Continuous and Discontinuous Games
... Theorem 1 (Glicksberg) Every continuous game has a mixed strategy Nash equilibrium. With continuous strategy spaces, the space of mixed strategies Σ is infinite-dimensional, therefore we need a more powerful fixed point theorem than the version of Kakutani we have used before. Here we adopt an alterna ...
... Theorem 1 (Glicksberg) Every continuous game has a mixed strategy Nash equilibrium. With continuous strategy spaces, the space of mixed strategies Σ is infinite-dimensional, therefore we need a more powerful fixed point theorem than the version of Kakutani we have used before. Here we adopt an alterna ...
a > -r
... • If a player mixes over a set of strategies, it must be the case that each of those strategies yields the same expected payoff • Thus the player is indifferent about which strategy is played • This indifference will occur when other players are mixing over their own strategies in the appropriate wa ...
... • If a player mixes over a set of strategies, it must be the case that each of those strategies yields the same expected payoff • Thus the player is indifferent about which strategy is played • This indifference will occur when other players are mixing over their own strategies in the appropriate wa ...
Imagine-self perspective-taking promotes Nash choices in - E-SGH
... strategy of a row player becomes strictly dominated. As a result there is a single strict pure strategy Nash equilibrium (T, L) There were four experimental groups numbering about one hundred participants each. Each group was given different instructions. Participants of the experiment were unde ...
... strategy of a row player becomes strictly dominated. As a result there is a single strict pure strategy Nash equilibrium (T, L) There were four experimental groups numbering about one hundred participants each. Each group was given different instructions. Participants of the experiment were unde ...
ppt
... Each player in a game has a payoff; this is a function of the decisions of all players. Each player seeks to maximise their own payoffs. ...
... Each player in a game has a payoff; this is a function of the decisions of all players. Each player seeks to maximise their own payoffs. ...
Game Theory and Business Practice
... Does the fact that a decision-making environment exhibits strategic interdependence matter? In the terminology of Game Theory let us talk of decision-makers as “players”, decisions as “actions”, competitors as “adversaries”, outcomes as “payoffs” and multi-player decision-making scenarios as “games” ...
... Does the fact that a decision-making environment exhibits strategic interdependence matter? In the terminology of Game Theory let us talk of decision-makers as “players”, decisions as “actions”, competitors as “adversaries”, outcomes as “payoffs” and multi-player decision-making scenarios as “games” ...
Managerial Economics
... Study of strategic interactions: how firms adopt alternative strategies by taking into account rival behaviour Structured and logical method of considering strategic situations. It makes possible breaking down a competitive situation into its key elements and analysing the dynamics between the playe ...
... Study of strategic interactions: how firms adopt alternative strategies by taking into account rival behaviour Structured and logical method of considering strategic situations. It makes possible breaking down a competitive situation into its key elements and analysing the dynamics between the playe ...
CUR 412: Game Theory and its Applications
... (c) (5 pts.) Write down the 2 × 2 matrix of payoffs for a single stage of the repeated game. (d) (10 pts.) Find the range of δ for which it is a subgame perfect Nash equilibrium when both firms play a modified grim trigger strategy: • If Def ect has never been played by either firm, then choose Coll ...
... (c) (5 pts.) Write down the 2 × 2 matrix of payoffs for a single stage of the repeated game. (d) (10 pts.) Find the range of δ for which it is a subgame perfect Nash equilibrium when both firms play a modified grim trigger strategy: • If Def ect has never been played by either firm, then choose Coll ...
07.9 - Sophia Antipolis
... It is an established fact [17] that a war of attrition causes the forager to stay longer than the “Charnov time”. Yet, this Charnov time itself, here x̂, depends in a complex fashion on the detailed interference model. In this respect, the article [7] does not invalidate the theoretical model; to th ...
... It is an established fact [17] that a war of attrition causes the forager to stay longer than the “Charnov time”. Yet, this Charnov time itself, here x̂, depends in a complex fashion on the detailed interference model. In this respect, the article [7] does not invalidate the theoretical model; to th ...
GAME THEORY A game represents a competitive or
... Player I, by playing his first (pure) strategy guarantees a gain of at least 2 = Min {8, 2, 9, 5}. Similarly the second strategy guarantees at least 5 = Min {6, 5, 7, 8}, and the third, −4 = Min {7, 3, −4, 7}. Thus the “row minimum” is the value guaranteed I for each pure strategy. Player I, if he s ...
... Player I, by playing his first (pure) strategy guarantees a gain of at least 2 = Min {8, 2, 9, 5}. Similarly the second strategy guarantees at least 5 = Min {6, 5, 7, 8}, and the third, −4 = Min {7, 3, −4, 7}. Thus the “row minimum” is the value guaranteed I for each pure strategy. Player I, if he s ...
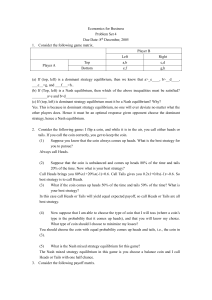
Economics for Business
... (a) If (top, left) is a dominant strategy equilibrium, then we know that a>_e____, b>__d____, ___c__>g, and ___f___>h.. (b) If (Top, left) is a Nash equilibrium, then which of the above inequalities must be satisfied? ________a>e and b>d______________________ (c) If (top, left) is dominant strategy ...
... (a) If (top, left) is a dominant strategy equilibrium, then we know that a>_e____, b>__d____, ___c__>g, and ___f___>h.. (b) If (Top, left) is a Nash equilibrium, then which of the above inequalities must be satisfied? ________a>e and b>d______________________ (c) If (top, left) is dominant strategy ...
Speedminton Study Guide
... To start play, a serving player/team must be determined. The server then gets three serves. After that, the opponent then gets three serves. This order continues throughout the entire game. The serve must be struck from within a players’ own court. A legal serve has the Speeder dropped from waist le ...
... To start play, a serving player/team must be determined. The server then gets three serves. After that, the opponent then gets three serves. This order continues throughout the entire game. The serve must be struck from within a players’ own court. A legal serve has the Speeder dropped from waist le ...
Oligoplies and Game Theory
... eventually leading to a price war. Therefore, the best option for the oligopolist is to produce at point E which is the equilibrium point ...
... eventually leading to a price war. Therefore, the best option for the oligopolist is to produce at point E which is the equilibrium point ...
EC-16 Tutorial on Computer Poker
... This result was published in the journal Science. Poker, and particularly Texas hold ’em, is tremendously popular for humans, and online poker is a multi-billion dollar industry. Computer poker has proved to be one of the most visible applications of research in computational game theory. In theory, ...
... This result was published in the journal Science. Poker, and particularly Texas hold ’em, is tremendously popular for humans, and online poker is a multi-billion dollar industry. Computer poker has proved to be one of the most visible applications of research in computational game theory. In theory, ...
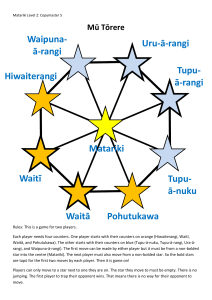
ā-rangi Matariki Waitā Waitī
... Each player needs three counters. One player starts with their counters on orange (Waitī, Waitā, and Tupuā-nuku). The other starts with their counters on blue (Tupu-ā-rangi, Ura-ā-rangi, and Waipuna-ā-rangi). The first move can be made by either player but it must be from a non-bolded star into the ...
... Each player needs three counters. One player starts with their counters on orange (Waitī, Waitā, and Tupuā-nuku). The other starts with their counters on blue (Tupu-ā-rangi, Ura-ā-rangi, and Waipuna-ā-rangi). The first move can be made by either player but it must be from a non-bolded star into the ...
Game Balancing Theory
... Any successful strategy for one side can be used by both sides Success is derived from execution, not strategy Or success is derived from fine details (a pawn in Chess) ...
... Any successful strategy for one side can be used by both sides Success is derived from execution, not strategy Or success is derived from fine details (a pawn in Chess) ...
Applications of Game Theory in the Computational Biology Domain
... • Negative payoff results in death – But who defines V and C? These variables are unclear for reallife competitions. ...
... • Negative payoff results in death – But who defines V and C? These variables are unclear for reallife competitions. ...
Ch. 13: Game Theory
... • When iterative elimination fails to predict a unique outcome, we can use a related approach. • The best response is a strategy that maximizes a player’s payoff given its beliefs about its rivals’ strategies. • A set of strategies is a Nash equilibrium if, when all other players use these strategie ...
... • When iterative elimination fails to predict a unique outcome, we can use a related approach. • The best response is a strategy that maximizes a player’s payoff given its beliefs about its rivals’ strategies. • A set of strategies is a Nash equilibrium if, when all other players use these strategie ...
CHT. 5 DATABASE MANAGEMENT
... equilibrium point is the only rational outcome of this game; and its corresponding strategies for the two sides are their best choices, called pure strategy. The value at the equilibrium point is called the value of the game. At the equilibrium point, neither side can benefit from a unilateral c ...
... equilibrium point is the only rational outcome of this game; and its corresponding strategies for the two sides are their best choices, called pure strategy. The value at the equilibrium point is called the value of the game. At the equilibrium point, neither side can benefit from a unilateral c ...
Lecture 8 (More on mixed strategies
... received regardless of what the other players do). Find all Nash equilibria in mixed strategies. Let’s find the “easy ones”. Are there any symmetric pure strategy equilibria? How about asymmetric pure strategy equilibria? How about symmetric mixed strategy equilibrium? Solve 40p^2+60*2p(1-p)+120(1-p ...
... received regardless of what the other players do). Find all Nash equilibria in mixed strategies. Let’s find the “easy ones”. Are there any symmetric pure strategy equilibria? How about asymmetric pure strategy equilibria? How about symmetric mixed strategy equilibrium? Solve 40p^2+60*2p(1-p)+120(1-p ...
Game Theory - Mr. P. Ronan
... play a game, each player – different firms, labour unions, management or policymakers – must consider the costs and benefits of alternative strategies as well as the possible strategies that might be adopted by other players. The purpose of each game is to win the payoff – market share, wages, profi ...
... play a game, each player – different firms, labour unions, management or policymakers – must consider the costs and benefits of alternative strategies as well as the possible strategies that might be adopted by other players. The purpose of each game is to win the payoff – market share, wages, profi ...
The Problem with Blondes
... as Nash equilibrium, the basis of his Nobel Prize in Economics in 1994. I didn’t know what a Nash equilibrium was, but after seeing that scene I had to look it up. I found that a Nash equilibrium is a set of strategies (one for each player) expressed as probabilities that each of a number of choices ...
... as Nash equilibrium, the basis of his Nobel Prize in Economics in 1994. I didn’t know what a Nash equilibrium was, but after seeing that scene I had to look it up. I found that a Nash equilibrium is a set of strategies (one for each player) expressed as probabilities that each of a number of choices ...
Note
... To compute the payoff of player 1 for this mixed strategy m we multiply each of his payoffs for a joint strategy by its probability and sum it up: ...
... To compute the payoff of player 1 for this mixed strategy m we multiply each of his payoffs for a joint strategy by its probability and sum it up: ...
PowerPoint
... Assume the same demand function and cost from the Cournot game from before Instead of the two players competing on quantity, assume that they compete on price Further assume that if they each have the same price, then they will split the market evenly Otherwise, the competitor with the lower pri ...
... Assume the same demand function and cost from the Cournot game from before Instead of the two players competing on quantity, assume that they compete on price Further assume that if they each have the same price, then they will split the market evenly Otherwise, the competitor with the lower pri ...
Game Theory and The Prisoner`s Dilemma
... Auctioneer and bidders Game theory has many applications outside of economics and that why it continues to be one of the most studied topics. Outside examples include: Presidential candidates Congress and the President Opposing generals at War ...
... Auctioneer and bidders Game theory has many applications outside of economics and that why it continues to be one of the most studied topics. Outside examples include: Presidential candidates Congress and the President Opposing generals at War ...