Projections of Climate Change
... The A1 storyline and scenario family: very rapid economic growth, global population that peaks in midcentury and declines thereafter, and the rapid introduction of new and more efficient technologies. Major underlying themes are convergence among regions, capacity building and increased cultural and ...
... The A1 storyline and scenario family: very rapid economic growth, global population that peaks in midcentury and declines thereafter, and the rapid introduction of new and more efficient technologies. Major underlying themes are convergence among regions, capacity building and increased cultural and ...
Key findings
... Beyond adaptation Adaptation to climate change is necessary to address impacts resulting from the warming which is already unavoidable due to past emissions However: • Adaptation alone cannot cope with all the projected impacts of climate change • The costs of adaptation and impacts will increase a ...
... Beyond adaptation Adaptation to climate change is necessary to address impacts resulting from the warming which is already unavoidable due to past emissions However: • Adaptation alone cannot cope with all the projected impacts of climate change • The costs of adaptation and impacts will increase a ...
Global Warming - Walker Institute
... The earth is represented by a grid of squares, typically of length 250 km, and by a stack of layers. This gives us a 3-D picture of the circulation of the atmosphere and oceans ...
... The earth is represented by a grid of squares, typically of length 250 km, and by a stack of layers. This gives us a 3-D picture of the circulation of the atmosphere and oceans ...
2Dclimate / Uploaded File
... – Anywhere pollen can be found, it will tell you the plant species that lived around the location at the time the sediments were deposited, thus the temperature range at the time of deposition ...
... – Anywhere pollen can be found, it will tell you the plant species that lived around the location at the time the sediments were deposited, thus the temperature range at the time of deposition ...
Study Guide - Unit 3 - Environmental Issues
... From the scientific majority’s point of view, the world puts out too many carbon emissions. The U.S. has the biggest economy in the history of the world, and is responsible for 1/3 of all the carbon emissions. On average, each U.S. citizen uses ten times the energy as people in developing regions (A ...
... From the scientific majority’s point of view, the world puts out too many carbon emissions. The U.S. has the biggest economy in the history of the world, and is responsible for 1/3 of all the carbon emissions. On average, each U.S. citizen uses ten times the energy as people in developing regions (A ...
II. Changes in climate
... Earth’s climate is now warmer than at any time in the last 1000 years 1. increased solar input (small warming effect) 2. Increased sulfate aerosols reflects radiation (small cooling effect) 3. Increased greenhouse gas concentrations (large warming effect) 4. Land-cover change creates a darker surfa ...
... Earth’s climate is now warmer than at any time in the last 1000 years 1. increased solar input (small warming effect) 2. Increased sulfate aerosols reflects radiation (small cooling effect) 3. Increased greenhouse gas concentrations (large warming effect) 4. Land-cover change creates a darker surfa ...
Derivation of the temperature increase equation: ΔT = 1.66 ln (C/Co)
... temperature. We assume that the atmosphere is transparent to visible radiation and heating only occurs at the Earth’s surface (Grey atmosphere). There is no convection and scattering can be neglected. Finally, we assume local thermodynamic equilibrium. This means that in a localised atmospheric volu ...
... temperature. We assume that the atmosphere is transparent to visible radiation and heating only occurs at the Earth’s surface (Grey atmosphere). There is no convection and scattering can be neglected. Finally, we assume local thermodynamic equilibrium. This means that in a localised atmospheric volu ...
Lesson 3 Climate Change
... temperatures over the last century , explain what physical and human factors have contributed to this. (6) ...
... temperatures over the last century , explain what physical and human factors have contributed to this. (6) ...
Climate Change Overview
... the eastern tropical pacific and a reduction in external radiative forcings. Over this time, energy continues to accumulate in the ocean. • Antarctica is loosing a surprising amount of mass, with the potential for much larger and more rapid contributions to future sea level. These changes appear to ...
... the eastern tropical pacific and a reduction in external radiative forcings. Over this time, energy continues to accumulate in the ocean. • Antarctica is loosing a surprising amount of mass, with the potential for much larger and more rapid contributions to future sea level. These changes appear to ...
Chapter 19 Home and classwork
... sunburns, cataracts, skin cancers, immune suppression, and reduced crop yields, particularly in the Southern Hemisphere. Note that students often confuse tropospheric ozone (air pollution) and stratospheric ozone (UV absorption), and confuse ozone depletion with global warming. ...
... sunburns, cataracts, skin cancers, immune suppression, and reduced crop yields, particularly in the Southern Hemisphere. Note that students often confuse tropospheric ozone (air pollution) and stratospheric ozone (UV absorption), and confuse ozone depletion with global warming. ...
Downlaod File - Prince Mohammad Bin Fahd University
... earth. However, there are some types of activities that cause global warming. One of these types is the emission of the carbon dioxide. Many of electrical industrial factories overall the world are burning enormous amount of coal in order to produce electricity, which make them to release a big amou ...
... earth. However, there are some types of activities that cause global warming. One of these types is the emission of the carbon dioxide. Many of electrical industrial factories overall the world are burning enormous amount of coal in order to produce electricity, which make them to release a big amou ...
Role play
... to try to prevent global warming." What don’t scientists know yet? Scientists do not agree on whether: 1) we know enough to ascribe past temperature changes to carbon dioxide levels; 2) we have enough data to confidently predict future temperature levels; and 3) at what level temperature change mi ...
... to try to prevent global warming." What don’t scientists know yet? Scientists do not agree on whether: 1) we know enough to ascribe past temperature changes to carbon dioxide levels; 2) we have enough data to confidently predict future temperature levels; and 3) at what level temperature change mi ...
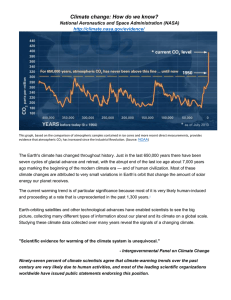
Climate change: How do we know?
... This graph, based on the comparison of atmospheric samples contained in ice cores and more recent direct measurements, provides evidence that atmospheric CO2 has increased since the Industrial Revolution. (Source: NOAA) ...
... This graph, based on the comparison of atmospheric samples contained in ice cores and more recent direct measurements, provides evidence that atmospheric CO2 has increased since the Industrial Revolution. (Source: NOAA) ...
Slide 1
... Greenhouse Effect & Global Warming • The “greenhouse effect” & global warming are not the same thing. – Global warming refers to a rise in the temperature of the surface of the earth ...
... Greenhouse Effect & Global Warming • The “greenhouse effect” & global warming are not the same thing. – Global warming refers to a rise in the temperature of the surface of the earth ...
Energy production outline
... Earth’s albedo varies daily and is dependent on season (cloud formations) and latitude. The global annual mean albedo will be taken to be 0.3 (30%) for Earth. ...
... Earth’s albedo varies daily and is dependent on season (cloud formations) and latitude. The global annual mean albedo will be taken to be 0.3 (30%) for Earth. ...
Global Warming and Climate Change in a Nutshell
... F) of which the 0.85 degrees has already occurred. (Some scientists, including James Hansen, believe that the 2-degree objective is insufficient and that it should actually be one degree.) Achieving the 2-degree temperature goal would require that new CO2 emissions by century end not exceed 1 trilli ...
... F) of which the 0.85 degrees has already occurred. (Some scientists, including James Hansen, believe that the 2-degree objective is insufficient and that it should actually be one degree.) Achieving the 2-degree temperature goal would require that new CO2 emissions by century end not exceed 1 trilli ...
climate change - International Presentation Association
... • Increased incidence of infectious diseases and their movement into ‘new’ regions e.g. malaria in some parts of world, tick-born encephalitis in Sweden. • Older persons are susceptible to thermal stress. One effect is increase in deaths due to heat e.g. in Paris in recent years. Prof Tony McMichael ...
... • Increased incidence of infectious diseases and their movement into ‘new’ regions e.g. malaria in some parts of world, tick-born encephalitis in Sweden. • Older persons are susceptible to thermal stress. One effect is increase in deaths due to heat e.g. in Paris in recent years. Prof Tony McMichael ...
Effects of Global Warming on Weather and Climate
... The Effects of Global Warming on Weather and Climate Global warming refers to the gradual rise in the overall temperature of the earth’s atmosphere caused by raised levels of carbon dioxide, chlorofluorocarbon, and other pollutants [3]. As a result of global warming, a set of changes are happening t ...
... The Effects of Global Warming on Weather and Climate Global warming refers to the gradual rise in the overall temperature of the earth’s atmosphere caused by raised levels of carbon dioxide, chlorofluorocarbon, and other pollutants [3]. As a result of global warming, a set of changes are happening t ...
ClimateChange1
... level has risen, and the concentrations of greenhouse gases have increased .” ...
... level has risen, and the concentrations of greenhouse gases have increased .” ...
This presentation - FRIENDS of the Environment
... Climate change refers to changes in a regions overall weather patterns, including precipitation, temperatures, cloud cover, and so on. ...
... Climate change refers to changes in a regions overall weather patterns, including precipitation, temperatures, cloud cover, and so on. ...
Climate Change and Extreme Weather
... Our changing climate history • Temperature Change: reconstruction of annualaverage Northern Hemisphere surface air temperatures derived from historical records, tree rings, and corals (blue), and air temperatures directly measured (purple). • CO2 Concentrations: record of global CO2 concentration f ...
... Our changing climate history • Temperature Change: reconstruction of annualaverage Northern Hemisphere surface air temperatures derived from historical records, tree rings, and corals (blue), and air temperatures directly measured (purple). • CO2 Concentrations: record of global CO2 concentration f ...
What is Climate Change?
... particularly in tropical and Polar Regions are already undergoing rapid decline. It is now widely believe that this rapid increase in global temperatures and changing climate is due to human activity. But what is it that we are doing that is so bad? Reducing Greenhouse gas emissions is the key to so ...
... particularly in tropical and Polar Regions are already undergoing rapid decline. It is now widely believe that this rapid increase in global temperatures and changing climate is due to human activity. But what is it that we are doing that is so bad? Reducing Greenhouse gas emissions is the key to so ...
PowerPoint - Susan Schwinning
... Thawing permaforst in the artic releases methane, a greenhouse gas Warming peatlands release CO2 Shrinking sea ice and glacial cover reflects less solar radiation (albedo = reflectance of solar radiation) Ocean warming reduces solubility of CO2 Warmer temperatures on water and land increas ...
... Thawing permaforst in the artic releases methane, a greenhouse gas Warming peatlands release CO2 Shrinking sea ice and glacial cover reflects less solar radiation (albedo = reflectance of solar radiation) Ocean warming reduces solubility of CO2 Warmer temperatures on water and land increas ...
Global warming
Global warming and climate change are terms for the observed century-scale rise in the average temperature of the Earth's climate system and its related effects.Multiple lines of scientific evidence show that the climate system is warming. Although the increase of near-surface atmospheric temperature is the measure of global warming often reported in the popular press, most of the additional energy stored in the climate system since 1970 has gone into ocean warming. The remainder has melted ice, and warmed the continents and atmosphere. Many of the observed changes since the 1950s are unprecedented over decades to millennia.Scientific understanding of global warming is increasing. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reported in 2014 that scientists were more than 95% certain that most of global warming is caused by increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases and other human (anthropogenic) activities. Climate model projections summarized in the report indicated that during the 21st century the global surface temperature is likely to rise a further 0.3 to 1.7 °C (0.5 to 3.1 °F) for their lowest emissions scenario using stringent mitigation and 2.6 to 4.8 °C (4.7 to 8.6 °F) for their highest. These findings have been recognized by the national science academies of the major industrialized nations.Future climate change and associated impacts will differ from region to region around the globe. Anticipated effects include warming global temperature, rising sea levels, changing precipitation, and expansion of deserts in the subtropics. Warming is expected to be greatest in the Arctic, with the continuing retreat of glaciers, permafrost and sea ice. Other likely changes include more frequent extreme weather events including heat waves, droughts, heavy rainfall, and heavy snowfall; ocean acidification; and species extinctions due to shifting temperature regimes. Effects significant to humans include the threat to food security from decreasing crop yields and the abandonment of populated areas due to flooding.Possible societal responses to global warming include mitigation by emissions reduction, adaptation to its effects, building systems resilient to its effects, and possible future climate engineering. Most countries are parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC),whose ultimate objective is to prevent dangerous anthropogenic climate change. The UNFCCC have adopted a range of policies designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and to assist in adaptation to global warming. Parties to the UNFCCC have agreed that deep cuts in emissions are required, and that future global warming should be limited to below 2.0 °C (3.6 °F) relative to the pre-industrial level.