AP BIOLOGY EXAM REVIEW GUIDE
... a. Biological catalysts (made of protein) that speed up rate of chemical reactions by lowering activation energy required for reaction to occur b. Enzyme has active site (exposed R groups) where reaction occurs c. Enzymes can break down substance (catabolic reaction) or build up substances (anabolic ...
... a. Biological catalysts (made of protein) that speed up rate of chemical reactions by lowering activation energy required for reaction to occur b. Enzyme has active site (exposed R groups) where reaction occurs c. Enzymes can break down substance (catabolic reaction) or build up substances (anabolic ...
ap biology exam review guide
... a. Biological catalysts (made of protein) that speed up rate of chemical reactions by lowering activation energy required for reaction to occur b. Enzyme has active site (exposed R groups) where reaction occurs c. Enzymes can break down substance (catabolic reaction) or build up substances (anabolic ...
... a. Biological catalysts (made of protein) that speed up rate of chemical reactions by lowering activation energy required for reaction to occur b. Enzyme has active site (exposed R groups) where reaction occurs c. Enzymes can break down substance (catabolic reaction) or build up substances (anabolic ...
AP Exam review
... a. Biological catalysts (made of protein) that speed up rate of chemical reactions by lowering activation energy required for reaction to occur b. Enzyme has active site (exposed R groups) where reaction occurs c. Enzymes can break down substance (catabolic reaction) or build up substances (anabolic ...
... a. Biological catalysts (made of protein) that speed up rate of chemical reactions by lowering activation energy required for reaction to occur b. Enzyme has active site (exposed R groups) where reaction occurs c. Enzymes can break down substance (catabolic reaction) or build up substances (anabolic ...
Complete AP Bio Exam Review
... a. Biological catalysts (made of protein) that speed up rate of chemical reactions by lowering activation energy required for reaction to occur b. Enzyme has active site (exposed R groups) where reaction occurs c. Enzymes can break down substance (catabolic reaction) or build up substances (anabolic ...
... a. Biological catalysts (made of protein) that speed up rate of chemical reactions by lowering activation energy required for reaction to occur b. Enzyme has active site (exposed R groups) where reaction occurs c. Enzymes can break down substance (catabolic reaction) or build up substances (anabolic ...
mc2 Chromatin - WordPress.com
... from Jiang and Pugh, Nature Rev.Genet. 10, 161 (2009) Histone chaperones incorporate histone variants ...
... from Jiang and Pugh, Nature Rev.Genet. 10, 161 (2009) Histone chaperones incorporate histone variants ...
WHITTIER UNION HIGH SCHOOL DISTRICT
... As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. Meiosis is an early step in sexual reproduction in which the pairs of chromosomes separate and segregate randomly during cell division to produce gametes containing one chromosome of each type. b. Only certain cells in a multicellular orga ...
... As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. Meiosis is an early step in sexual reproduction in which the pairs of chromosomes separate and segregate randomly during cell division to produce gametes containing one chromosome of each type. b. Only certain cells in a multicellular orga ...
effective: september 2003 curriculum guidelines
... Non-Mendelian Inheritance: multiple alleles, sex linkage and multigenic inheritance experiments using Dro sophila: how to differentiate an autosomal character from a sex-linked character. preparation of plant tissue for microsc opic chro mosome analysis. Molecu lar Basis of Life basic chemical formu ...
... Non-Mendelian Inheritance: multiple alleles, sex linkage and multigenic inheritance experiments using Dro sophila: how to differentiate an autosomal character from a sex-linked character. preparation of plant tissue for microsc opic chro mosome analysis. Molecu lar Basis of Life basic chemical formu ...
NATURE - Biology
... Tissue – A group of cells Organs – A group of tissues Systems – A group of organs that work together Population – A group of the same kind of organisms Community – All the organisms in the ecosystem Ecosystem – All the living and nonliving things in one place At which level does life begin? Cells Wh ...
... Tissue – A group of cells Organs – A group of tissues Systems – A group of organs that work together Population – A group of the same kind of organisms Community – All the organisms in the ecosystem Ecosystem – All the living and nonliving things in one place At which level does life begin? Cells Wh ...
2014 Biology STAAR EOC Review
... Unlike a cell, a virus lacks structures to take in food, break apart food for energy, or synthesize molecules. Because viruses are noncellular and cannot perform most functions of life, scientists classify viruses as nonliving particles. However, viruses are able to perform one life function- reprod ...
... Unlike a cell, a virus lacks structures to take in food, break apart food for energy, or synthesize molecules. Because viruses are noncellular and cannot perform most functions of life, scientists classify viruses as nonliving particles. However, viruses are able to perform one life function- reprod ...
gene duplications
... Substitutions can change the amino acid sequence, and thus the structure and function, of the polypeptides. By characterizing nucleic acid sequences and the primary structures of proteins, molecular evolutionists can determine how rapidly these macromolecules have changed and why they ...
... Substitutions can change the amino acid sequence, and thus the structure and function, of the polypeptides. By characterizing nucleic acid sequences and the primary structures of proteins, molecular evolutionists can determine how rapidly these macromolecules have changed and why they ...
Themes and Concepts of Biology
... bacterial cells belong to the domain Bacteria, while the (b) extremophiles, seen all together as colored mats in this hot spring, belong to domain Archaea. Both the (c) sun ower and (d) lion are part of domain Eukarya. (credit a: modi cation of work by Rocky Mountain Laboratories, NIAID, NIH; credit ...
... bacterial cells belong to the domain Bacteria, while the (b) extremophiles, seen all together as colored mats in this hot spring, belong to domain Archaea. Both the (c) sun ower and (d) lion are part of domain Eukarya. (credit a: modi cation of work by Rocky Mountain Laboratories, NIAID, NIH; credit ...
AP Biology
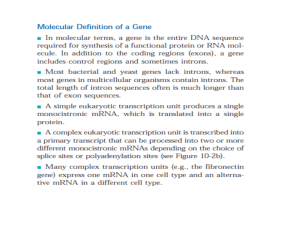
... During transcription, one of the two DNA strands called the template strand provides a template for ordering the sequence of nucleotides in an RNA transcript ...
... During transcription, one of the two DNA strands called the template strand provides a template for ordering the sequence of nucleotides in an RNA transcript ...
Living Organisms Assessment Name: Date: 1. How do bacteria
... 17. A. Acquired traits are passed from parents to offspring. B. Inherited traits are passed from parents to offspring. C. Behaviors are never inherited. D. Behaviors are always inherited. 18. Which of these traits can a tree NOT pass to its offspring? A. the shape of its leaves B. roots that grow t ...
... 17. A. Acquired traits are passed from parents to offspring. B. Inherited traits are passed from parents to offspring. C. Behaviors are never inherited. D. Behaviors are always inherited. 18. Which of these traits can a tree NOT pass to its offspring? A. the shape of its leaves B. roots that grow t ...
vert strand 3 - csi-parent-student
... Scope and Sequence – Classification of Plants and Animals a. Explain how similarities are the basis for classification b. Distinguish between plants (which use sunlight to make their own food) and animals (which must consume ...
... Scope and Sequence – Classification of Plants and Animals a. Explain how similarities are the basis for classification b. Distinguish between plants (which use sunlight to make their own food) and animals (which must consume ...
Comprehensive Review Packet - 2013-2014
... a. Biological catalysts (made of protein) that speed up rate of chemical reactions by lowering activation energy required for reaction to occur b. Enzyme has active site (exposed R groups) where reaction occurs c. Enzymes can break down substance (catabolic reaction) or build up substances (anabolic ...
... a. Biological catalysts (made of protein) that speed up rate of chemical reactions by lowering activation energy required for reaction to occur b. Enzyme has active site (exposed R groups) where reaction occurs c. Enzymes can break down substance (catabolic reaction) or build up substances (anabolic ...
11.1 the work of gregor mendel answer key biology
... biblical account of Creation Scientists who are against the biblical view. modern genetics: Traits are determined by genes bassed from parent to offspring Alleles can be dominant and others recessive adult have two copies of each gene from. First Semester Biology 2012-2013 . AUGUST: SEPTEMBER: OCTOB ...
... biblical account of Creation Scientists who are against the biblical view. modern genetics: Traits are determined by genes bassed from parent to offspring Alleles can be dominant and others recessive adult have two copies of each gene from. First Semester Biology 2012-2013 . AUGUST: SEPTEMBER: OCTOB ...
HS Life Science Alignment
... HS-LS1-7 Use a model to illustrate that cellular respiration is a chemical process whereby the bonds of food molecules and oxygen molecules are broken and the bonds in new compounds are formed resulting in a net transfer of energy. ...
... HS-LS1-7 Use a model to illustrate that cellular respiration is a chemical process whereby the bonds of food molecules and oxygen molecules are broken and the bonds in new compounds are formed resulting in a net transfer of energy. ...
A-level Human Biology Question paper Unit 3 - Pathogens
... a tumour. Some tumours are benign but others are malignant. ...
... a tumour. Some tumours are benign but others are malignant. ...
pictures/graphs, etc. EOC Biology Rview Packet 2012-2013
... "The Swedish study has shown this further effect in animals and I would certainly expect the same mechanism to exist in the human stomach " - Nigel Benjamin Nigel 'Ben' Benjamin, now a consultant in acute medicine at the Peninsula Medical School in Plymouth, UK, discovered a different protective mec ...
... "The Swedish study has shown this further effect in animals and I would certainly expect the same mechanism to exist in the human stomach " - Nigel Benjamin Nigel 'Ben' Benjamin, now a consultant in acute medicine at the Peninsula Medical School in Plymouth, UK, discovered a different protective mec ...
Wizard Test Maker
... level steady (2) the maintenance of a constant body temperature (3) cell division that is involved in normal growth (4) a rapid rise in the number of red blood cells 5016 Organisms undergo constant chemical changes as they maintain an internal balance known as (1) interdependence (3) synthesis (4) r ...
... level steady (2) the maintenance of a constant body temperature (3) cell division that is involved in normal growth (4) a rapid rise in the number of red blood cells 5016 Organisms undergo constant chemical changes as they maintain an internal balance known as (1) interdependence (3) synthesis (4) r ...
File
... role of meiosis in sexual reproduction, including how these processes may contribute to or limit genetic variation. • Describe specific events occurring in each of the stages of the cell cycle and/or phases of mitosis. • Explain how mitosis forms new cells and its role in maintaining chromosome numb ...
... role of meiosis in sexual reproduction, including how these processes may contribute to or limit genetic variation. • Describe specific events occurring in each of the stages of the cell cycle and/or phases of mitosis. • Explain how mitosis forms new cells and its role in maintaining chromosome numb ...
BIOLOGY Specification
... 11.2. Recall the structure and function of the female reproductive system to include: a. the ovaries b. oviducts c. uterus d. cervix e. vagina. 11.3. Recall the menstrual cycle in terms of changes in the uterus and ovaries (no knowledge of control by hormones is required). 11.4. Outline sexual inter ...
... 11.2. Recall the structure and function of the female reproductive system to include: a. the ovaries b. oviducts c. uterus d. cervix e. vagina. 11.3. Recall the menstrual cycle in terms of changes in the uterus and ovaries (no knowledge of control by hormones is required). 11.4. Outline sexual inter ...
Scientific Method Web Resources
... We are Getting Nerdy! Mel and Gerdy are two life science teachers with a true passion for curriculum design. We LOVE creating time-saving, fun and engaging activities for our classrooms & we’re excited to be sharing them with you. We look forward to hearing your feedback on this product. ...
... We are Getting Nerdy! Mel and Gerdy are two life science teachers with a true passion for curriculum design. We LOVE creating time-saving, fun and engaging activities for our classrooms & we’re excited to be sharing them with you. We look forward to hearing your feedback on this product. ...