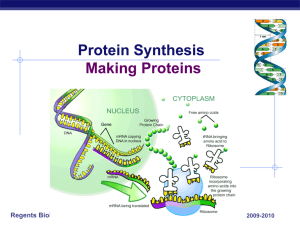
Panspermia and Horizontal Gene Transfer
... the potential reservoir of genes that can be transferred both locally and globally by phage is enormous. …There is little restriction to the types of genes carried by the viral community, suggesting that they influence a wide range of processes, including biogeochemical cycling, short-term adaptatio ...
... the potential reservoir of genes that can be transferred both locally and globally by phage is enormous. …There is little restriction to the types of genes carried by the viral community, suggesting that they influence a wide range of processes, including biogeochemical cycling, short-term adaptatio ...
Macromolecules are very large biomolecules formed by a process of
... In polymerization many small molecule are connected together to make a large molecule. The small molecules are called monomers. Monomers may all be identical or different. They are connected like the beads in a necklace. There are four groups of macromolecules: 1. Carbohydrates – composed of sugar m ...
... In polymerization many small molecule are connected together to make a large molecule. The small molecules are called monomers. Monomers may all be identical or different. They are connected like the beads in a necklace. There are four groups of macromolecules: 1. Carbohydrates – composed of sugar m ...
File
... eventually disintegrate. The final egg cell is provided with the larger Cells are diploid (human diploid # = 46 or 23 homologous pairs) supply of stored nutrients RESULTS: Four daughter cells (sex cells) ½ # of chromosomes (haploid) with genetic variation (n = 23) Sex cells combine during sexual rep ...
... eventually disintegrate. The final egg cell is provided with the larger Cells are diploid (human diploid # = 46 or 23 homologous pairs) supply of stored nutrients RESULTS: Four daughter cells (sex cells) ½ # of chromosomes (haploid) with genetic variation (n = 23) Sex cells combine during sexual rep ...
LC Biology Sample Paper 6 HL Solutions
... in sexual reproduction: meiosis produces (1) haploid gametes: when these fuse the diploid number is restored. (2) The random splitting of pairs of chromosomes forms a base for evolution where each member of the species shows slight variations from the next. 2x(2) (ii) Diagram to include: ovaries, fa ...
... in sexual reproduction: meiosis produces (1) haploid gametes: when these fuse the diploid number is restored. (2) The random splitting of pairs of chromosomes forms a base for evolution where each member of the species shows slight variations from the next. 2x(2) (ii) Diagram to include: ovaries, fa ...
Cells
... o harmful if they reduce an organism’s chances for reproduction or survival o helpful if they improve an organism’s chances for survival o neutral if they do not produce an obvious changes in an organism (silent mutation) o lethal if they result in the immediate death of an organism Mutations can ...
... o harmful if they reduce an organism’s chances for reproduction or survival o helpful if they improve an organism’s chances for survival o neutral if they do not produce an obvious changes in an organism (silent mutation) o lethal if they result in the immediate death of an organism Mutations can ...
The 56th Annual - State Science Day
... division occur quickly for the shoot regrowth 41. Which of the following is not true of genetic switches? A) They allow different structures to evolve within an individual organism B) They determine when and where a gene is turned on or off C) They control how a molecular tool kit is used D) They in ...
... division occur quickly for the shoot regrowth 41. Which of the following is not true of genetic switches? A) They allow different structures to evolve within an individual organism B) They determine when and where a gene is turned on or off C) They control how a molecular tool kit is used D) They in ...
Language Arts 2 column notes - SJSEighthGradePortfolio1027
... the inheritance of traits in humans, a family tree that tracks which members of a family have a particular trait. Karyotype - a picture of all the chromosomes in a cell. Section 3 – Advances in Genetics Selective breeding, cloning and genetic engineering are three methods for developing organisms wi ...
... the inheritance of traits in humans, a family tree that tracks which members of a family have a particular trait. Karyotype - a picture of all the chromosomes in a cell. Section 3 – Advances in Genetics Selective breeding, cloning and genetic engineering are three methods for developing organisms wi ...
Biology High School Standards Review Worksheet 1. The Chemistry
... can be used by cells for energy and for repair and growth. Text: 36.2 Digestion 4.2 Explain how the circulatory system (heart, arteries, veins, capillaries, red blood cells) transports nutrients and oxygen to cells and removes cell wastes. Describe how the kidneys and the liver are closely associate ...
... can be used by cells for energy and for repair and growth. Text: 36.2 Digestion 4.2 Explain how the circulatory system (heart, arteries, veins, capillaries, red blood cells) transports nutrients and oxygen to cells and removes cell wastes. Describe how the kidneys and the liver are closely associate ...
31 March 2011
... • Explain experimental techniques used to investigate evolution 5. Understand the metabolic complexity of cells and organisms. • Provide examples of diverse mechanisms used by cells/organisms to extract energy from the environment • Explain the reactions of energy transformation that occur in mitoch ...
... • Explain experimental techniques used to investigate evolution 5. Understand the metabolic complexity of cells and organisms. • Provide examples of diverse mechanisms used by cells/organisms to extract energy from the environment • Explain the reactions of energy transformation that occur in mitoch ...
chapter 1
... Organisms make up populations, localized groups of organisms belonging to the same species. Populations of several species in the same area combine to form a biological community. Populations interact with their physical environment to form an ecosystem. The biosphere consists of all the environment ...
... Organisms make up populations, localized groups of organisms belonging to the same species. Populations of several species in the same area combine to form a biological community. Populations interact with their physical environment to form an ecosystem. The biosphere consists of all the environment ...
... inheriting gene laden chromosomes sexual life cycles stages & products of meiosis genetic variation eukaryotic chromosomes structure of chromosomes Mendelian inheritance sex-linked genes linked genes inheritance patterns Mendel’s laws probability complex inheritance pattern ...
A - Hatboro
... BASIC GENETICS CONCEPTS 111. ____ The appearance of an organism is its a) genotype b) phenotype 112. ____ The different versions of genes are called a) centromeres b) centrioles ...
... BASIC GENETICS CONCEPTS 111. ____ The appearance of an organism is its a) genotype b) phenotype 112. ____ The different versions of genes are called a) centromeres b) centrioles ...
MCAS And Final Review Packet 2014
... hemoglobin? Explain. No GGA and GGU both produce the same amino acid and therefore the same protein – redundancy 3. Does a mutation in DNA always result in a phenotypic change? Explain your answer using the evidence you have gathered from this problem. No some mutations do not change the aa sequence ...
... hemoglobin? Explain. No GGA and GGU both produce the same amino acid and therefore the same protein – redundancy 3. Does a mutation in DNA always result in a phenotypic change? Explain your answer using the evidence you have gathered from this problem. No some mutations do not change the aa sequence ...
Topics 1-6
... 2.5.5 Explain how mitosis produces two genetically identical nuclei. During DNA replication, each ...
... 2.5.5 Explain how mitosis produces two genetically identical nuclei. During DNA replication, each ...
What is the purpose of mitosis?
... occurs in each system? Circulatory – pulse rate increases to bring more nutrients and oxygen to muscles. Respiratory – breathing rate increases to exchange ...
... occurs in each system? Circulatory – pulse rate increases to bring more nutrients and oxygen to muscles. Respiratory – breathing rate increases to exchange ...
Biology - Bibb County Schools
... Which of the following environmental changes can cause an increase in the rates of chemical reactions in cells? A increased temperature B decreased enzyme concentrations C increased activation energy requirement D decreased diffusion rates ...
... Which of the following environmental changes can cause an increase in the rates of chemical reactions in cells? A increased temperature B decreased enzyme concentrations C increased activation energy requirement D decreased diffusion rates ...
Biology Frameworks
... 3.5 Describe how Mendel’s laws of segregation and independent assortment can be observed through patterns of inheritance (e.g., dihybrid crosses). 3.6 Use a Punnett Square to determine the probabilities for genotype and phenotype combinations in monohybrid crosses. 4. Anatomy and Physiology Central ...
... 3.5 Describe how Mendel’s laws of segregation and independent assortment can be observed through patterns of inheritance (e.g., dihybrid crosses). 3.6 Use a Punnett Square to determine the probabilities for genotype and phenotype combinations in monohybrid crosses. 4. Anatomy and Physiology Central ...
Biology EOC Review Packet - Watchung Hills Regional High School
... Ribosomes- make proteins, cell membrane- controls what enters or exits, nucleus- stores DNA, etc. When do Cells divide? During mitosis or meiosis. For growth and repair, or reproduction How do cells ensure that the new cells will have all the same information that the old cells do? Cells copy their ...
... Ribosomes- make proteins, cell membrane- controls what enters or exits, nucleus- stores DNA, etc. When do Cells divide? During mitosis or meiosis. For growth and repair, or reproduction How do cells ensure that the new cells will have all the same information that the old cells do? Cells copy their ...
Week 4 Evolution Ideas and Evidence
... 2. Gene flow: movement of genes from one population to another adding variation to the recipient population 3. Sex: recombines genetic material from two dif ferent parents which can lead to new gene combinations, and thus new variety 4. Recombination: During meiosis (the process which replicat ...
... 2. Gene flow: movement of genes from one population to another adding variation to the recipient population 3. Sex: recombines genetic material from two dif ferent parents which can lead to new gene combinations, and thus new variety 4. Recombination: During meiosis (the process which replicat ...
Questions From Old Exams
... (abbreviated by their one-letter designation), draw a double-stranded DNA molecule with five base pairs below. Indicate covalent bonds between the P, S, and/or bases using solid lines and indicate hydrogen bonds with dotted or dashed lines. There should be 10 total nucleotides in your drawing. Examp ...
... (abbreviated by their one-letter designation), draw a double-stranded DNA molecule with five base pairs below. Indicate covalent bonds between the P, S, and/or bases using solid lines and indicate hydrogen bonds with dotted or dashed lines. There should be 10 total nucleotides in your drawing. Examp ...
The Study of Life
... • All living things are made of cells • Cells are the basic unit of life – The smallest organisms are made of only one cell ...
... • All living things are made of cells • Cells are the basic unit of life – The smallest organisms are made of only one cell ...
Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life
... Living organisms often transform one form of energy to another. ○ Chlorophyll molecules within the tree’s leaves harness the energy of sunlight and use it to drive photosynthesis, converting water and carbon dioxide to sugar and oxygen. ○ The chemical energy in sugar is then passed along by plants a ...
... Living organisms often transform one form of energy to another. ○ Chlorophyll molecules within the tree’s leaves harness the energy of sunlight and use it to drive photosynthesis, converting water and carbon dioxide to sugar and oxygen. ○ The chemical energy in sugar is then passed along by plants a ...
Co-Requisite – Characteristics of Science
... c. Using Mendel’s laws, explain the role of meiosis in reproductive variability. What is meiosis? _________________________________________________________________________ How does meiosis play a role in reproductive variability? _____________________________________________ ________________________ ...
... c. Using Mendel’s laws, explain the role of meiosis in reproductive variability. What is meiosis? _________________________________________________________________________ How does meiosis play a role in reproductive variability? _____________________________________________ ________________________ ...