the full interview as a Word file.
... size ever and we have forest fires raging in southern California and we’re hearing there will be more hurricanes on the way – put it in a global context for us, please. Dr. Epstein: The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) in 2001 and this is 2000 scientist reporting from 100 nations to ...
... size ever and we have forest fires raging in southern California and we’re hearing there will be more hurricanes on the way – put it in a global context for us, please. Dr. Epstein: The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) in 2001 and this is 2000 scientist reporting from 100 nations to ...
Chapter 19 part B - Duluth High School
... Help Slow Climate Change? • CCS-Carbon capture and storage – result of slow response by governments • Injection of sulfate particles into the stratosphere – Would it have a cooling effect? – Would it accelerate O3 depletion? ...
... Help Slow Climate Change? • CCS-Carbon capture and storage – result of slow response by governments • Injection of sulfate particles into the stratosphere – Would it have a cooling effect? – Would it accelerate O3 depletion? ...
Download country indicators
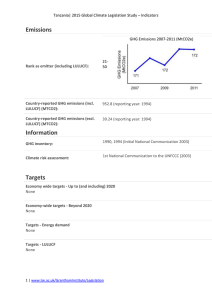
... Economy wide targets - Up to (and including) 2020 Reduce emissions by 16% below 2020 business-as-usual levels if there is a legally binding global agreement in which all countries implement their commitments in good faith Source: ...
... Economy wide targets - Up to (and including) 2020 Reduce emissions by 16% below 2020 business-as-usual levels if there is a legally binding global agreement in which all countries implement their commitments in good faith Source: ...
Harmonized Carbon Taxes What are
... Temperature record and projections to 2200, Vostok core, Antarctica ...
... Temperature record and projections to 2200, Vostok core, Antarctica ...
Chapter 10 – Assessing and Responding to Climate Change
... Expected Changes Due to Climate • In order to evaluate the risks of human-caused climate change, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) was formed • To achieve this, several thousand scientists voluntarily share and synthesize their work to come up with current projected models for cl ...
... Expected Changes Due to Climate • In order to evaluate the risks of human-caused climate change, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) was formed • To achieve this, several thousand scientists voluntarily share and synthesize their work to come up with current projected models for cl ...
COC-McBean Climate Change - Canadians for Action on Climate
... Most of the observed increase in global average temperatures since the mid-20th century is very likely due to the observed increase in anthropogenic greenhouse gas concentrations. Observations ...
... Most of the observed increase in global average temperatures since the mid-20th century is very likely due to the observed increase in anthropogenic greenhouse gas concentrations. Observations ...
Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Continue Climbing
... remote expanses of Alaska and in the far South Pacific,” he said. Greenhouse gases trap radiation within the Earth’s atmosphere causing it to warm. Human activities, such as fossil fuel burning and agriculture, are major emitters of greenhouse gases which are drivers of climate change. After water v ...
... remote expanses of Alaska and in the far South Pacific,” he said. Greenhouse gases trap radiation within the Earth’s atmosphere causing it to warm. Human activities, such as fossil fuel burning and agriculture, are major emitters of greenhouse gases which are drivers of climate change. After water v ...
Climate change action planning
... IPCC, 2007, Summary for Policymakers. In: Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Solomon, S., D. Qin, M. Manning, Z. Chen, M. Marquis, K.B. Averyt, M.Tignor and H.L. Miller (ed ...
... IPCC, 2007, Summary for Policymakers. In: Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Solomon, S., D. Qin, M. Manning, Z. Chen, M. Marquis, K.B. Averyt, M.Tignor and H.L. Miller (ed ...
1 - Talal Abu-Ghazaleh Organization
... the challenge of offsetting the tremendous growth by China, India and other emerging economies seems insurmountable. d. It seems insensitive if not immoral to tell emerging economies to stay “in the dark” rather than contribute to greenhouse gases. After all, the West used carbon-based energy to bu ...
... the challenge of offsetting the tremendous growth by China, India and other emerging economies seems insurmountable. d. It seems insensitive if not immoral to tell emerging economies to stay “in the dark” rather than contribute to greenhouse gases. After all, the West used carbon-based energy to bu ...
Weather Prediction by Numerical Process Lewis Fry Richardson 1922
... With SRES A2 (fast FF emission): as CO2 increases •Capacity of land and ocean to store carbon decreases (slowing of photosyn; reduce soil C ...
... With SRES A2 (fast FF emission): as CO2 increases •Capacity of land and ocean to store carbon decreases (slowing of photosyn; reduce soil C ...
Impacts_L12_2011_post
... Global Warming and Sea Level Rise (SLR) Major variations in geological history (-150 to +40 meters) Sources in future: - Thermal expansion (up to 2 meters in next 500 years) ...
... Global Warming and Sea Level Rise (SLR) Major variations in geological history (-150 to +40 meters) Sources in future: - Thermal expansion (up to 2 meters in next 500 years) ...
IPCC Average global temperature has increased 0.8°C since 1906.
... Average global temperature has increased 0.8°C since 1906. ...
... Average global temperature has increased 0.8°C since 1906. ...
Presentation Title, Arial Regular 29pt Sub title, Arial
... • Broader institutional and community capacity building around the risks of climate change – need thorough vulnerability assessments conducted in partnership with governments and communities ...
... • Broader institutional and community capacity building around the risks of climate change – need thorough vulnerability assessments conducted in partnership with governments and communities ...
Lecture 19
... • There are about 20 such “greenhouse” gases but the focus has been on CO2 • CFC’s or chlorofluorocarbons are a man made chemical that make up a smaller portion of GHG, but have properties that give them a warming potential several thousand times greater than carbon dioxide • In September 2006 U.S. ...
... • There are about 20 such “greenhouse” gases but the focus has been on CO2 • CFC’s or chlorofluorocarbons are a man made chemical that make up a smaller portion of GHG, but have properties that give them a warming potential several thousand times greater than carbon dioxide • In September 2006 U.S. ...
State GHG Iniatives
... AZ: Climate Change Advisory Group established in February 2005 by executive order to produce an inventory of Arizona’s greenhouse gas emissions and develop recommendations to reduce Arizona’s greenhouse gas emissions. CA: Climate Change Advisory Committee established in 2004 by the California Energy ...
... AZ: Climate Change Advisory Group established in February 2005 by executive order to produce an inventory of Arizona’s greenhouse gas emissions and develop recommendations to reduce Arizona’s greenhouse gas emissions. CA: Climate Change Advisory Committee established in 2004 by the California Energy ...
Projection of future changes (2010-2099) of mean temperature and
... using the scenarios to drive dynamic ecosystem models to assess the vegetation response to the projected climate scenarios. We used climate scenarios derived from the World Climate Research Program (WCRP) Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP3) multi-model datasets. The datasets are based on t ...
... using the scenarios to drive dynamic ecosystem models to assess the vegetation response to the projected climate scenarios. We used climate scenarios derived from the World Climate Research Program (WCRP) Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP3) multi-model datasets. The datasets are based on t ...
587_7 - UW Atmospheric Sciences
... Thus radiative forcing for greenhouse gases is calculated assuming no change in temperature ...
... Thus radiative forcing for greenhouse gases is calculated assuming no change in temperature ...
Climate Change
... • It is global in it’s origin and effects • The effect is NOT marginal – potential impacts are extremely large and lethal • The risk and uncertainty associated are extremely large – the variance of the effect dominates the average effect • The impact is to be felt over the long run (hundreds if not ...
... • It is global in it’s origin and effects • The effect is NOT marginal – potential impacts are extremely large and lethal • The risk and uncertainty associated are extremely large – the variance of the effect dominates the average effect • The impact is to be felt over the long run (hundreds if not ...
Heartland-Takle-01 - Department of Geological & Atmospheric
... Increased tropospheric ozone (high) Accelerated loss of soil carbon (high) Phenological stages are shortened (high) Weeds grow more rapidly under elevated atmospheric CO2 (high) Weeds migrate northward and are less sensitive to herbicides (high) Plants have increased water used efficiency (high) ...
... Increased tropospheric ozone (high) Accelerated loss of soil carbon (high) Phenological stages are shortened (high) Weeds grow more rapidly under elevated atmospheric CO2 (high) Weeds migrate northward and are less sensitive to herbicides (high) Plants have increased water used efficiency (high) ...
Are You suprised
... lower now due to the Montreal Protocol of 1987. e. Water vapor is the most abundant greenhouse gas, and its concentration increases as tropospheric temperatures rise. F. Aerosols may exert a cooling effect on the lower atmosphere. 1. Microscopic droplets and particles can have either a warming or a ...
... lower now due to the Montreal Protocol of 1987. e. Water vapor is the most abundant greenhouse gas, and its concentration increases as tropospheric temperatures rise. F. Aerosols may exert a cooling effect on the lower atmosphere. 1. Microscopic droplets and particles can have either a warming or a ...
Theory of global cooling | SpringerLink
... with period P, in order for energy to travel from one hemisphere (for instance, as experienced in a day) to the other, it must be conducted through the materials that make up the surface. This process is sufficiently slow that each hemisphere can be thought of as being isolated from the other. Day a ...
... with period P, in order for energy to travel from one hemisphere (for instance, as experienced in a day) to the other, it must be conducted through the materials that make up the surface. This process is sufficiently slow that each hemisphere can be thought of as being isolated from the other. Day a ...
Science-Based Targets Key to Private-Sector
... Companies Busting the Status Quo Rather than waiting for some global agreement that may never come regarding how the 1,000 gigatons of carbon dioxide budget should be allocated across nations and sectors, companies have begun to assess what their share of the budget, and associated emission reductio ...
... Companies Busting the Status Quo Rather than waiting for some global agreement that may never come regarding how the 1,000 gigatons of carbon dioxide budget should be allocated across nations and sectors, companies have begun to assess what their share of the budget, and associated emission reductio ...
Global warming
Global warming and climate change are terms for the observed century-scale rise in the average temperature of the Earth's climate system and its related effects.Multiple lines of scientific evidence show that the climate system is warming. Although the increase of near-surface atmospheric temperature is the measure of global warming often reported in the popular press, most of the additional energy stored in the climate system since 1970 has gone into ocean warming. The remainder has melted ice, and warmed the continents and atmosphere. Many of the observed changes since the 1950s are unprecedented over decades to millennia.Scientific understanding of global warming is increasing. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reported in 2014 that scientists were more than 95% certain that most of global warming is caused by increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases and other human (anthropogenic) activities. Climate model projections summarized in the report indicated that during the 21st century the global surface temperature is likely to rise a further 0.3 to 1.7 °C (0.5 to 3.1 °F) for their lowest emissions scenario using stringent mitigation and 2.6 to 4.8 °C (4.7 to 8.6 °F) for their highest. These findings have been recognized by the national science academies of the major industrialized nations.Future climate change and associated impacts will differ from region to region around the globe. Anticipated effects include warming global temperature, rising sea levels, changing precipitation, and expansion of deserts in the subtropics. Warming is expected to be greatest in the Arctic, with the continuing retreat of glaciers, permafrost and sea ice. Other likely changes include more frequent extreme weather events including heat waves, droughts, heavy rainfall, and heavy snowfall; ocean acidification; and species extinctions due to shifting temperature regimes. Effects significant to humans include the threat to food security from decreasing crop yields and the abandonment of populated areas due to flooding.Possible societal responses to global warming include mitigation by emissions reduction, adaptation to its effects, building systems resilient to its effects, and possible future climate engineering. Most countries are parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC),whose ultimate objective is to prevent dangerous anthropogenic climate change. The UNFCCC have adopted a range of policies designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and to assist in adaptation to global warming. Parties to the UNFCCC have agreed that deep cuts in emissions are required, and that future global warming should be limited to below 2.0 °C (3.6 °F) relative to the pre-industrial level.