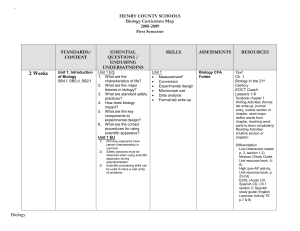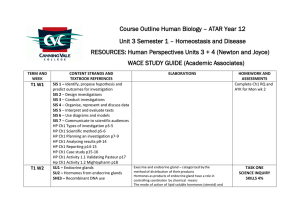
Course Outline Human Biology – ATAR Year 12 Unit 3 Semester 1
... changes in the internal and external environments facilitate the maintenance of optimal conditions for the functioning of cells. Feedback systems involving the autonomic nervous system, the endocrine system and behavioural mechanisms maintain the internal environment for body temperature, body fluid ...
... changes in the internal and external environments facilitate the maintenance of optimal conditions for the functioning of cells. Feedback systems involving the autonomic nervous system, the endocrine system and behavioural mechanisms maintain the internal environment for body temperature, body fluid ...
Biology EOC review - Duplin County Schools
... can compose enzymes, hormones, antibodies, and structural components ...
... can compose enzymes, hormones, antibodies, and structural components ...
Biology EOC Study Guide - Auburndale High School
... can compose enzymes, hormones, antibodies, and structural components ...
... can compose enzymes, hormones, antibodies, and structural components ...
interactive_textbook reading
... Your body is made mostly of water. The cells that make up your body are about 70% to 85% water. Cells need water to keep their inside environments stable. Most of the chemical reactions that happen in cells need water. Your body loses water as you breathe, sweat, or get rid of wastes, such as urine. ...
... Your body is made mostly of water. The cells that make up your body are about 70% to 85% water. Cells need water to keep their inside environments stable. Most of the chemical reactions that happen in cells need water. Your body loses water as you breathe, sweat, or get rid of wastes, such as urine. ...
Week 1 - Speyside High School
... What you need to learn this week: Selective Breeding Humans have contributed to the evolution of both crop plants and domesticated animals by selective breeding The parents are selected for desirable characteristics such as high yield Offspring that reach a standard for the desired characteris ...
... What you need to learn this week: Selective Breeding Humans have contributed to the evolution of both crop plants and domesticated animals by selective breeding The parents are selected for desirable characteristics such as high yield Offspring that reach a standard for the desired characteris ...
standards - Henry County Schools
... diverse range of traits. Independent assortment and crossing over during meiosis results in genetic diversity. Mutations are changes in DNA that may or may not affect phenotype. DNA is identified as the genetic material in all cells and transcription converts genes into a RNA molecule. DNA technolog ...
... diverse range of traits. Independent assortment and crossing over during meiosis results in genetic diversity. Mutations are changes in DNA that may or may not affect phenotype. DNA is identified as the genetic material in all cells and transcription converts genes into a RNA molecule. DNA technolog ...
ap biology exam review guide
... a. Biological catalysts (made of protein) that speed up rate of chemical reactions by lowering activation energy required for reaction to occur b. Enzyme has active site (exposed R groups) where reaction occurs c. Enzymes can break down substance (catabolic reaction) or build up substances (anabolic ...
... a. Biological catalysts (made of protein) that speed up rate of chemical reactions by lowering activation energy required for reaction to occur b. Enzyme has active site (exposed R groups) where reaction occurs c. Enzymes can break down substance (catabolic reaction) or build up substances (anabolic ...
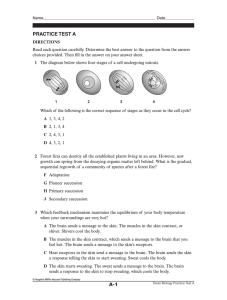
Name
... Principles of Genetics: What are inheritable traits and how are they transmitted from one generation to the next? o What is an inheritable trait? What is a gene? What is meiosis? ½ DNA + ½ DNA = 1 whole DNA Structure of DNA: Be familiar with the structure of DNA. What is a nucleotide? (phospha ...
... Principles of Genetics: What are inheritable traits and how are they transmitted from one generation to the next? o What is an inheritable trait? What is a gene? What is meiosis? ½ DNA + ½ DNA = 1 whole DNA Structure of DNA: Be familiar with the structure of DNA. What is a nucleotide? (phospha ...
Comprehension Questions
... There are four base sequences which code for the amino acid glycine. These are CCA, CCC, CCG and CCT. There are also four base sequences coding for the amino acid proline. These are GGA, GGC, GGG and GGT. Pieces of DNA which have a sequence where the same base is repeated many times are called “slip ...
... There are four base sequences which code for the amino acid glycine. These are CCA, CCC, CCG and CCT. There are also four base sequences coding for the amino acid proline. These are GGA, GGC, GGG and GGT. Pieces of DNA which have a sequence where the same base is repeated many times are called “slip ...
Chapter 16.
... The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick Griffith (1928) Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944) Hershey & Chase (1952) Watson & Crick (1953) Meselson & Stahl (1958) ...
... The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick Griffith (1928) Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944) Hershey & Chase (1952) Watson & Crick (1953) Meselson & Stahl (1958) ...
2 The Necessities of Life
... As you just read, organisms can get their food in three different ways. However, all organisms must break down their food to use the nutrients. Nutrients are molecules. Molecules are made of two or more atoms joined together. Most molecules in living things are combinations of carbon, nitrogen, oxyg ...
... As you just read, organisms can get their food in three different ways. However, all organisms must break down their food to use the nutrients. Nutrients are molecules. Molecules are made of two or more atoms joined together. Most molecules in living things are combinations of carbon, nitrogen, oxyg ...
M.Sc. (Prev.) ZOOLOGY Exam. –2014 Distribution of Marks Paper
... IV. Permanent preparations and their study : 1. Preparation of cultures of Amoeba, Paramaecium and Euglena.Study of these protozoans using vital dyes. 2. Permanent preparations of Amoeba. Paramaecium and Euglena from cultures, vorticella from the pond water; flagellates from the gut of white ant; Re ...
... IV. Permanent preparations and their study : 1. Preparation of cultures of Amoeba, Paramaecium and Euglena.Study of these protozoans using vital dyes. 2. Permanent preparations of Amoeba. Paramaecium and Euglena from cultures, vorticella from the pond water; flagellates from the gut of white ant; Re ...
Characteristics of Life 1.01
... parent(s) to offspring each generation. The basic units of heredity are the genes, coded segments of a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecule. Mutation is change in the DNA of a gene Only mutations that occur in sex cells (egg, sperm) are passed on Most mutations that cause change are ...
... parent(s) to offspring each generation. The basic units of heredity are the genes, coded segments of a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecule. Mutation is change in the DNA of a gene Only mutations that occur in sex cells (egg, sperm) are passed on Most mutations that cause change are ...
Daphne High School ACOS General Biology Project This sheet must
... 19. Comparing sperm and egg formation in terms of ploidy Example: ploidy—haploid, diploid (P. 148 fig. 3) 20. Comparing sexual and asexual reproduction (Ch 7 p.150) 21. Apply Mendel’s law to determine phenotypic and genotypic probabilities of offspring. (Ch 8 sect. 3) 22. Defining important genetic ...
... 19. Comparing sperm and egg formation in terms of ploidy Example: ploidy—haploid, diploid (P. 148 fig. 3) 20. Comparing sexual and asexual reproduction (Ch 7 p.150) 21. Apply Mendel’s law to determine phenotypic and genotypic probabilities of offspring. (Ch 8 sect. 3) 22. Defining important genetic ...
april break review packet
... a. Biological catalysts (made of protein) that speed up rate of chemical reactions by lowering activation energy required for reaction to occur b. Enzyme has active site (exposed R groups) where reaction occurs c. Enzymes can break down substance (catabolic reaction) or build up substances (anabolic ...
... a. Biological catalysts (made of protein) that speed up rate of chemical reactions by lowering activation energy required for reaction to occur b. Enzyme has active site (exposed R groups) where reaction occurs c. Enzymes can break down substance (catabolic reaction) or build up substances (anabolic ...
Biology Review
... F. I am the father of genetics by from my work with pea plants. G. I am the scientists who erroneously came up with the idea that traits are acquired from animals from their use or disuse. H. I disproved the idea of spontaneous generation by using covered and uncovered jars of rotting meat. I. I am ...
... F. I am the father of genetics by from my work with pea plants. G. I am the scientists who erroneously came up with the idea that traits are acquired from animals from their use or disuse. H. I disproved the idea of spontaneous generation by using covered and uncovered jars of rotting meat. I. I am ...
Biology Keystone Exam Review Packet
... A) Sodium and potassium ions move by active transport, and glucose moves by osmosis. B) Sodium and potassium ions move by active transport, and glucose moves by facilitated diffusion. Due to the fact that they are highly charged molecules (and “hate” the nonpolar cell membrane and can’t pass through ...
... A) Sodium and potassium ions move by active transport, and glucose moves by osmosis. B) Sodium and potassium ions move by active transport, and glucose moves by facilitated diffusion. Due to the fact that they are highly charged molecules (and “hate” the nonpolar cell membrane and can’t pass through ...
Biology Keystone Exam Review Packet
... A) Sodium and potassium ions move by active transport, and glucose moves by osmosis. B) Sodium and potassium ions move by active transport, and glucose moves by facilitated diffusion. Due to the fact that they are highly charged molecules (and “hate” the nonpolar cell membrane and can’t pass through ...
... A) Sodium and potassium ions move by active transport, and glucose moves by osmosis. B) Sodium and potassium ions move by active transport, and glucose moves by facilitated diffusion. Due to the fact that they are highly charged molecules (and “hate” the nonpolar cell membrane and can’t pass through ...
Glossary - Hodder Education
... adenine a purine organic base, found in the coenzymes ATP and NADP, and in nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) in which it pairs with thymine adenosine diphosphate (ADP) a nucleotide, present in every living cell, made of adenosine and two phosphate groups linked in series, and important in energy transfer ...
... adenine a purine organic base, found in the coenzymes ATP and NADP, and in nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) in which it pairs with thymine adenosine diphosphate (ADP) a nucleotide, present in every living cell, made of adenosine and two phosphate groups linked in series, and important in energy transfer ...
DNA Structure and Replication
... The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick Griffith (1928) Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944) Hershey & Chase (1952) Watson & Crick (1953) Meselson & Stahl (1958) ...
... The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick Griffith (1928) Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944) Hershey & Chase (1952) Watson & Crick (1953) Meselson & Stahl (1958) ...
File
... humans’ use of fossil fuels. Fossil fuels result from the gradual transformation of layers of organic matter in sediment into natural gas, coal, and petroleum. When fossil fuels are burned, they release a gas that can be used by plants for photosynthesis. High levels of this gas in the atmosphere ...
... humans’ use of fossil fuels. Fossil fuels result from the gradual transformation of layers of organic matter in sediment into natural gas, coal, and petroleum. When fossil fuels are burned, they release a gas that can be used by plants for photosynthesis. High levels of this gas in the atmosphere ...
Developmental Gene Regulation and the
... organisms apparently left traces of themselves in Vendian age deposits, in the form of burrows and tracks that only a bilaterally symmetrical animal could have produced (see, for example, Fedonkin, 1994). Thus the great mystery that we would all like to understand is not quite so lurid as implied by ...
... organisms apparently left traces of themselves in Vendian age deposits, in the form of burrows and tracks that only a bilaterally symmetrical animal could have produced (see, for example, Fedonkin, 1994). Thus the great mystery that we would all like to understand is not quite so lurid as implied by ...
Graph 1: Rabbits Over Time
... 1.03 Formulate and revise scientific explanations and models of biological phenomena using logic and evidence to: explain observations, make inferences and predictions, explain the relationship between evidence and explanation. Bromothymol blue turns to bromothymol yellow in the presence of carbon d ...
... 1.03 Formulate and revise scientific explanations and models of biological phenomena using logic and evidence to: explain observations, make inferences and predictions, explain the relationship between evidence and explanation. Bromothymol blue turns to bromothymol yellow in the presence of carbon d ...
File - HABITAT (Home)
... development, and motility sometime during the organism's life history One of three domains. This domain only has one kingdom, the archeabacteria. Taxonomic kingdom of ancient (over 3.5 billion years old) group of prokaryotes; These bacteria tend to live in extreme environments (very hot, highly acid ...
... development, and motility sometime during the organism's life history One of three domains. This domain only has one kingdom, the archeabacteria. Taxonomic kingdom of ancient (over 3.5 billion years old) group of prokaryotes; These bacteria tend to live in extreme environments (very hot, highly acid ...