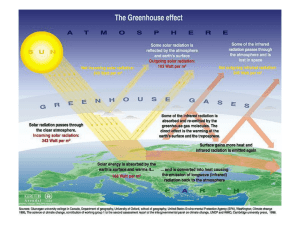
... Carbon dioxide (CO2) Methane (CH4) Nitrous oxide (N2O) Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) Ozone (O3) ...
... Carbon dioxide (CO2) Methane (CH4) Nitrous oxide (N2O) Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) Ozone (O3) ...
Ch 13 Sec 3 Global Warming Note Taking Guide
... • Millions of tons of carbon dioxide are released into the atmosphere each year from _______________ that burn coal or oil, and cars that burn _______________. Millions of trees are _______________ in tropical rainforest to clear the land for farming. • We also release other greenhouse gases, such a ...
... • Millions of tons of carbon dioxide are released into the atmosphere each year from _______________ that burn coal or oil, and cars that burn _______________. Millions of trees are _______________ in tropical rainforest to clear the land for farming. • We also release other greenhouse gases, such a ...
Common Misconceptions about Climate Change
... ozone depletion, play only a minor role in climate change. The depletion of the stratospheric ozone layer, including the ozone hole, is a serious environmental problem because it causes an increase in ultraviolet radiation, which can harm people, animals, and plants. This is a different problem from ...
... ozone depletion, play only a minor role in climate change. The depletion of the stratospheric ozone layer, including the ozone hole, is a serious environmental problem because it causes an increase in ultraviolet radiation, which can harm people, animals, and plants. This is a different problem from ...
Carbon Footprints
... of habitat. The world could be miserable place for both humans and animals. A huge increase in the temperature will also occur. Most of the world’s glaciers will completely melt by 2025. Moreover, the entire Greenland ice sheet could melt completely in the next century. Also, severe droughts and ter ...
... of habitat. The world could be miserable place for both humans and animals. A huge increase in the temperature will also occur. Most of the world’s glaciers will completely melt by 2025. Moreover, the entire Greenland ice sheet could melt completely in the next century. Also, severe droughts and ter ...
Global Warming - Frontenac Secondary School
... Evidence of climate change includes increasing temperatures recorded in the last 100 years, rising sea levels, and decreasing snow cover in the Northern Hemisphere. Most of the observed increases in global temperatures have occurred since the mid-20th century. The change is very likely due to the ob ...
... Evidence of climate change includes increasing temperatures recorded in the last 100 years, rising sea levels, and decreasing snow cover in the Northern Hemisphere. Most of the observed increases in global temperatures have occurred since the mid-20th century. The change is very likely due to the ob ...
Under 2 Degrees Celsius: - Veerabhadran Ramanathan
... The report - written by over thirty experts in climate science, economics, policy, and national security, from China, EU, India, UK and US – takes a new approach to staying below 2ºC and thus avoid extreme and unmanageable climate changes. The report identifies 4 building blocks for climate policy s ...
... The report - written by over thirty experts in climate science, economics, policy, and national security, from China, EU, India, UK and US – takes a new approach to staying below 2ºC and thus avoid extreme and unmanageable climate changes. The report identifies 4 building blocks for climate policy s ...
Climate Change: Lines of Evidence video questions
... 1. All of these data show that average earth surface temperatures have increased by _________ oF over the last 100 years, with much of this increase taking place over the last ________years. 2. Other indicators of global warming? What changes have occurred? a. Heat waves? ...
... 1. All of these data show that average earth surface temperatures have increased by _________ oF over the last 100 years, with much of this increase taking place over the last ________years. 2. Other indicators of global warming? What changes have occurred? a. Heat waves? ...
The Science of Global Warming
... 2. Global warming is caused by human activity. - “Anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions have increased since the pre-industrial era, driven largely by economic and population growth, and are now higher than ever.” ...
... 2. Global warming is caused by human activity. - “Anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions have increased since the pre-industrial era, driven largely by economic and population growth, and are now higher than ever.” ...
Climate change
... Weather: the short-term (hourly, daily) state of the atmosphere, determined by variables such as temperature, wind, moisture, and pressure. Climate: The long-term (years, decades – typically 30 years plus) average weather of a region: typical weather patterns, the frequency and intensity of stor ...
... Weather: the short-term (hourly, daily) state of the atmosphere, determined by variables such as temperature, wind, moisture, and pressure. Climate: The long-term (years, decades – typically 30 years plus) average weather of a region: typical weather patterns, the frequency and intensity of stor ...
W5 - North Pacific Marine Science Organization
... Co-Convenors: Michael G. Foreman (Canada) and Yasuhiro Yamanaka (Japan) The most recent set of global climate model projections have been submitted to, and are being analyzed by, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) for the publication of their Fourth Assessment Report in 2007. PICES ...
... Co-Convenors: Michael G. Foreman (Canada) and Yasuhiro Yamanaka (Japan) The most recent set of global climate model projections have been submitted to, and are being analyzed by, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) for the publication of their Fourth Assessment Report in 2007. PICES ...
Document
... Risk assessment: Based on earlier IPCC modeling 450 ppm is presented as equating to 50% probability of a 2 degrees C global mean temperature warming above pre-industrial Would you fly in an aircraft with a 50% chance of reaching it’s destination? ...
... Risk assessment: Based on earlier IPCC modeling 450 ppm is presented as equating to 50% probability of a 2 degrees C global mean temperature warming above pre-industrial Would you fly in an aircraft with a 50% chance of reaching it’s destination? ...
A Comparative Study of Climate Change and Glacier Loss in the
... S Increase in low-level clouds, which also increase surface warming – positive feedback loops ...
... S Increase in low-level clouds, which also increase surface warming – positive feedback loops ...
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)
... are immediate. The benefits, such as fewer severe storms, floods, and droughts will occur in the future and will benefit people everywhere, whether they pay for the relevant technology or not. It is hard to put a price on these positive outcomes. * If laws and regulations around the world aren't equ ...
... are immediate. The benefits, such as fewer severe storms, floods, and droughts will occur in the future and will benefit people everywhere, whether they pay for the relevant technology or not. It is hard to put a price on these positive outcomes. * If laws and regulations around the world aren't equ ...
Increasing the use and usability of participatory assessments
... (other targets than the 6EAP target of +2C global temperature increase?) • Global greenhouse gas and carbon dioxide concentration levels consistent with global climate change target(s) • Possible convergence of per capita emissions and by which year • Possible emission targets for industrialized cou ...
... (other targets than the 6EAP target of +2C global temperature increase?) • Global greenhouse gas and carbon dioxide concentration levels consistent with global climate change target(s) • Possible convergence of per capita emissions and by which year • Possible emission targets for industrialized cou ...
PPT
... By mid decade island states have demanded a decrease in greenhouse gasses to prevent sea level rise and in 1997 the Kyoto Protocol calls for over 5% cut in emissions by ...
... By mid decade island states have demanded a decrease in greenhouse gasses to prevent sea level rise and in 1997 the Kyoto Protocol calls for over 5% cut in emissions by ...
Climate Sensitivity - Earth and Environmental Sciences
... the radiative forcing responsible for the climate change. Radiative forcing is the change in energy balance (in and out) at the Earth's surface. In this case we will use three known past examples of climate change to predict a forth – our future. We know that 20,000 years ago there were large ice sh ...
... the radiative forcing responsible for the climate change. Radiative forcing is the change in energy balance (in and out) at the Earth's surface. In this case we will use three known past examples of climate change to predict a forth – our future. We know that 20,000 years ago there were large ice sh ...
Open Our Color Tri Fold
... High and Low Temperatures Many extreme temperature conditions are becoming more common. Since the 1970s, unusually hot summer temperatures have become more common in the United States, and heat waves have become more frequent— although the most severe heat waves in U.S. history remain those that occ ...
... High and Low Temperatures Many extreme temperature conditions are becoming more common. Since the 1970s, unusually hot summer temperatures have become more common in the United States, and heat waves have become more frequent— although the most severe heat waves in U.S. history remain those that occ ...
Tues Jan 6 - UW Atmospheric Sciences
... 0.7°C rise in global-mean temperature so far; enough to have noticeable impacts Global-mean temperature is projected to rise to 2-3°C by 2100 (CO2 doubling) Note that 1°C = 1.8°F, so we’re taling about a ~5°F temperature rise Temperature rise expected to be larger over land than sea Expect even larg ...
... 0.7°C rise in global-mean temperature so far; enough to have noticeable impacts Global-mean temperature is projected to rise to 2-3°C by 2100 (CO2 doubling) Note that 1°C = 1.8°F, so we’re taling about a ~5°F temperature rise Temperature rise expected to be larger over land than sea Expect even larg ...
File - bridgebuilders trust network
... amount of heavy precipitation than decreases Increases in intensity and/or duration of ...
... amount of heavy precipitation than decreases Increases in intensity and/or duration of ...
power point - Altair-PYP-Exhibition-2010
... a change of the weather condition or a change in the dispersion of weather with respect to an average , for example, greater or fewer weather events. Climate change may be limited to a specific region or occur in the whole planet ...
... a change of the weather condition or a change in the dispersion of weather with respect to an average , for example, greater or fewer weather events. Climate change may be limited to a specific region or occur in the whole planet ...
Global warming
Global warming and climate change are terms for the observed century-scale rise in the average temperature of the Earth's climate system and its related effects.Multiple lines of scientific evidence show that the climate system is warming. Although the increase of near-surface atmospheric temperature is the measure of global warming often reported in the popular press, most of the additional energy stored in the climate system since 1970 has gone into ocean warming. The remainder has melted ice, and warmed the continents and atmosphere. Many of the observed changes since the 1950s are unprecedented over decades to millennia.Scientific understanding of global warming is increasing. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reported in 2014 that scientists were more than 95% certain that most of global warming is caused by increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases and other human (anthropogenic) activities. Climate model projections summarized in the report indicated that during the 21st century the global surface temperature is likely to rise a further 0.3 to 1.7 °C (0.5 to 3.1 °F) for their lowest emissions scenario using stringent mitigation and 2.6 to 4.8 °C (4.7 to 8.6 °F) for their highest. These findings have been recognized by the national science academies of the major industrialized nations.Future climate change and associated impacts will differ from region to region around the globe. Anticipated effects include warming global temperature, rising sea levels, changing precipitation, and expansion of deserts in the subtropics. Warming is expected to be greatest in the Arctic, with the continuing retreat of glaciers, permafrost and sea ice. Other likely changes include more frequent extreme weather events including heat waves, droughts, heavy rainfall, and heavy snowfall; ocean acidification; and species extinctions due to shifting temperature regimes. Effects significant to humans include the threat to food security from decreasing crop yields and the abandonment of populated areas due to flooding.Possible societal responses to global warming include mitigation by emissions reduction, adaptation to its effects, building systems resilient to its effects, and possible future climate engineering. Most countries are parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC),whose ultimate objective is to prevent dangerous anthropogenic climate change. The UNFCCC have adopted a range of policies designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and to assist in adaptation to global warming. Parties to the UNFCCC have agreed that deep cuts in emissions are required, and that future global warming should be limited to below 2.0 °C (3.6 °F) relative to the pre-industrial level.