Review Questions Part 3 (Chapters 10-12, 14)
... 12.1 Which properties define an oligopolistic market? Why does it make sense to use game theory to study oligopolistic markets? 12.2 Suppose two firms (or countries as in our world oil market example) operate in a market. If they collude: Which quantity would they want to jointly provide and which p ...
... 12.1 Which properties define an oligopolistic market? Why does it make sense to use game theory to study oligopolistic markets? 12.2 Suppose two firms (or countries as in our world oil market example) operate in a market. If they collude: Which quantity would they want to jointly provide and which p ...
Game Theory Seminar Lecture 1
... models can at best capture important aspects Players are considered rational determine what is best for them given that others are doing the same No unique prescription not clear what players should do ...
... models can at best capture important aspects Players are considered rational determine what is best for them given that others are doing the same No unique prescription not clear what players should do ...
10/(1+ δ)
... For both players to prefer alternating equilibrium strategies, both 10/(1- δ2) and δ[10/(1- δ2)] must be greater than 3/(1- δ). Since the discount factor is a number between zero and one, 10/(1- δ2) > δ[10/(1- δ2)], and so if δ[10/(1- δ2)] > 3/(1- δ), then 3/(1- δ) > 10/(1- δ2), so, for both players ...
... For both players to prefer alternating equilibrium strategies, both 10/(1- δ2) and δ[10/(1- δ2)] must be greater than 3/(1- δ). Since the discount factor is a number between zero and one, 10/(1- δ2) > δ[10/(1- δ2)], and so if δ[10/(1- δ2)] > 3/(1- δ), then 3/(1- δ) > 10/(1- δ2), so, for both players ...
N-Player Games
... • Suppose that all people value their time at v per minute. What is the equilibrium outcome with a toll of T? • To equalize costs going the two ways, set 30v=(21+X/2)v+T. This implies 30=21+X/2+T/v and X=18-2(T/v). • If you want efficient use of the road, you would have X=9. Then 9=18-2(T/v) so 9=2( ...
... • Suppose that all people value their time at v per minute. What is the equilibrium outcome with a toll of T? • To equalize costs going the two ways, set 30v=(21+X/2)v+T. This implies 30=21+X/2+T/v and X=18-2(T/v). • If you want efficient use of the road, you would have X=9. Then 9=18-2(T/v) so 9=2( ...
Towards a Constructive Theory of Networked Interactions
... 2. it is NP-complete to find a “tiny” bit more info than “just” a Nash equilibrium; e.g., the following are NP-complete: - find two Nash equilibria, if more than one exist - find a Nash equilibrium whose third bit is one, if any ...
... 2. it is NP-complete to find a “tiny” bit more info than “just” a Nash equilibrium; e.g., the following are NP-complete: - find two Nash equilibria, if more than one exist - find a Nash equilibrium whose third bit is one, if any ...
gs2.aamas07 - Carnegie Mellon School of Computer Science
... • Automatic method for performing abstractions in a broad class of sequential games of imperfect information • Equilibrium-preserving game transformation – certain information sets are merged, and – certain nodes within an information set are collapsed ...
... • Automatic method for performing abstractions in a broad class of sequential games of imperfect information • Equilibrium-preserving game transformation – certain information sets are merged, and – certain nodes within an information set are collapsed ...
Probability Project: Design Your Own Game
... ❖ Is the game fair? Show the mathematical calculations for the expected value of winning the game. ❖ If the game is not fair, how could you change the game to make it fair? ...
... ❖ Is the game fair? Show the mathematical calculations for the expected value of winning the game. ❖ If the game is not fair, how could you change the game to make it fair? ...
Chapter 13 Alternative Concepts
... Strong Nash equilibrium Another variation of the notion of a Nash equilibrium focusses on the concept of a coalition, by which we mean a nonempty subset of all players. Given a subset K := {k1 , . . . , km } of N := {1, . . . , n} we abbreviate the sequence (sk1 , . . . , skm ) of strategies to sK ...
... Strong Nash equilibrium Another variation of the notion of a Nash equilibrium focusses on the concept of a coalition, by which we mean a nonempty subset of all players. Given a subset K := {k1 , . . . , km } of N := {1, . . . , n} we abbreviate the sequence (sk1 , . . . , skm ) of strategies to sK ...
ppt
... Gain Floor, Loss Ceiling, Saddle Point, Value of Game The Gain Floor of a two-player zero-sum game A, written (A), is the worst outcome for player 1 if he picks his best strategy i*: (A) =min j A i*,j The Loss Ceiling (likewise) is the best outcome for player 1 (hence worst for player 2) if playe ...
... Gain Floor, Loss Ceiling, Saddle Point, Value of Game The Gain Floor of a two-player zero-sum game A, written (A), is the worst outcome for player 1 if he picks his best strategy i*: (A) =min j A i*,j The Loss Ceiling (likewise) is the best outcome for player 1 (hence worst for player 2) if playe ...
nim
... • This states that in order to win, the goal is to reach a nim-sum of 0 after each turn until all turns are finished • Nim Sum: evaluated by taking the exclusive-or of the corresponding numbers when the numbers are given in binary form • Exclusive-or is used for adding two or more numbers in binary ...
... • This states that in order to win, the goal is to reach a nim-sum of 0 after each turn until all turns are finished • Nim Sum: evaluated by taking the exclusive-or of the corresponding numbers when the numbers are given in binary form • Exclusive-or is used for adding two or more numbers in binary ...
avivzoharjan09 - CS
... The modified Lemma At every round of punishment, at least one of two things must happen: 1. One of the players learns a previously unknown value 2. or, the deviator has a higher cost than any other player. Once a player learns a new value, he will broadcast it to the other honest players. This way, ...
... The modified Lemma At every round of punishment, at least one of two things must happen: 1. One of the players learns a previously unknown value 2. or, the deviator has a higher cost than any other player. Once a player learns a new value, he will broadcast it to the other honest players. This way, ...
Nash Equilibrium (existence)
... The algorithm for computing a NE is now straightforward. For all possible supports S1 , S2 (since we do not know them in advance), we solve the equations. Whenever we find a valid solution, we can output it, as it is a NE. Unfortunately, this algorithm has worst-case exponential running time, since ...
... The algorithm for computing a NE is now straightforward. For all possible supports S1 , S2 (since we do not know them in advance), we solve the equations. Whenever we find a valid solution, we can output it, as it is a NE. Unfortunately, this algorithm has worst-case exponential running time, since ...
Proofs_A4_Review - Kelvin-2011-2012-Sem02
... 8. Complete the conclusion for the following deductive argument: If an integer is an even number, then its square is also even. Six is an even number, therefore… ...
... 8. Complete the conclusion for the following deductive argument: If an integer is an even number, then its square is also even. Six is an even number, therefore… ...
Intelligent Autonomous Agents
... • Individual rationality: Participating in the negotiation (or individual deal) is no worse than not participating • Stability: No agents can increase their utility by changing their strategies • Symmetry: No agent should be inherently preferred, e.g. dictator ...
... • Individual rationality: Participating in the negotiation (or individual deal) is no worse than not participating • Stability: No agents can increase their utility by changing their strategies • Symmetry: No agent should be inherently preferred, e.g. dictator ...
An Approach to Bounded Rationality
... In particular, the pair of mixed strategies which are the empirical distributions of play over time approaches the set of Nash equilibrium of the stage game. Inverse-polynomial rates of convergence (that are polynomial also in the size of the game) can be given for such algorithms. Hence no-regret a ...
... In particular, the pair of mixed strategies which are the empirical distributions of play over time approaches the set of Nash equilibrium of the stage game. Inverse-polynomial rates of convergence (that are polynomial also in the size of the game) can be given for such algorithms. Hence no-regret a ...
computing game-theoretic solutions - CS.Duke
... • District attorney has evidence to convict them of a minor crime (1 year in jail); knows that they committed a major crime together (additional 2 years in jail) but cannot prove it • Offers them a deal: – If both confess to the major crime, they each get a 1 year reduction – If only one confesses, ...
... • District attorney has evidence to convict them of a minor crime (1 year in jail); knows that they committed a major crime together (additional 2 years in jail) but cannot prove it • Offers them a deal: – If both confess to the major crime, they each get a 1 year reduction – If only one confesses, ...
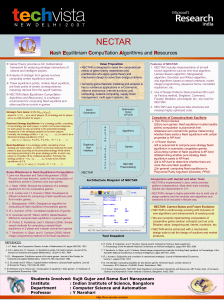
NECTAR: Nash Equilibrium Computation Algorithms
... environment for computing Nash equilibria and other equilibrium points in games. Strategic Form Game: G=(N,(Si)iЄN,(ui)iЄN), where N = {1,2,…,n} is set of players, Si is strategy set for player i and ui is utility function for player i. Dominant Strategy Equilibrium: It is a strategy profile, consis ...
... environment for computing Nash equilibria and other equilibrium points in games. Strategic Form Game: G=(N,(Si)iЄN,(ui)iЄN), where N = {1,2,…,n} is set of players, Si is strategy set for player i and ui is utility function for player i. Dominant Strategy Equilibrium: It is a strategy profile, consis ...
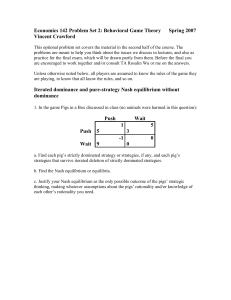
Economics 142 Problem Set 2: Behavioral Game Theory Spring
... each firm’s type is drawn as explained above. Show that the expected number of entrants is closer to the ex post optimal number (2) than in your equilibrium from part (a), and that that the probability of exactly 2 entrants is higher than in (a). (In experiments subjects’ initial responses come syst ...
... each firm’s type is drawn as explained above. Show that the expected number of entrants is closer to the ex post optimal number (2) than in your equilibrium from part (a), and that that the probability of exactly 2 entrants is higher than in (a). (In experiments subjects’ initial responses come syst ...
Game theory
... The prisoner’s dilemma is one of the most popular games studied in game theory that has been portrayed in countless movies and crime television shows. The prisoner’s dilemma shows why two individuals might not agree, even if it appears that it is best to agree. In this scenario, two partners in crim ...
... The prisoner’s dilemma is one of the most popular games studied in game theory that has been portrayed in countless movies and crime television shows. The prisoner’s dilemma shows why two individuals might not agree, even if it appears that it is best to agree. In this scenario, two partners in crim ...
Slide 1
... Map of proportions for Hawk-Dove game. Note that where the curve meets the straight line at a gradient of less than 1 (the middle point), that is a stable equilibrium. Where it meets it at a gradient greater than 1, it is an unstable equilibrium. ...
... Map of proportions for Hawk-Dove game. Note that where the curve meets the straight line at a gradient of less than 1 (the middle point), that is a stable equilibrium. Where it meets it at a gradient greater than 1, it is an unstable equilibrium. ...