Pride/Hughes/Kapoor Business, 10th Edition
... competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly. Pure, or perfect, competition is the market situation in which there are many buyers and sellers of a product, and no single buyer or seller is powerful enough to affect the price of that product. All buyers and sellers together determi ...
... competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly. Pure, or perfect, competition is the market situation in which there are many buyers and sellers of a product, and no single buyer or seller is powerful enough to affect the price of that product. All buyers and sellers together determi ...
Advertising - WordPress.com
... it truly better than the others? Probably not. These days, many products are nearly identical to one another in quality and price. If products are almost the same, what makes consumers buy one brand instead of another? Although we might not like to admit it, commercials on ...
... it truly better than the others? Probably not. These days, many products are nearly identical to one another in quality and price. If products are almost the same, what makes consumers buy one brand instead of another? Although we might not like to admit it, commercials on ...
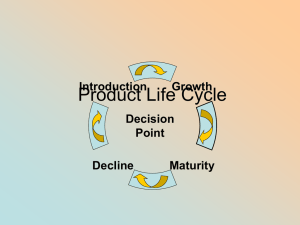
Product Life Cycle
... stage, product must be visible • Companies will advertise heavily at this stage • The product will either catch on or fail ...
... stage, product must be visible • Companies will advertise heavily at this stage • The product will either catch on or fail ...
Advertising
... and desirable. The better a product sounds, the more likely you are to buy it. ...
... and desirable. The better a product sounds, the more likely you are to buy it. ...
April 8 Product Life Cycle BMI3C
... Psychologists have proven that generally, consumers go through five (sometimes six) steps when making a purchase. This study goes hand in hand with understanding consumer psychology of WHY WE BUY. ...
... Psychologists have proven that generally, consumers go through five (sometimes six) steps when making a purchase. This study goes hand in hand with understanding consumer psychology of WHY WE BUY. ...
EKSPORT - IMPORT MANAGEMENT
... – Adaptation – The strategy of altering products to meet the needs of local markets – Global Standardization – The standardization of products across markets & ultimately the standardization of the marketing mix worldwide ...
... – Adaptation – The strategy of altering products to meet the needs of local markets – Global Standardization – The standardization of products across markets & ultimately the standardization of the marketing mix worldwide ...
Class 28 12-1 Products Power Point Presentation
... “…‘right to exclude others from making, using, offering for sale, or selling’ the invention in the U.S. for 20 years.” Patent can be for a product idea or an ...
... “…‘right to exclude others from making, using, offering for sale, or selling’ the invention in the U.S. for 20 years.” Patent can be for a product idea or an ...
Services
... Shopping products are less frequently purchased consumer products and services that customers compare carefully on suitability, quality, price, and style. III. Specialty products are consumer products and services with unique characteristics or brand identification for which a significant group of b ...
... Shopping products are less frequently purchased consumer products and services that customers compare carefully on suitability, quality, price, and style. III. Specialty products are consumer products and services with unique characteristics or brand identification for which a significant group of b ...
Consumers Need Voice in Driving Products
... They understand the importance of packaging and presenting these products so that they appeal to their target markets. They understand the value of good marketplace relationships and promotion. Smart management doesn't make a decision to introduce a new product without the facts in front of them--fa ...
... They understand the importance of packaging and presenting these products so that they appeal to their target markets. They understand the value of good marketplace relationships and promotion. Smart management doesn't make a decision to introduce a new product without the facts in front of them--fa ...
HUMAN FACTORS IN DESIGN MARKET PULL TECHNOLOGICAL
... • Larger handles / buttons for users with reduced mobility. ...
... • Larger handles / buttons for users with reduced mobility. ...
Marketing Mngmt I
... – unsought goods-consumer doesn’t know about product or does know & ignores them (casket) ...
... – unsought goods-consumer doesn’t know about product or does know & ignores them (casket) ...
Sales Promotions - Loudoun County Public Schools
... given away at retail stores – mostly used to introduce new products Sponsorship – companies pay a fee to promote its products at or on a set location Promotional Tie-Ins – (cross-promotion) sales promotional arrangements between one or more retailers or manufacturer Product Placement – consumer prom ...
... given away at retail stores – mostly used to introduce new products Sponsorship – companies pay a fee to promote its products at or on a set location Promotional Tie-Ins – (cross-promotion) sales promotional arrangements between one or more retailers or manufacturer Product Placement – consumer prom ...
The Consumer and Sports Product
... listen to sports or read, use, purchase and/or collect sports items. A purchase by a sports consumer is like a “vote” ...
... listen to sports or read, use, purchase and/or collect sports items. A purchase by a sports consumer is like a “vote” ...
Principles of Marketing-Lecture Slides 4
... Product planners need to think about the product on three levels. Each level adds more customer value. The most basic level is the core product, which provides core benefit to the consumer and addresses the question: What is the buyer really buying? Core Product :The problem solving services or core ...
... Product planners need to think about the product on three levels. Each level adds more customer value. The most basic level is the core product, which provides core benefit to the consumer and addresses the question: What is the buyer really buying? Core Product :The problem solving services or core ...
Software Marketing
... market structure; market and technology trends, preparing and communicating plans that support implementation of these initiatives Assist corporate marketing to drive integrated marketing and sales strategies across the market. Articulating and Understanding customer requirements, leading product de ...
... market structure; market and technology trends, preparing and communicating plans that support implementation of these initiatives Assist corporate marketing to drive integrated marketing and sales strategies across the market. Articulating and Understanding customer requirements, leading product de ...
FALL 2002 BA 303 FOR EXAMINATION ONE L.P. CHEW
... products. In other words, auto parts suppliers are able to deliver superior value as a result of their distinctive competencies in a limited product line. A manufacturer's decision rules on what to buy or make should be based on analyses of those products and processes for which they have a distinct ...
... products. In other words, auto parts suppliers are able to deliver superior value as a result of their distinctive competencies in a limited product line. A manufacturer's decision rules on what to buy or make should be based on analyses of those products and processes for which they have a distinct ...
Standard 16 Lesson 1 PowerPoint 1
... differentiate the brand from those of other sellers. • Consistency in package imagery allows a consumer to associate that image with the product. • Slogans: Song or phrase designed to remind you of a product. ...
... differentiate the brand from those of other sellers. • Consistency in package imagery allows a consumer to associate that image with the product. • Slogans: Song or phrase designed to remind you of a product. ...
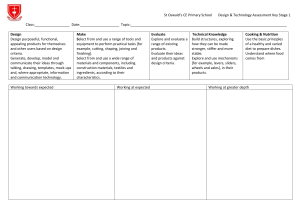
KS1 Assessment - St.Oswald`s CE Primary School`s website
... Class:__________________ Date:____________________ Topic:________________________________________________________________________________ Design Design purposeful, functional, appealing products for themselves and other users based on design criteria. Generate, develop, model and communicate their i ...
... Class:__________________ Date:____________________ Topic:________________________________________________________________________________ Design Design purposeful, functional, appealing products for themselves and other users based on design criteria. Generate, develop, model and communicate their i ...
U 3 Study Guide key
... advertisements can “presell” products – that is, they can influence people to make up their minds about a purchase before they shop Disadvantages of using advertising advertising cannot focus well on individual needs because the message is the same for all customers some forms of advertising, ...
... advertisements can “presell” products – that is, they can influence people to make up their minds about a purchase before they shop Disadvantages of using advertising advertising cannot focus well on individual needs because the message is the same for all customers some forms of advertising, ...
here - School of Food Science and Nutrition
... (Occasional travel to other sites will be required) ...
... (Occasional travel to other sites will be required) ...