B - Sewanhaka Central High School District
... centimeters of soil. All of the containers were placed in the same sunny location. The height of the plants were measured and recorded for 5 weeks. ...
... centimeters of soil. All of the containers were placed in the same sunny location. The height of the plants were measured and recorded for 5 weeks. ...
eoct review - Model High School
... a. Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis and cell reproduction. b.Explain how enzymes function as catalysts. c. Identify the function of the four major macromolecules (i.e., carbohydrates, proteins, ...
... a. Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis and cell reproduction. b.Explain how enzymes function as catalysts. c. Identify the function of the four major macromolecules (i.e., carbohydrates, proteins, ...
Science FCAT Review 2010 - Mr. Martin's 8th Grade Science
... on those organisms. A complete answer will need to include two triggering abiotic factors (fertilizer is required) and at least on abiotic effect and one biotic effect. ...
... on those organisms. A complete answer will need to include two triggering abiotic factors (fertilizer is required) and at least on abiotic effect and one biotic effect. ...
Period: ______ Date
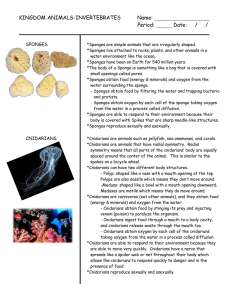
... *Cnidarians are animals such as jellyfish, sea anemones, and corals. *Cnidarians are animals that have radial symmetry. Radial symmetry means that all parts of the cnidarians’ body are equally spaced around the center of the animal. This is similar to the spokes on a bicycle wheel. *Cnidarians can h ...
... *Cnidarians are animals such as jellyfish, sea anemones, and corals. *Cnidarians are animals that have radial symmetry. Radial symmetry means that all parts of the cnidarians’ body are equally spaced around the center of the animal. This is similar to the spokes on a bicycle wheel. *Cnidarians can h ...
6.1 Evidence of evolution – Questions and answers Q1. Bk Ch6 S6.1
... Transitional or intermediate forms of organisms have structural similarities with organisms that preceded them on Earth as well as with more recent forms. This suggests that one group of organisms evolved from another or from a common ancestor. For example, Archaeopteryx was a flying dinosaur that l ...
... Transitional or intermediate forms of organisms have structural similarities with organisms that preceded them on Earth as well as with more recent forms. This suggests that one group of organisms evolved from another or from a common ancestor. For example, Archaeopteryx was a flying dinosaur that l ...
Evolution: Exhibition Notes 2
... discovered in rocks of this age in Western Australia and South Africa. The fossils are of two types: finely layered structures called stromatolites; and microscopic spheroidal or thread-like structures. These fossils show that life originated within the first 1,000 million years of the Earth’s exist ...
... discovered in rocks of this age in Western Australia and South Africa. The fossils are of two types: finely layered structures called stromatolites; and microscopic spheroidal or thread-like structures. These fossils show that life originated within the first 1,000 million years of the Earth’s exist ...
2015 PreAP Biology Final Exam Study Guide Part 1 of 2
... b. during half-life periods of 5,715 years. d. so rapidly that it can be observed easily. 11. The major idea that Darwin presented in his book The Origin of Species was that a. species change over time and never compete with each other. b. animals change, but plants remain the same over time. c. spe ...
... b. during half-life periods of 5,715 years. d. so rapidly that it can be observed easily. 11. The major idea that Darwin presented in his book The Origin of Species was that a. species change over time and never compete with each other. b. animals change, but plants remain the same over time. c. spe ...
Bio 101 H.W. 3
... organism. In your answer, be sure to: 42. Identify one possible negative effect of this solution. 43. State one solution to this problem. 44. Identify one problem caused by this resistance. 45. Describe how this process is involved in the production of a population of resistant organisms. 46. Identi ...
... organism. In your answer, be sure to: 42. Identify one possible negative effect of this solution. 43. State one solution to this problem. 44. Identify one problem caused by this resistance. 45. Describe how this process is involved in the production of a population of resistant organisms. 46. Identi ...
Mechanisms of Action
... 7. Improves Osteoblast and Osteoclast Production: Faster regeneration of bone is derived by hyperbaric oxygen’s ability to stimulate and increase production of specialized cells (osteoblasts and osteoclasts) responsible for bone repair and formation. 8. Increases Fibroblast and Collagen Production: ...
... 7. Improves Osteoblast and Osteoclast Production: Faster regeneration of bone is derived by hyperbaric oxygen’s ability to stimulate and increase production of specialized cells (osteoblasts and osteoclasts) responsible for bone repair and formation. 8. Increases Fibroblast and Collagen Production: ...
document
... Cells within the blastula eventually develop into three distinct layers of cells endoderm, ectoderm, and mesoderm . These layers are called the primary tissue layers because they give rise to all of the tissues and organs of the adult body. ...
... Cells within the blastula eventually develop into three distinct layers of cells endoderm, ectoderm, and mesoderm . These layers are called the primary tissue layers because they give rise to all of the tissues and organs of the adult body. ...
Chapter 7 notes
... Get one plastic cup filled with “food” and empty it out slowly in front of you on a paper plate. There are 20 food items in each cup. The empty cup now represents your “stomach.” One student will hold the beak and one student will hold the stomach. When your teacher tells you, use your beak to pick ...
... Get one plastic cup filled with “food” and empty it out slowly in front of you on a paper plate. There are 20 food items in each cup. The empty cup now represents your “stomach.” One student will hold the beak and one student will hold the stomach. When your teacher tells you, use your beak to pick ...
Enzymes
... Based on this information, which statement accurately compares organelles to organs? 1.Functions are carried out more efficiently by organs than by organelles. 2.Organs maintain homeostasis while organelles do not. 3.Organelles carry out functions similar to those of organs. 4.Organelles function in ...
... Based on this information, which statement accurately compares organelles to organs? 1.Functions are carried out more efficiently by organs than by organelles. 2.Organs maintain homeostasis while organelles do not. 3.Organelles carry out functions similar to those of organs. 4.Organelles function in ...
Powerpoint pdf
... B. Feeding If choanocytes specialized for feeding, how are other cell types nourished? via another cell type - amoeboid cells that move throughout the sponge, collecting and further digesting material from choanocytes, then passing it on to other cells... ...
... B. Feeding If choanocytes specialized for feeding, how are other cell types nourished? via another cell type - amoeboid cells that move throughout the sponge, collecting and further digesting material from choanocytes, then passing it on to other cells... ...
Animal Body Systems
... Cells within the blastula eventually develop into three distinct layers of cells endoderm, ectoderm, and mesoderm . These layers are called the primary tissue layers because they give rise to all of the tissues and organs of the adult body. ...
... Cells within the blastula eventually develop into three distinct layers of cells endoderm, ectoderm, and mesoderm . These layers are called the primary tissue layers because they give rise to all of the tissues and organs of the adult body. ...
STERNGRR Examples in representative organisms
... they move wastes from their cells to the organs of excretion) Excretion (How organisms get rid of their waste and balance their fluids (pH, salt concentration, water)) Regulation (How organisms control body processeshormones?,nervous system?) Nutrition (How organisms break down and absorb foods. Het ...
... they move wastes from their cells to the organs of excretion) Excretion (How organisms get rid of their waste and balance their fluids (pH, salt concentration, water)) Regulation (How organisms control body processeshormones?,nervous system?) Nutrition (How organisms break down and absorb foods. Het ...
animals
... Cells within the blastula eventually develop into three distinct layers of cells endoderm, ectoderm, and mesoderm . These layers are called the primary tissue layers because they give rise to all of the tissues and organs of the adult body. ...
... Cells within the blastula eventually develop into three distinct layers of cells endoderm, ectoderm, and mesoderm . These layers are called the primary tissue layers because they give rise to all of the tissues and organs of the adult body. ...
chpt 26 animals - St John Brebeuf
... resembles a mouth or gut, and they have no specialized tissues or organ systems Most biologists believe that sponges evolved from single-celled ancestors separately from other multicellular animals The evolutionary line that gave rise to sponges was a dead end that produced no other groups of animal ...
... resembles a mouth or gut, and they have no specialized tissues or organ systems Most biologists believe that sponges evolved from single-celled ancestors separately from other multicellular animals The evolutionary line that gave rise to sponges was a dead end that produced no other groups of animal ...
Chapter 26 Power Point
... resembles a mouth or gut, and they have no specialized tissues or organ systems Most biologists believe that sponges evolved from single-celled ancestors separately from other multicellular animals The evolutionary line that gave rise to sponges was a dead end that produced no other groups of animal ...
... resembles a mouth or gut, and they have no specialized tissues or organ systems Most biologists believe that sponges evolved from single-celled ancestors separately from other multicellular animals The evolutionary line that gave rise to sponges was a dead end that produced no other groups of animal ...
Slide 1
... • What is the implication of this uniformity in the basic building blocks of life, even though there are many millions of organisms both extant and extinct??? • These structures and processes emerged at the very beginning of life on this planet and have been conserved in all organisms ...
... • What is the implication of this uniformity in the basic building blocks of life, even though there are many millions of organisms both extant and extinct??? • These structures and processes emerged at the very beginning of life on this planet and have been conserved in all organisms ...
Practice Quiz 1 Quarter IV
... d. All of the above ____ 63. The hypothesis that evolution occurs at a slow, constant rate is known as a. gradualism. c. natural selection. b. slow motion. d. adaptation. ____ 64. The hypothesis that evolution occurs at an irregular rate through geologic time is known as a. directional evolution. c. ...
... d. All of the above ____ 63. The hypothesis that evolution occurs at a slow, constant rate is known as a. gradualism. c. natural selection. b. slow motion. d. adaptation. ____ 64. The hypothesis that evolution occurs at an irregular rate through geologic time is known as a. directional evolution. c. ...
Year 9 Term 2: Body Systems and Responses
... in their environment identify that living things are made of cells identify that substances move into and out of cells distinguish between unicellular and multicellular organisms explain why multicellular organisms require specialised organs and systems (limitations of diffusion) describe some examp ...
... in their environment identify that living things are made of cells identify that substances move into and out of cells distinguish between unicellular and multicellular organisms explain why multicellular organisms require specialised organs and systems (limitations of diffusion) describe some examp ...
Precambrian body plans

Until the late 1950’s, the Precambrian era was not believed to have hosted multicellular organisms. However, with radiometric dating techniques, it has been found that fossils initially found in the Ediacara Hills in Southern Australia date back to the late Precambrian era. These fossils are body impressions of organisms shaped like disks, fronds and some with ribbon patterns that were most likely tentacles.These are the earliest multicellular organisms in Earth’s history, despite the fact that unicellularity had been around for a long time before that. The requirements for multicellularity were embedded in the genes of some of these cells, specifically choanoflagellates. These are thought to be the precursors for all multicellular organisms. They are highly related to sponges (Porifera), which are the simplest multicellular organisms.In order to understand the transition to multicellularity during the Precambrian, it is important to look at the requirements for multicellularity—both biological and environmental.