Document
... Glycolysis starts and ends in the cytoplasm of all prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells An energy investment of ATP starts glycolysis ...
... Glycolysis starts and ends in the cytoplasm of all prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells An energy investment of ATP starts glycolysis ...
Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
... There are 4 fatty acyl desaturase enzymes in mammals designated 9 , 6, 5, and 4 fatty acyl-CoA desaturase Mammals cannot incorporate a double bond beyond 9; plants can. Mammals can synthesize long chain unsaturated fatty acids using desaturation and elongation ...
... There are 4 fatty acyl desaturase enzymes in mammals designated 9 , 6, 5, and 4 fatty acyl-CoA desaturase Mammals cannot incorporate a double bond beyond 9; plants can. Mammals can synthesize long chain unsaturated fatty acids using desaturation and elongation ...
THE CITRIC ACID CYCLE
... The oxaloacetate then reacts with acetyl CoA forming the unstable compound, citryl CoA The formation of citryl CoA causes the enzyme to completely close and brings enzyme residues in close contact so that water can hydrolyze off the CoA After desorbing CoA and citrate, the enzyme returns to its ...
... The oxaloacetate then reacts with acetyl CoA forming the unstable compound, citryl CoA The formation of citryl CoA causes the enzyme to completely close and brings enzyme residues in close contact so that water can hydrolyze off the CoA After desorbing CoA and citrate, the enzyme returns to its ...
Carbohydrate metabolism2
... MAJOR FEATURES OF SKELETAL MUSCLE S METABOLISM 1.Skeletal muscle functions under both aerobic (resting) and anaerobic (eg, sprinting) conditions, so both aerobic and anaerobic glycolysis operate, depending on conditions. 2.Skeletal muscle contains myoglobin as a reservoir of oxygen. 3.Insulin acts ...
... MAJOR FEATURES OF SKELETAL MUSCLE S METABOLISM 1.Skeletal muscle functions under both aerobic (resting) and anaerobic (eg, sprinting) conditions, so both aerobic and anaerobic glycolysis operate, depending on conditions. 2.Skeletal muscle contains myoglobin as a reservoir of oxygen. 3.Insulin acts ...
Cellular Respiration Harvesting Chemical Energy
... – about 146 ATP (energy molecules) from a triglyceride • Proteins are least likely to be broken down to make ATP. – amino acids not usually needed for energy – about the same amount of energy as a carbohydrate ...
... – about 146 ATP (energy molecules) from a triglyceride • Proteins are least likely to be broken down to make ATP. – amino acids not usually needed for energy – about the same amount of energy as a carbohydrate ...
lecture11&12-RS_Major Metabolic Pathways of
... Glycolysis: An Overview Glycolysis, the major pathway for glucose oxidation, occurs in the cytosol of all cells. It is unique, in that it can function either aerobically or anaerobically, depending on the availability of oxygen and intact mitochondria. It allows tissues to survive in presence ...
... Glycolysis: An Overview Glycolysis, the major pathway for glucose oxidation, occurs in the cytosol of all cells. It is unique, in that it can function either aerobically or anaerobically, depending on the availability of oxygen and intact mitochondria. It allows tissues to survive in presence ...
Glycolysis is the major oxidative pathway for glucose
... Glycolysis: An Overview Glycolysis, the major pathway for glucose oxidation, occurs in the cytosol of all cells. It is unique, in that it can function either aerobically or anaerobically, depending on the availability of oxygen and intact mitochondria. It allows tissues to survive in presence ...
... Glycolysis: An Overview Glycolysis, the major pathway for glucose oxidation, occurs in the cytosol of all cells. It is unique, in that it can function either aerobically or anaerobically, depending on the availability of oxygen and intact mitochondria. It allows tissues to survive in presence ...
Overview of Metabolism Chapter
... metabolism that require removal of electrons (i.e., virtually all pathways that degrade fuel molecules) must stop. However, most cells can continue glycolysis, at least for a short time, because they have the ability to oxidize NADH through an alternative pathway that does not require oxygen: fermen ...
... metabolism that require removal of electrons (i.e., virtually all pathways that degrade fuel molecules) must stop. However, most cells can continue glycolysis, at least for a short time, because they have the ability to oxidize NADH through an alternative pathway that does not require oxygen: fermen ...
Exam#2-`95
... 3. Increased lactate production occurs when ………… a. there is insufficient oxygen b. pyruvate production exceeds the capacity of mitochondrial respiration c. there is increased fast twitch motor unit recruitment d. there is a slight build up/increase in cytosolic NADH e. all of the above 4. When star ...
... 3. Increased lactate production occurs when ………… a. there is insufficient oxygen b. pyruvate production exceeds the capacity of mitochondrial respiration c. there is increased fast twitch motor unit recruitment d. there is a slight build up/increase in cytosolic NADH e. all of the above 4. When star ...
Ch 9 Cell Respiration HW Packet
... Circle the correct answer and then explain why the other answers are NOT correct. 1. The primary purpose of cellular respiration in living organisms is to (A) remove excess carbon dioxide from the cells. (B) create water by combining oxygen and hydrogen ions. (C) produce biologically useful energy i ...
... Circle the correct answer and then explain why the other answers are NOT correct. 1. The primary purpose of cellular respiration in living organisms is to (A) remove excess carbon dioxide from the cells. (B) create water by combining oxygen and hydrogen ions. (C) produce biologically useful energy i ...
respiration 2010
... Respiration Take Place? • It actually takes place in two parts of the cell: Glycolysis occurs in the Cytoplasm ...
... Respiration Take Place? • It actually takes place in two parts of the cell: Glycolysis occurs in the Cytoplasm ...
The Electron Transport System of Mitochondria
... region between the inner and outer membranes. It has an important role in the primary function of mitochondria, which is oxidative phosphorylation. The matrix contains the enzymes that are responsible for the citric acid cycle reactions. The matrix also contains dissolved oxygen, water, carbon dioxi ...
... region between the inner and outer membranes. It has an important role in the primary function of mitochondria, which is oxidative phosphorylation. The matrix contains the enzymes that are responsible for the citric acid cycle reactions. The matrix also contains dissolved oxygen, water, carbon dioxi ...
Anaerobic glycolysis
... a. ATP is formed by oxidative phosphorylation b. Two molecules of ATP are used in the beginning of the pathway c. Pyruvate kinase is the rate-limiting enzyme d. One molecule of pyruvate and 3 olecules of CO2 are formed from the oxidation of 1 glucose e. The reactions take place in the matrix of the ...
... a. ATP is formed by oxidative phosphorylation b. Two molecules of ATP are used in the beginning of the pathway c. Pyruvate kinase is the rate-limiting enzyme d. One molecule of pyruvate and 3 olecules of CO2 are formed from the oxidation of 1 glucose e. The reactions take place in the matrix of the ...
Ch. 22 Glycolysis • Explain how glucose is universal fuel, oxidized in
... 1 glucose + 2 ADP + 2 Pi -> 2 lactate + 2 ATP + 2 H2O + 2 H+ ...
... 1 glucose + 2 ADP + 2 Pi -> 2 lactate + 2 ATP + 2 H2O + 2 H+ ...
Review Questions for Respiration
... Circle the correct answer. 1. NAD+ is a (reactant/product) of glycolysis. 2. NAD+ is a (reactant/product) of the link reaction (or the oxidation of pyruvate). 3. NAD+ is a (reactant/product) of the ETC. 4. NAD+ is a (reactant/product) of the Krebs cycle. 5. Water is a (reactant/product) of the ETC. ...
... Circle the correct answer. 1. NAD+ is a (reactant/product) of glycolysis. 2. NAD+ is a (reactant/product) of the link reaction (or the oxidation of pyruvate). 3. NAD+ is a (reactant/product) of the ETC. 4. NAD+ is a (reactant/product) of the Krebs cycle. 5. Water is a (reactant/product) of the ETC. ...
Characterization of Ubiquitin/Proteasome
... In 1996, the complete DNA sequence of S. cerevisiae’s ~6000-gene genome was released in electronic form, making it the first eukaryotic species to have its genome completely sequenced (Goffeau, et al., 1996). This pioneering event led to the use of S. cerevisiae as a “model organism” for interpretin ...
... In 1996, the complete DNA sequence of S. cerevisiae’s ~6000-gene genome was released in electronic form, making it the first eukaryotic species to have its genome completely sequenced (Goffeau, et al., 1996). This pioneering event led to the use of S. cerevisiae as a “model organism” for interpretin ...
KHARKIV NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
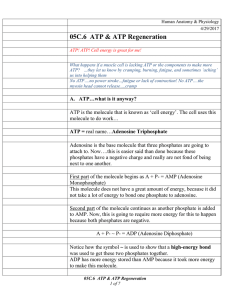
... Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) plays a central role in the conversion of energy in biological systems. It is formed from NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP) by oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). ATP is a nucleotide consisting of adenine, a ribose, and a triphospha ...
... Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) plays a central role in the conversion of energy in biological systems. It is formed from NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP) by oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). ATP is a nucleotide consisting of adenine, a ribose, and a triphospha ...
LP - Columbia University
... It is thought that it's the build-up of acidity from lactic acid that makes your muscles hurt if they are doing anaerobic glycolysis too long (acidity sensed as pain by neurons in the muscle). (Fermentation) So pyruvate is a crossroads: If no oxygen, then if you are E. coli or humans, you carry out ...
... It is thought that it's the build-up of acidity from lactic acid that makes your muscles hurt if they are doing anaerobic glycolysis too long (acidity sensed as pain by neurons in the muscle). (Fermentation) So pyruvate is a crossroads: If no oxygen, then if you are E. coli or humans, you carry out ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... Summarize the operation of the electron transport system. Describe an electron transport chain. Describe the cytochromes and their functions. Discuss oxidative phosphorylation. Name the final electron acceptor at the end of the oxidative transport chain. Give the numbers of ATP produced by NADH and ...
... Summarize the operation of the electron transport system. Describe an electron transport chain. Describe the cytochromes and their functions. Discuss oxidative phosphorylation. Name the final electron acceptor at the end of the oxidative transport chain. Give the numbers of ATP produced by NADH and ...
Chapter 17 - FIU Faculty Websites
... The vitamin thiamine is found in brown rice, but not in white (polished) rice. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activity can be inhibited by mercury and arsenite, which bind to the two sulfurs of dihydrolipoamide. 2, 3-Dimercaptopropanol can counter the effects of arsenite poisoning by forming a compl ...
... The vitamin thiamine is found in brown rice, but not in white (polished) rice. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activity can be inhibited by mercury and arsenite, which bind to the two sulfurs of dihydrolipoamide. 2, 3-Dimercaptopropanol can counter the effects of arsenite poisoning by forming a compl ...
01 - ALCA
... As we know, when a carbon is pulled off, hydrogens come with it. So…the ‘oneseater taxi’ NAD will be there to grab up hydrogens along with another taxi that can carry two hydrogens. This taxi or acceptor is known as FAD. ...
... As we know, when a carbon is pulled off, hydrogens come with it. So…the ‘oneseater taxi’ NAD will be there to grab up hydrogens along with another taxi that can carry two hydrogens. This taxi or acceptor is known as FAD. ...
attached paper highlights
... demand such as cold, exercise, and fasting. Data are accumulating which show PGC-1a to be a master regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis in mammals. Ectopic expression of PGC-1a in myotubes strongly induces the expression of downstream transcription factors such as NRFs and Tfam.17 Unlike NRFs or Tf ...
... demand such as cold, exercise, and fasting. Data are accumulating which show PGC-1a to be a master regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis in mammals. Ectopic expression of PGC-1a in myotubes strongly induces the expression of downstream transcription factors such as NRFs and Tfam.17 Unlike NRFs or Tf ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • Some organisms (facultative anaerobes), including yeast and many bacteria, can survive using either fermentation or respiration. • At a cellular level, human muscle cells can behave as facultative anaerobes, but nerve cells cannot. • For facultative anaerobes, pyruvate is a fork in the metabolic ...
... • Some organisms (facultative anaerobes), including yeast and many bacteria, can survive using either fermentation or respiration. • At a cellular level, human muscle cells can behave as facultative anaerobes, but nerve cells cannot. • For facultative anaerobes, pyruvate is a fork in the metabolic ...
PP Chapter 9 - WordPress.com
... • Obligate anaerobes carry out fermentation or anaerobic respiration and cannot survive in the presence of O2 • Yeast and many bacteria are facultative anaerobes, meaning that they can survive using either fermentation or cellular respiration • In a facultative anaerobe, pyruvate is a fork in the m ...
... • Obligate anaerobes carry out fermentation or anaerobic respiration and cannot survive in the presence of O2 • Yeast and many bacteria are facultative anaerobes, meaning that they can survive using either fermentation or cellular respiration • In a facultative anaerobe, pyruvate is a fork in the m ...
Mitochondrion

The mitochondrion (plural mitochondria) is a double membrane-bound organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. The word mitochondrion comes from the Greek μίτος, mitos, i.e. ""thread"", and χονδρίον, chondrion, i.e. ""granule"" or ""grain-like"".Mitochondria range from 0.5 to 1.0 μm in diameter. A considerable variation can be seen in the structure and size of this organelle. Unless specifically stained, they are not visible. These structures are described as ""the powerhouse of the cell"" because they generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy. In addition to supplying cellular energy, mitochondria are involved in other tasks, such as signaling, cellular differentiation, and cell death, as well as maintaining control of the cell cycle and cell growth. Mitochondria have been implicated in several human diseases, including mitochondrial disorders, cardiac dysfunction, and heart failure. A recent University of California study including ten children diagnosed with severe autism suggests that autism may be correlated with mitochondrial defects as well.Several characteristics make mitochondria unique. The number of mitochondria in a cell can vary widely by organism, tissue, and cell type. For instance, red blood cells have no mitochondria, whereas liver cells can have more than 2000. The organelle is composed of compartments that carry out specialized functions. These compartments or regions include the outer membrane, the intermembrane space, the inner membrane, and the cristae and matrix. Mitochondrial proteins vary depending on the tissue and the species. In humans, 615 distinct types of protein have been identified from cardiac mitochondria, whereas in rats, 940 proteins have been reported. The mitochondrial proteome is thought to be dynamically regulated. Although most of a cell's DNA is contained in the cell nucleus, the mitochondrion has its own independent genome. Further, its DNA shows substantial similarity to bacterial genomes.