Chapter 8
... • Following glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from food • These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation ...
... • Following glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from food • These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation ...
Considerations on the structures involved in the
... binucleate hepatocytes cords and visible points of mitochondria throughout the cytoplasm. Hepatocytes constitute around 7085% of the liver's mass. The liver is an organ within which energy is stored in the form of the nucleoside adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In this context, mitochondria play an imp ...
... binucleate hepatocytes cords and visible points of mitochondria throughout the cytoplasm. Hepatocytes constitute around 7085% of the liver's mass. The liver is an organ within which energy is stored in the form of the nucleoside adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In this context, mitochondria play an imp ...
Answer Set 2
... Thus, a reaction that is endergonic under standard conditions can be converted into an exergonic reaction by maintaining the [products]/[reactants] ratio below the equilibrium value. This conversion is usually attained by using the products in another coupled reaction as soon as they are formed. 4. ...
... Thus, a reaction that is endergonic under standard conditions can be converted into an exergonic reaction by maintaining the [products]/[reactants] ratio below the equilibrium value. This conversion is usually attained by using the products in another coupled reaction as soon as they are formed. 4. ...
Seminario Glúcidos 3 y lípidos 1. Comente los mecanismos de
... enzymatic activity of the various particulate fractions has been described by the Rockefeller group (7, 8), Schneider (9), and other investigators. For instance, quantitative assayshave revealed that most of the succinoxidase and cytochrome oxidase activity is present in the mitochondria or “large g ...
... enzymatic activity of the various particulate fractions has been described by the Rockefeller group (7, 8), Schneider (9), and other investigators. For instance, quantitative assayshave revealed that most of the succinoxidase and cytochrome oxidase activity is present in the mitochondria or “large g ...
A: Objective type questions: Choose the correct answers Most
... All are characteristics of anabolism EXCEPT: a. assembly of complex molecules. b. formation of new covalent bonds. c. ATP provides energy. d. NADPH is an electron donor. e. all are true. Ans. E ...
... All are characteristics of anabolism EXCEPT: a. assembly of complex molecules. b. formation of new covalent bonds. c. ATP provides energy. d. NADPH is an electron donor. e. all are true. Ans. E ...
Glycogen Metabolism, Electron Transport/Oxidative Phosphorylation
... Oxidative Phosphorylation • The only aerobic (oxygen-requiring) energy process in the body of the three main parts of cellular respiration • Oxidative = oxidation, oxygen • Phosphorylation = attaching a P directly to ADP, making ATP • Making ATP via oxidation ...
... Oxidative Phosphorylation • The only aerobic (oxygen-requiring) energy process in the body of the three main parts of cellular respiration • Oxidative = oxidation, oxygen • Phosphorylation = attaching a P directly to ADP, making ATP • Making ATP via oxidation ...
lecture 6 ppt
... Steps of Respiration • Steps of respiration: 1. glycolysis - cytosol Coenzyme Junction 2. Citric acid cycle - mitochondrial matrix 3. ETC - inner mitochondrial membrane 4. Chemiosmosis - inner membrane to intermembrane space ...
... Steps of Respiration • Steps of respiration: 1. glycolysis - cytosol Coenzyme Junction 2. Citric acid cycle - mitochondrial matrix 3. ETC - inner mitochondrial membrane 4. Chemiosmosis - inner membrane to intermembrane space ...
Exam 4 key fall 2010
... creating a proton gradient. This gradient is used by proton-dependant ATP synthetase to make ATP. ...
... creating a proton gradient. This gradient is used by proton-dependant ATP synthetase to make ATP. ...
The citric acid cycle is the
... transformation of acetyl-CoA to oxaloacetate. Thus, for every succinate that enters the reversed cycle, two succinates are returned, making the cycle highly autocatalytic. • Because TCA cycle intermediates are involved in many biosynthetic pathways, a reversed TCA cycle would be a bountifuland broad ...
... transformation of acetyl-CoA to oxaloacetate. Thus, for every succinate that enters the reversed cycle, two succinates are returned, making the cycle highly autocatalytic. • Because TCA cycle intermediates are involved in many biosynthetic pathways, a reversed TCA cycle would be a bountifuland broad ...
Week III Lecture I slides
... Oxygen molecules diffuse across the plasma membrane into the cell, then into the mitochondria ...
... Oxygen molecules diffuse across the plasma membrane into the cell, then into the mitochondria ...
Chapter 19 Lipid Metabolism
... Can synthesize fatty acids from sugars, some amino acids, and other fatty acids. →Fatty acids are synthesized from acetyl-CoA in the cytosol. The body synthesizes palmitic acid (16:0), and then modifies it to form other fatty acids. Synthesis of Palmitic Acid 8 acetyl-CoA + 7 ATP +14NADPH +14H+ → pa ...
... Can synthesize fatty acids from sugars, some amino acids, and other fatty acids. →Fatty acids are synthesized from acetyl-CoA in the cytosol. The body synthesizes palmitic acid (16:0), and then modifies it to form other fatty acids. Synthesis of Palmitic Acid 8 acetyl-CoA + 7 ATP +14NADPH +14H+ → pa ...
CHAPTER-IV LIPID METABOLISM BETA
... For sources that use the larger ATP production numbers described above, the total would be 129 ATP ={(8-1)*17+12-2} equivalents per palmitate. Beta-oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids changes the ATP yield due to the requirement of two possible additional enzymes. Ketogenesis Ketogenesis is the pro ...
... For sources that use the larger ATP production numbers described above, the total would be 129 ATP ={(8-1)*17+12-2} equivalents per palmitate. Beta-oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids changes the ATP yield due to the requirement of two possible additional enzymes. Ketogenesis Ketogenesis is the pro ...
ATP – The Energy of Life - Liberation Chiropractic and Wellness
... When the mitochondria have a short supply of oxygen and fuel (polysaccharides6) to make ATP properly, they can have their own, independent genetics damaged by the very free radicals (rogue electrons) that result from making energy, and this is the start of the life-destroying mitochondrial diseases ...
... When the mitochondria have a short supply of oxygen and fuel (polysaccharides6) to make ATP properly, they can have their own, independent genetics damaged by the very free radicals (rogue electrons) that result from making energy, and this is the start of the life-destroying mitochondrial diseases ...
biol 161 aerobic cellular respiration
... C. If NADH or FADH2 gives an electron to the first protein of the electron transport chain, is the NADH or FADH2 oxidized or reduced? Is the protein oxidized or reduced? D. Will the first protein then pass electrons to the next protein in the electron transport chain? E. Many of the carriers in the ...
... C. If NADH or FADH2 gives an electron to the first protein of the electron transport chain, is the NADH or FADH2 oxidized or reduced? Is the protein oxidized or reduced? D. Will the first protein then pass electrons to the next protein in the electron transport chain? E. Many of the carriers in the ...
Synthesis and Degradation of Lipids
... - Vit. B12 is specifically bound in intestine by intrinsic factor - complex absorbed in intestinal mucosa -> blood - bound to transcobalamins in blood for uptake by tissue - not usually a dietary disease but result from insufficient secretion of intrinsic factor ...
... - Vit. B12 is specifically bound in intestine by intrinsic factor - complex absorbed in intestinal mucosa -> blood - bound to transcobalamins in blood for uptake by tissue - not usually a dietary disease but result from insufficient secretion of intrinsic factor ...
Studies on the extra-mitochondrial CoA
... fatty acids containing 2–4 or 4–10 carbons, respectively, and long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase (ACSL) specifically activate fatty acids with more than 10 carbon atoms [4,6]. These enzymes are located in various cell compartments and exhibit wide tissue distribution, with highest activity associated wi ...
... fatty acids containing 2–4 or 4–10 carbons, respectively, and long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase (ACSL) specifically activate fatty acids with more than 10 carbon atoms [4,6]. These enzymes are located in various cell compartments and exhibit wide tissue distribution, with highest activity associated wi ...
A new mitochondrial DNA mutation at 14577 T/C is probably a major
... Therefore, these 6 substitutions were also in linkage disequilibrium (P < 0.0001) (Table 2). Among the 3 patients with 14577 T/C substitution, we observed nucleotide differences at 16093 and 182 in the D-loop region compared with the Cambridge Sequence (8). Although we suppose that these 3 patients ...
... Therefore, these 6 substitutions were also in linkage disequilibrium (P < 0.0001) (Table 2). Among the 3 patients with 14577 T/C substitution, we observed nucleotide differences at 16093 and 182 in the D-loop region compared with the Cambridge Sequence (8). Although we suppose that these 3 patients ...
Higher Human Biology HW 3
... A. Slow twitch muscle fibres are good for long distance running because they have fewer mitochondria and greater blood supply than fast twitch muscle fibres. B. Slow twitch muscle fibres are good for long distance running because they have more mitochondria and lesser blood supply than fast twitch m ...
... A. Slow twitch muscle fibres are good for long distance running because they have fewer mitochondria and greater blood supply than fast twitch muscle fibres. B. Slow twitch muscle fibres are good for long distance running because they have more mitochondria and lesser blood supply than fast twitch m ...
1 mg/kg/day - Autism One
... from anaerobic metabolism An electrochemical gradient is produced across the inner membrane Mitochondria are primary source of ROS by electron leak from the electron transport chain; 1-2% of oxygen normally produces free radicals ...
... from anaerobic metabolism An electrochemical gradient is produced across the inner membrane Mitochondria are primary source of ROS by electron leak from the electron transport chain; 1-2% of oxygen normally produces free radicals ...
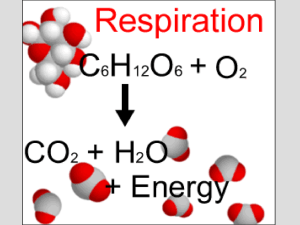
Cellular Respiration
... Equation for Cellular Respiration • C6H12O6 + O2 6 CO2 + 6H2O + ENERGY (ATP) ...
... Equation for Cellular Respiration • C6H12O6 + O2 6 CO2 + 6H2O + ENERGY (ATP) ...
Plant Mitochondrial Electron Transfer and Molecular
... tissues for respiration is carbohydrate(CHpO).The complete oxidation of a carbohydrate releases a large amount of free energy, much of which is coupled to the conversion of ADP and Pi to ATI? When sucrose (Cl2H=0,1) is the substrate, aerobic respiration can be divided into three distinct phases: gly ...
... tissues for respiration is carbohydrate(CHpO).The complete oxidation of a carbohydrate releases a large amount of free energy, much of which is coupled to the conversion of ADP and Pi to ATI? When sucrose (Cl2H=0,1) is the substrate, aerobic respiration can be divided into three distinct phases: gly ...
Plant Mitochondrial Electron Transfer and Molecular
... tissues for respiration is carbohydrate(CHpO).The complete oxidation of a carbohydrate releases a large amount of free energy, much of which is coupled to the conversion of ADP and Pi to ATI? When sucrose (Cl2H=0,1) is the substrate, aerobic respiration can be divided into three distinct phases: gly ...
... tissues for respiration is carbohydrate(CHpO).The complete oxidation of a carbohydrate releases a large amount of free energy, much of which is coupled to the conversion of ADP and Pi to ATI? When sucrose (Cl2H=0,1) is the substrate, aerobic respiration can be divided into three distinct phases: gly ...
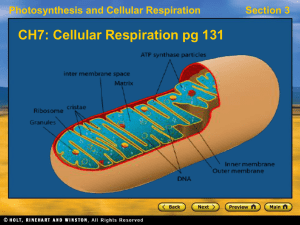
Mitochondrion

The mitochondrion (plural mitochondria) is a double membrane-bound organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. The word mitochondrion comes from the Greek μίτος, mitos, i.e. ""thread"", and χονδρίον, chondrion, i.e. ""granule"" or ""grain-like"".Mitochondria range from 0.5 to 1.0 μm in diameter. A considerable variation can be seen in the structure and size of this organelle. Unless specifically stained, they are not visible. These structures are described as ""the powerhouse of the cell"" because they generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy. In addition to supplying cellular energy, mitochondria are involved in other tasks, such as signaling, cellular differentiation, and cell death, as well as maintaining control of the cell cycle and cell growth. Mitochondria have been implicated in several human diseases, including mitochondrial disorders, cardiac dysfunction, and heart failure. A recent University of California study including ten children diagnosed with severe autism suggests that autism may be correlated with mitochondrial defects as well.Several characteristics make mitochondria unique. The number of mitochondria in a cell can vary widely by organism, tissue, and cell type. For instance, red blood cells have no mitochondria, whereas liver cells can have more than 2000. The organelle is composed of compartments that carry out specialized functions. These compartments or regions include the outer membrane, the intermembrane space, the inner membrane, and the cristae and matrix. Mitochondrial proteins vary depending on the tissue and the species. In humans, 615 distinct types of protein have been identified from cardiac mitochondria, whereas in rats, 940 proteins have been reported. The mitochondrial proteome is thought to be dynamically regulated. Although most of a cell's DNA is contained in the cell nucleus, the mitochondrion has its own independent genome. Further, its DNA shows substantial similarity to bacterial genomes.