Lecture 24 (Slides) October 18
... electrons. These atoms are usually chemically unstable. Two such atoms can come together to form a molecule with no unpaired electrons. This process can involve the formation of covalent chemical bonds and is highly exothermic. ...
... electrons. These atoms are usually chemically unstable. Two such atoms can come together to form a molecule with no unpaired electrons. This process can involve the formation of covalent chemical bonds and is highly exothermic. ...
Atoms
... What is the atomic number of boron, B? What is the atomic mass of silicon, Si? How many protons does a chlorine atom have? How many electrons does a neutral neon atom have? • Will an atom with 6 protons, 6 neutrons and 6 electrons be electrically neutral? • Will an atom with 27 protons, 32 neutrons ...
... What is the atomic number of boron, B? What is the atomic mass of silicon, Si? How many protons does a chlorine atom have? How many electrons does a neutral neon atom have? • Will an atom with 6 protons, 6 neutrons and 6 electrons be electrically neutral? • Will an atom with 27 protons, 32 neutrons ...
Unit 3 Practice Test
... A. Non-metals generally have the higher electronegativities and tend to attract electrons to themselves in a chemical bond. B. Elements with high ionization energies tend to have small atomic radii. C. Elements with high electronegativities generally form ions with small radii. D. The second ionizat ...
... A. Non-metals generally have the higher electronegativities and tend to attract electrons to themselves in a chemical bond. B. Elements with high ionization energies tend to have small atomic radii. C. Elements with high electronegativities generally form ions with small radii. D. The second ionizat ...
GOAL 1 - All Living Things are Made Up of Matter Matter is the Stuff
... Periodic Table of Elements Back in 1869, Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev organized all the know elements into a chart according to their properties. Today the chart is known as the periodic table of elements. The periodic table is made up of horizontal rows and vertical columns of boxes. Each box c ...
... Periodic Table of Elements Back in 1869, Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev organized all the know elements into a chart according to their properties. Today the chart is known as the periodic table of elements. The periodic table is made up of horizontal rows and vertical columns of boxes. Each box c ...
3.1 The Atom: From Philosophical Idea to Theory
... Electrons have so little mass that atoms must contain other particles that account for most of the mass ...
... Electrons have so little mass that atoms must contain other particles that account for most of the mass ...
transcript for this video
... jump was 1804, with Dalton thinking about matter consisting of tiny balls, which again was the atom idea but with more evidence to back it up. The Plum Pudding Model diagram is labelled, so, it explains what we thought was happening with Thompson’s Plum Pudding Model in terms of the electrons embedd ...
... jump was 1804, with Dalton thinking about matter consisting of tiny balls, which again was the atom idea but with more evidence to back it up. The Plum Pudding Model diagram is labelled, so, it explains what we thought was happening with Thompson’s Plum Pudding Model in terms of the electrons embedd ...
Elements and Compounds
... • Atoms of the same element can have different masses. • They always have the same number of protons, but they can have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. • The difference in the number of neutrons accounts for the difference in ...
... • Atoms of the same element can have different masses. • They always have the same number of protons, but they can have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. • The difference in the number of neutrons accounts for the difference in ...
Chapter 3
... Electrons have so little mass that atoms must contain other particles that account for most of the mass ...
... Electrons have so little mass that atoms must contain other particles that account for most of the mass ...
Concepts to know for the Unit 3 test
... 6. Use the periodic table to correlate the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom. a. Atomic number: Number of protons b. Mass number: Number of protons + number of neutrons c. Number of electrons: Same as # of protons in neutral atom a. # Electrons > # Protons NEGATIVE charge b. # ...
... 6. Use the periodic table to correlate the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom. a. Atomic number: Number of protons b. Mass number: Number of protons + number of neutrons c. Number of electrons: Same as # of protons in neutral atom a. # Electrons > # Protons NEGATIVE charge b. # ...
Practice Multiple Choice Questions for the Chemistry Final Exam
... Who was the schoolmaster who studied chemistry and proposed an atomic theory? a) John Dalton b) Jons Berzehus c) Robert Brown d) Dmitri Mendeleev ...
... Who was the schoolmaster who studied chemistry and proposed an atomic theory? a) John Dalton b) Jons Berzehus c) Robert Brown d) Dmitri Mendeleev ...
Investigating Atoms and Atomic Theory
... in the periodic table. Also known as Families. Families may be one column, or several columns put together. The elements in each group or family, have similar characteristics. Families have names rather than numbers. (Just like your family has a common last name.) ...
... in the periodic table. Also known as Families. Families may be one column, or several columns put together. The elements in each group or family, have similar characteristics. Families have names rather than numbers. (Just like your family has a common last name.) ...
Chapter 4 - H - Regional School District 17
... networks similar? Both networks are used to transport objects from one location to another. The comparison is an example of an analogy. An analogy uses a similarity to compare two objects or systems. A familiar object is often used to help explain a less familiar object. ...
... networks similar? Both networks are used to transport objects from one location to another. The comparison is an example of an analogy. An analogy uses a similarity to compare two objects or systems. A familiar object is often used to help explain a less familiar object. ...
The atomic number tells how many protons Protons make an atom
... with different atomic masses are called isotopes Gold has a mass of 196.97 That means MOST gold atoms have 197 p+ and no, but some rare atoms will have only 196. They ALL have 79 p+. Most have 118no, but a few may have 117 no. ...
... with different atomic masses are called isotopes Gold has a mass of 196.97 That means MOST gold atoms have 197 p+ and no, but some rare atoms will have only 196. They ALL have 79 p+. Most have 118no, but a few may have 117 no. ...
2.1 PowerPoint
... Atoms are indestructible and cannot be divided into smaller particles(Atoms are indivisible) All atoms of one element are exactly alike, but they are different from atoms of other elements. ...
... Atoms are indestructible and cannot be divided into smaller particles(Atoms are indivisible) All atoms of one element are exactly alike, but they are different from atoms of other elements. ...
Electrons in Energy Level
... • The mass of a neutron is almost the same as the mass of a proton. However an electron is about 2,000 times lighter than a proton. • The sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus is the mass number of that particular atom. * Mass number is also called atomic weight/atomic mass ...
... • The mass of a neutron is almost the same as the mass of a proton. However an electron is about 2,000 times lighter than a proton. • The sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus is the mass number of that particular atom. * Mass number is also called atomic weight/atomic mass ...
02 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... • Electrons in the outer shell are therefore called valence electrons. ...
... • Electrons in the outer shell are therefore called valence electrons. ...
AtomMoleculeNaming_G1
... • Elements: A First Look at the Periodic Table • Compounds: Introduction to Bonding • Formulas, Names, and Masses of Compounds • Mixtures: Classification and Separation ...
... • Elements: A First Look at the Periodic Table • Compounds: Introduction to Bonding • Formulas, Names, and Masses of Compounds • Mixtures: Classification and Separation ...
DEFINING THE ATOM
... individual atoms? In your own words, state the main ideas of Dalton’s atomic theory. According to Dalton’s atomic theory, is it impossible to convert atoms of one element into atoms of another? Explain. ...
... individual atoms? In your own words, state the main ideas of Dalton’s atomic theory. According to Dalton’s atomic theory, is it impossible to convert atoms of one element into atoms of another? Explain. ...
TEST on Atomic Structure
... _____ 55) How do the isotopes Carbon-12 and Carbon-13 differ? a. Carbon-12 has one more electron than hydrogen-1. b. Carbon-12 has 12 neutrons; carbon-13 has 13 neutrons c. Carbon-13 has one more neutron than carbon-12 d. Carbon-13 has one more proton that carbon-12 _____ 56) The atomic mass of an ...
... _____ 55) How do the isotopes Carbon-12 and Carbon-13 differ? a. Carbon-12 has one more electron than hydrogen-1. b. Carbon-12 has 12 neutrons; carbon-13 has 13 neutrons c. Carbon-13 has one more neutron than carbon-12 d. Carbon-13 has one more proton that carbon-12 _____ 56) The atomic mass of an ...
atoms
... Click the Forward button to go to the next slide. Click the Previous button to return to the previous slide. Click the Home button to return to the Chapter Menu. Click the Return button in a feature to return to the main presentation. Click the Exit button or press the Escape key [Esc] to end the sl ...
... Click the Forward button to go to the next slide. Click the Previous button to return to the previous slide. Click the Home button to return to the Chapter Menu. Click the Return button in a feature to return to the main presentation. Click the Exit button or press the Escape key [Esc] to end the sl ...
Summer Work
... 3. The number of protons in one atom of an element determines the atom’s __________________ , and the number of electrons determines ___________________ of an element. 4. The atomic number tells you the number of ______________________ in one atom of an element. It also tells you the number of _____ ...
... 3. The number of protons in one atom of an element determines the atom’s __________________ , and the number of electrons determines ___________________ of an element. 4. The atomic number tells you the number of ______________________ in one atom of an element. It also tells you the number of _____ ...
OKEMOS PUBLIC SCHOOLS
... one electron is promoted from the s to the d level to get a ½ filled and a full sublevel (more stable)__________________________________________________________________ ...
... one electron is promoted from the s to the d level to get a ½ filled and a full sublevel (more stable)__________________________________________________________________ ...
C:\Users\Jim\Documents\school stuff\atomic structure.wpd
... abundances of the different isotopes of each element would be different. Heavier isotopes are just that, they tend to sink lower into the earth over time than lighter ones. In the formation of the solar system, lighter atoms tended to get pushed farther from the sun by the solar wind than heavier at ...
... abundances of the different isotopes of each element would be different. Heavier isotopes are just that, they tend to sink lower into the earth over time than lighter ones. In the formation of the solar system, lighter atoms tended to get pushed farther from the sun by the solar wind than heavier at ...
Atoms Molecules and Ions Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... embedded in a positively charged “pudding,” thus it was called the “plum p pudding” p g model. ...
... embedded in a positively charged “pudding,” thus it was called the “plum p pudding” p g model. ...
The Chemistry of Life ppt
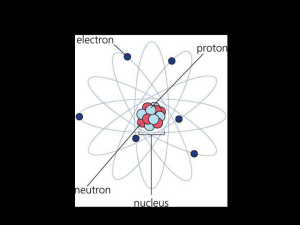
... • The center of the atom is called the nucleus. • Electrons live in something called shells. • Shells are areas that surround the center of an atom. • A shell is sometimes called an orbital or energy level. ...
... • The center of the atom is called the nucleus. • Electrons live in something called shells. • Shells are areas that surround the center of an atom. • A shell is sometimes called an orbital or energy level. ...