gallagher chapter 41
... Conclusions from the study of the Electron 4. Eugen Goldstein in 1886 observed what is now called the “proton” - particles with a positive charge, and a relative mass of 1 (or 1840 times that of an electron) 5. 1932 – James Chadwick confirmed the existence of the “neutron” – a particle with no char ...
... Conclusions from the study of the Electron 4. Eugen Goldstein in 1886 observed what is now called the “proton” - particles with a positive charge, and a relative mass of 1 (or 1840 times that of an electron) 5. 1932 – James Chadwick confirmed the existence of the “neutron” – a particle with no char ...
Atomic Number
... Discovery of the Electron • Because of Dalton’s atomic theory, most scientists in the 1800s believed that the atom was like a tiny solid ball that could not be broken up into parts. • In 1897, a British physicist, J.J. Thomson, discovered that this solid-ball model was not ...
... Discovery of the Electron • Because of Dalton’s atomic theory, most scientists in the 1800s believed that the atom was like a tiny solid ball that could not be broken up into parts. • In 1897, a British physicist, J.J. Thomson, discovered that this solid-ball model was not ...
PPT - hss-1.us
... combination of the words – "mono" and "atomic," and means "single atom." It is usually applied to gases: a monatomic gas is one in which atoms are not bound to each other. – At standard temperature and pressure (STP), all of the noble gases are monatomic. These are helium, neon, argon, krypton, xeno ...
... combination of the words – "mono" and "atomic," and means "single atom." It is usually applied to gases: a monatomic gas is one in which atoms are not bound to each other. – At standard temperature and pressure (STP), all of the noble gases are monatomic. These are helium, neon, argon, krypton, xeno ...
Chapter 4 - H - Regional School District 17
... objects from one location to another. The comparison is an example of an analogy. An analogy uses a similarity to compare two objects or systems. A familiar object is often used to help explain a less familiar object. 1. Atoms in compounds are like bricks in a wall. Explain this analogy. 2. Think of ...
... objects from one location to another. The comparison is an example of an analogy. An analogy uses a similarity to compare two objects or systems. A familiar object is often used to help explain a less familiar object. 1. Atoms in compounds are like bricks in a wall. Explain this analogy. 2. Think of ...
biology biology - Napa Valley College
... An element’s properties depend on the structure of its atoms Each element consists of unique atoms An atom is the smallest unit of matter that still retains the properties of an element ...
... An element’s properties depend on the structure of its atoms Each element consists of unique atoms An atom is the smallest unit of matter that still retains the properties of an element ...
Atomic Structure - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Protons have a charge of +1 and are located in the nucleus with neutrons. Both are 1,840 times larger than electrons. ...
... Protons have a charge of +1 and are located in the nucleus with neutrons. Both are 1,840 times larger than electrons. ...
II. Masses of Atoms
... • A MOLECULE OF CARBON MONOXIDE, CO, HAS ONE ATOM OF OXYGEN WHILE A MOLECULE OF CARBON DIOXIDE, CO2, HAS TWO. IN A SAMPLE OF CO CONTAINING 1 G OF CARBON, 1.33 G OF OXYGEN WILL COMBINE WITH THE CARBON TO FORM THE MOLECULE. WHAT IS THE MASS OF OXYGEN IN A SAMPLE OF CO2 CONTAINING 1 G OF CARBON? A.1.33 ...
... • A MOLECULE OF CARBON MONOXIDE, CO, HAS ONE ATOM OF OXYGEN WHILE A MOLECULE OF CARBON DIOXIDE, CO2, HAS TWO. IN A SAMPLE OF CO CONTAINING 1 G OF CARBON, 1.33 G OF OXYGEN WILL COMBINE WITH THE CARBON TO FORM THE MOLECULE. WHAT IS THE MASS OF OXYGEN IN A SAMPLE OF CO2 CONTAINING 1 G OF CARBON? A.1.33 ...
The Chemistry of Life Chapter 2
... • The center of the atom is called the nucleus. • Electrons live in something called shells. • Shells are areas that surround the center of an atom. • A shell is sometimes called an orbital or energy level. ...
... • The center of the atom is called the nucleus. • Electrons live in something called shells. • Shells are areas that surround the center of an atom. • A shell is sometimes called an orbital or energy level. ...
SCSD Physical Science 9th - Shenandoah Community Schools
... Complete shell tend to be chemically inert (I,D,M) Closed shell with one or two valance electrons highly reactive (I,D,M) Less than a closed shell with one or two valance electrons highly reactive (I,D,M) o The number of valence electrons of an element is determined by its periodic table (I,D,M) o R ...
... Complete shell tend to be chemically inert (I,D,M) Closed shell with one or two valance electrons highly reactive (I,D,M) Less than a closed shell with one or two valance electrons highly reactive (I,D,M) o The number of valence electrons of an element is determined by its periodic table (I,D,M) o R ...
atom
... protons, and neutrons), but the atom is still the smallest body that retains the unique identity of an element Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element in a chemical reaction All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determines the che ...
... protons, and neutrons), but the atom is still the smallest body that retains the unique identity of an element Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element in a chemical reaction All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determines the che ...
Notes 4.3 filled in
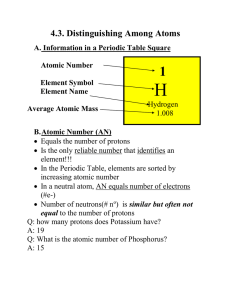
... B. Atomic Number (AN) Equals the number of protons Is the only reliable number that identifies an element!!! In the Periodic Table, elements are sorted by increasing atomic number In a neutral atom, AN equals number of electrons (#e-) Number of neutrons(# no) is similar but often not equal ...
... B. Atomic Number (AN) Equals the number of protons Is the only reliable number that identifies an element!!! In the Periodic Table, elements are sorted by increasing atomic number In a neutral atom, AN equals number of electrons (#e-) Number of neutrons(# no) is similar but often not equal ...
Ionic Bonding
... eight electrons in their outer energy levels (or two in the case of helium). These noble gas structures are thought of as being in some way a "desirable" thing for an atom to have. You may well have been left with the strong impression that when other atoms react, they try to organize things such th ...
... eight electrons in their outer energy levels (or two in the case of helium). These noble gas structures are thought of as being in some way a "desirable" thing for an atom to have. You may well have been left with the strong impression that when other atoms react, they try to organize things such th ...
Atomic Structure-PRACTICE TEST
... TRUE or FALSE - the atomic mass increases by ONE from element to element (atomic number) TRUE or FALSE - the elements become more non metallic TRUE or FALSE - the ionization energy of the elements generally decreases TRUE or FALSE - the elements are arranged according to increasing atomic number TRU ...
... TRUE or FALSE - the atomic mass increases by ONE from element to element (atomic number) TRUE or FALSE - the elements become more non metallic TRUE or FALSE - the ionization energy of the elements generally decreases TRUE or FALSE - the elements are arranged according to increasing atomic number TRU ...
CHEM 400 - El Camino College
... Have an understanding of the process of measurement as a comparison with a standard. Know that a unit of measurement serves as a standard. Know why measured quantities have a certain limited number of significant digits. How many significant figures should be written when you use a digital balance? ...
... Have an understanding of the process of measurement as a comparison with a standard. Know that a unit of measurement serves as a standard. Know why measured quantities have a certain limited number of significant digits. How many significant figures should be written when you use a digital balance? ...
Solutions - Dynamic Science
... The smallest particle of matter. The smallest possible sugar crystal. The smallest particle of water. The energy given off during a chemical reaction. ...
... The smallest particle of matter. The smallest possible sugar crystal. The smallest particle of water. The energy given off during a chemical reaction. ...
Atomic Structure and Elements
... abundant form of hydrogen does not have a neutron. However, in rare instances isotopes form. Below are the isotopes of ...
... abundant form of hydrogen does not have a neutron. However, in rare instances isotopes form. Below are the isotopes of ...
Periodic Table Extra Practice ANSWER KEY 2014
... 1.4 I can describe the charge and location of protons, neutrons, and electrons within the nucleus and shells of an atom. The periodic table is, in many ways, the world’s greatest cheat sheet. The periodic table lists all of the elements (simple substances that make up more complex materials) like go ...
... 1.4 I can describe the charge and location of protons, neutrons, and electrons within the nucleus and shells of an atom. The periodic table is, in many ways, the world’s greatest cheat sheet. The periodic table lists all of the elements (simple substances that make up more complex materials) like go ...
Lecture 2 - Columbia University
... Pure substance (an idealization): A pure substance does not change its chemical characteristics upon exhaustive attempts of purification. Atomic interpretation: A pure substance possesses a structure that is composed of a definite number and kinds of atoms that are connected in a specific manner. ...
... Pure substance (an idealization): A pure substance does not change its chemical characteristics upon exhaustive attempts of purification. Atomic interpretation: A pure substance possesses a structure that is composed of a definite number and kinds of atoms that are connected in a specific manner. ...
Atom - Perry Local Schools
... zinc sulfide coating in the tube (some sort of radiation was produced) -Cathode ray was the name given to this spark of light, this eventually led to the invention of the tv. -Conclusions: streams of charged particles were passing through the tube, they carried a negative charge. -later negatively c ...
... zinc sulfide coating in the tube (some sort of radiation was produced) -Cathode ray was the name given to this spark of light, this eventually led to the invention of the tv. -Conclusions: streams of charged particles were passing through the tube, they carried a negative charge. -later negatively c ...
Section 1 The Development of Atomic Theory
... • The mass number equals the total number of subatomic particles in the nucleus. – mass number: the sum of the numbers of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom ...
... • The mass number equals the total number of subatomic particles in the nucleus. – mass number: the sum of the numbers of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom ...
Document
... The mass of one mole is called “molar mass” E.g. 1 mol Li = 6.94 g Li This is expressed as 6.94 g/mol What are the following molar masses? S 32.06 g/mol SO2 64.06 g/mol Cu3(BO3)2 308.27 g/mol ...
... The mass of one mole is called “molar mass” E.g. 1 mol Li = 6.94 g Li This is expressed as 6.94 g/mol What are the following molar masses? S 32.06 g/mol SO2 64.06 g/mol Cu3(BO3)2 308.27 g/mol ...
atomic structure - saedsurnaturales
... Moving across each period, you can see that the number of occupied energy levels is the same as the period number. As you go across each period from left to right, an energy level gradually becomes filled with electrons. The highest occupied energy level contains just one electron on the left-hand s ...
... Moving across each period, you can see that the number of occupied energy levels is the same as the period number. As you go across each period from left to right, an energy level gradually becomes filled with electrons. The highest occupied energy level contains just one electron on the left-hand s ...
Student midterm review sheet
... What subatomic particles are taken into account in an element’s atomic mass? What is an isotope? Calculate the atomic mass of an element using a weighted average ...
... What subatomic particles are taken into account in an element’s atomic mass? What is an isotope? Calculate the atomic mass of an element using a weighted average ...
Name the three parts of an atom and where they are located
... The mass of an atom; the # protons + # of neutrons What parts of the atom account for the atomic mass? protons & neutrons What is an isotope? An atom that has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons Are isotopes always the same element? Why? Yes, the # of protons determines an ...
... The mass of an atom; the # protons + # of neutrons What parts of the atom account for the atomic mass? protons & neutrons What is an isotope? An atom that has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons Are isotopes always the same element? Why? Yes, the # of protons determines an ...