Human Body Systems
... can be absorbed and moved by the blood stream which delivers it to your cells for energy. ...
... can be absorbed and moved by the blood stream which delivers it to your cells for energy. ...
TYPES OF RECEPTORS
... estrogens and gonadotropins are used in treatment of sterility and menstrual disturbances. Huggins received the Nobel Prize in 1966 for the introduction of a new form of cancer therapy in which sex hormones are used to retard their growth. He used androgens for breast cancer and estrogens for pr ...
... estrogens and gonadotropins are used in treatment of sterility and menstrual disturbances. Huggins received the Nobel Prize in 1966 for the introduction of a new form of cancer therapy in which sex hormones are used to retard their growth. He used androgens for breast cancer and estrogens for pr ...
The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues
... 2. Organ – performs a specific function in your body. 2. Organ system – a set of organs or structures in the body that have a common function. 2. Organ Systems 3. Circulatory System – moves blood and oxygen through the body. 3. Endocrine System – makes hormones the body needs. 3. Urinary System – co ...
... 2. Organ – performs a specific function in your body. 2. Organ system – a set of organs or structures in the body that have a common function. 2. Organ Systems 3. Circulatory System – moves blood and oxygen through the body. 3. Endocrine System – makes hormones the body needs. 3. Urinary System – co ...
Midterm 2010 Key B
... a. the desirable body weight b. the maximum weight for an individual before health problems become manifest c. d. the minimum weight for an individual before health problems become obvious d. the weight to which the body tends to return after weight loss, or weight gain e. neither a, b, c, nor d 19. ...
... a. the desirable body weight b. the maximum weight for an individual before health problems become manifest c. d. the minimum weight for an individual before health problems become obvious d. the weight to which the body tends to return after weight loss, or weight gain e. neither a, b, c, nor d 19. ...
Digestive System - El Camino College
... Body is an open system Why? Respiratory, digestive and excretory systems allow for exchange with external environment Circulatory system in charge of transport within the body Blood exchanges materials with each cell via interstitial fluid ...
... Body is an open system Why? Respiratory, digestive and excretory systems allow for exchange with external environment Circulatory system in charge of transport within the body Blood exchanges materials with each cell via interstitial fluid ...
Chapter 12 Nutrition
... i. Essential Amino Acids - must be supplied in the diet ii. Nonessential Amino Acids - can be synthesized from other amino acids Different for each species - table 12-2 3. Lipids - fats and oils a. Immediate energy supply OR stored as a reserve b. Insulation from cold c. Source of essential fatty ac ...
... i. Essential Amino Acids - must be supplied in the diet ii. Nonessential Amino Acids - can be synthesized from other amino acids Different for each species - table 12-2 3. Lipids - fats and oils a. Immediate energy supply OR stored as a reserve b. Insulation from cold c. Source of essential fatty ac ...
Organization of the Body and General Systems
... • Anatomical Position: Body upright, arms/legs straight, palms forward, feet flat and eyes open • Bilateral Symmetry: arrangement of body parts along a central axis, so that the body is divided into equal right and left halves • Body Plan ...
... • Anatomical Position: Body upright, arms/legs straight, palms forward, feet flat and eyes open • Bilateral Symmetry: arrangement of body parts along a central axis, so that the body is divided into equal right and left halves • Body Plan ...
DEVINE - FLC Mid-Atlantic Region
... Eastern Regional Research Center 600 East Mermaid Lane Wyndmoor, PA 19038 ...
... Eastern Regional Research Center 600 East Mermaid Lane Wyndmoor, PA 19038 ...
Large number of receptors reduces cellular response time - Q-bio
... in simple models, this variability reduction does not interfere with the receptor specificity to ligands achieved by the Kinetic Proofreading mechanism. Thus cells can activate accurately in time and specifically to certain molecular signals. Keywords — spare receptors, kinetic proofreading, first p ...
... in simple models, this variability reduction does not interfere with the receptor specificity to ligands achieved by the Kinetic Proofreading mechanism. Thus cells can activate accurately in time and specifically to certain molecular signals. Keywords — spare receptors, kinetic proofreading, first p ...
fatty foods in obesity management - Philippine Association for the
... OBESITY PARADOX: In Laos, for example, where 39% of the population live below the national poverty line, more than 21% of the total population are undernourished, yet 35% of men and 49% of women are overweight. This double burden of malnutrition (under-nutrition and over-nutrition) (Food and Agricul ...
... OBESITY PARADOX: In Laos, for example, where 39% of the population live below the national poverty line, more than 21% of the total population are undernourished, yet 35% of men and 49% of women are overweight. This double burden of malnutrition (under-nutrition and over-nutrition) (Food and Agricul ...
Respiration Cellular Respiration Understand the
... ■ Control the rate at which cells burn fuels from food to produce energy ■ Essential for normal physical and mental development. Negative and Positive Feedback Control Hormone production is self regulated ○ Positive feedback a response is initiated by a stimulus ○ Negative Feedback the output of a ...
... ■ Control the rate at which cells burn fuels from food to produce energy ■ Essential for normal physical and mental development. Negative and Positive Feedback Control Hormone production is self regulated ○ Positive feedback a response is initiated by a stimulus ○ Negative Feedback the output of a ...
Requirements of Living Organisms (from external environment)
... energy from food in cellular respiration ...
... energy from food in cellular respiration ...
Healthy Body Notes
... ▫ Help body function properly ▫ Found in fruits and vegetables • Lipids ▫ Can provide energy and help with growth ▫ Includes fats and oils ▫ Foods fried in oil or butter contain large amounts of lipids ...
... ▫ Help body function properly ▫ Found in fruits and vegetables • Lipids ▫ Can provide energy and help with growth ▫ Includes fats and oils ▫ Foods fried in oil or butter contain large amounts of lipids ...
Organ Systems and Homeostasis - Mr. St. Peter's
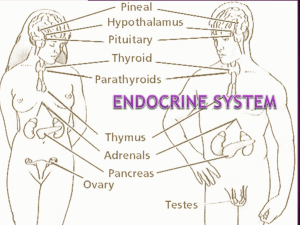
... •11. Endocrine: Glands- Hypothalamus, pituitary, pineal, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenals pancreas, ovaries (females), testes (males) Function: Controls growth, development, and metabolism, maintains homeostasis ...
... •11. Endocrine: Glands- Hypothalamus, pituitary, pineal, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenals pancreas, ovaries (females), testes (males) Function: Controls growth, development, and metabolism, maintains homeostasis ...
B 11.A
... The hypothalamus detects stress such as being attacked. The nervous system releases adrenaline into the bloodstream. ...
... The hypothalamus detects stress such as being attacked. The nervous system releases adrenaline into the bloodstream. ...
pogil 3
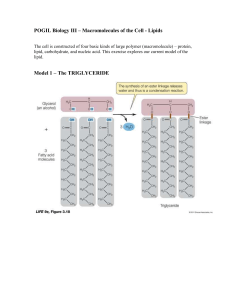
... POGIL Biology III – Macromolecules of the Cell - Lipids The cell is constructed of four basic kinds of large polymer (macromolecule) – protein, lipid, carbohydrate, and nucleic acid. This exercise explores our current model of the lipid. ...
... POGIL Biology III – Macromolecules of the Cell - Lipids The cell is constructed of four basic kinds of large polymer (macromolecule) – protein, lipid, carbohydrate, and nucleic acid. This exercise explores our current model of the lipid. ...
Ultrametabolism The Simple Plan for Automatic
... Lang IA, et.al. Association of urinary bisphenol A concentration with medical disorders and laboratory abnormalities in adults. JAMA. 2008 Sep 17;300(11):1303-10. Codru N, et.al Task Force on Environment, Rej R, Carpenter DO. Diabetes in relation to serum levels of polychlorinated biphenyls and chlo ...
... Lang IA, et.al. Association of urinary bisphenol A concentration with medical disorders and laboratory abnormalities in adults. JAMA. 2008 Sep 17;300(11):1303-10. Codru N, et.al Task Force on Environment, Rej R, Carpenter DO. Diabetes in relation to serum levels of polychlorinated biphenyls and chlo ...
Document
... Can range in size from less than ____________ to more than ________! • Mostly _________-like in appearance. The body segments are separated internally by walls of tissue called ________. • Singular ~ _____________. ...
... Can range in size from less than ____________ to more than ________! • Mostly _________-like in appearance. The body segments are separated internally by walls of tissue called ________. • Singular ~ _____________. ...
Student Resource 1: Types of Nutrients
... (e.g., eating a chicken breast would give your body protein, helping to repair muscles; eating whole-wheat spaghetti noodles would give your body carbohydrates to provide energy). Carbohydrates are the body’s main source of energy. ●● An important form of this nutrient is dietary fibre. ●● Insoluble ...
... (e.g., eating a chicken breast would give your body protein, helping to repair muscles; eating whole-wheat spaghetti noodles would give your body carbohydrates to provide energy). Carbohydrates are the body’s main source of energy. ●● An important form of this nutrient is dietary fibre. ●● Insoluble ...
No Slide Title
... Hormonal Targeting of Nuclear Complexes to Chromatin In the absence of ligand, a silencing mediator of retinoid and thyroid hormone receptor (SMRT)-mSin3a-histone deacetylase-1 (HDAC-1) complex associates with the nuclear retinoic acid receptor (RAR)-retinoid X receptor (RXR) heterodimeric complex. ...
... Hormonal Targeting of Nuclear Complexes to Chromatin In the absence of ligand, a silencing mediator of retinoid and thyroid hormone receptor (SMRT)-mSin3a-histone deacetylase-1 (HDAC-1) complex associates with the nuclear retinoic acid receptor (RAR)-retinoid X receptor (RXR) heterodimeric complex. ...
intro to anatom
... Responds to changes both internal and external by activating muscles and glands. (motor impulses) Includes all of the sensory organs (eyes, ears, touch receptors, taste buds, and smell receptors) Major organs are the brain, spinal cord, and all of the major nerves. ...
... Responds to changes both internal and external by activating muscles and glands. (motor impulses) Includes all of the sensory organs (eyes, ears, touch receptors, taste buds, and smell receptors) Major organs are the brain, spinal cord, and all of the major nerves. ...
Section 35–1 Human Body Systems
... blood cell formation b. Provides oxygen and removes carbon dioxide c. Coordinates the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environments d. Helps produce voluntary movement, circulate blood, and move food e. Controls growth, development, metabolism, and reproduction f. Eliminates w ...
... blood cell formation b. Provides oxygen and removes carbon dioxide c. Coordinates the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environments d. Helps produce voluntary movement, circulate blood, and move food e. Controls growth, development, metabolism, and reproduction f. Eliminates w ...
Document
... Hypothalamus and Pituitary GlandThyroid and ParathyroidAdrenal GlandsPancreasPineal, Thymus, & Reproductive- ...
... Hypothalamus and Pituitary GlandThyroid and ParathyroidAdrenal GlandsPancreasPineal, Thymus, & Reproductive- ...
Paula Deen Suffers from Easily Curable Diabetes
... Paula’s body has been tested and proven to be strong. More than six decades of severe malnutrition have not killed her yet. I marvel at how much abuse the average person can tolerate and still survive, albeit compromised. The calories she is consuming in excess of her needs cause her to gain body fa ...
... Paula’s body has been tested and proven to be strong. More than six decades of severe malnutrition have not killed her yet. I marvel at how much abuse the average person can tolerate and still survive, albeit compromised. The calories she is consuming in excess of her needs cause her to gain body fa ...
Obesogen
Obesogens are foreign chemical compounds that disrupt normal development and balance of lipid metabolism, which in some cases, can lead to obesity. Obesogens may be functionally defined as chemicals that inappropriately alter lipid homeostasis and fat storage, change metabolic setpoints, disrupt energy balance or modify the regulation of appetite and satiety to promote fat accumulation and obesity.There are many different proposed mechanisms through which obesogens can interfere with the body's adipose tissue biology. These mechanisms include alterations in the action of metabolic sensors; dysregulation of sex steroid synthesis, action or breakdown; changes in the central integration of energy balance including the regulation of appetite and satiety; and reprogramming of metabolic setpoints. Some of these proposed pathways include inappropriate modulation of nuclear receptor function which therefore allows the compounds to be classified as endocrine disrupting chemicals that act to mimic hormones in the body, altering the normal homeostasis maintained by the endocrine system.Obesogens have been detected in the body both as a result of intentional administration of obesogenic chemicals in the form of pharmaceutical drugs such as diethylstilbestrol, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, and thiazolidinedione and as a result of unintentional exposure to environmental obesogens such as tributyltin, bisphenol A, diethylhexylphthalate, and perfluorooctanoate. Emerging evidence from laboratories around the world suggests that other chemicals will be confirmed as falling under this proposed classification in the near future, and that there may be some serious biological effects due to exposure to these chemicals that still remain undiscovered. Until now, 20 chemicals have been found responsible for making one fat.The term obesogen was coined by Felix Grün and Bruce Blumberg of the University of California, Irvine. The topic of this proposed class of chemical compounds and how to counteract their effects is explored at length in the book The New American Diet. Paula Baillie-Hamilton, a doctor in the UK, was the first one to have identified how obesogens make it difficult to lose weight. She published her results in the Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine in 2002.