Introduction to Chemistry for Coach Keith`s Biology
... Organisms eat plants, break down the sugars, and release energy along with CO 2 & H2O Exergonic reactions involve a net release of energy; while endergonic reactions involve a net absorption of energy Energy must be added to the reactants for most chemical reactions to occur; called activation energ ...
... Organisms eat plants, break down the sugars, and release energy along with CO 2 & H2O Exergonic reactions involve a net release of energy; while endergonic reactions involve a net absorption of energy Energy must be added to the reactants for most chemical reactions to occur; called activation energ ...
No Slide Title
... Atoms of each element are distinguished by a specific number of protons or Atomic number. The sum of protons and neutrons produce the Atomic mass (weight) of the element. Atoms of the same element with different number of neutrons are called isotopes and some isotopes are radioactive. ...
... Atoms of each element are distinguished by a specific number of protons or Atomic number. The sum of protons and neutrons produce the Atomic mass (weight) of the element. Atoms of the same element with different number of neutrons are called isotopes and some isotopes are radioactive. ...
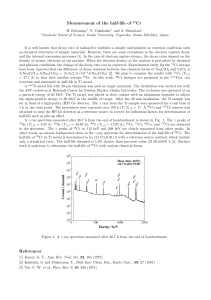
Measurement of the half-life of
... It is well known that decay rate of radioactive nuclides is usually independent on external conditions such as chemical structures of sample materials. However, there are some exceptions in the electron capture decay and the internal conversion processes [1]. In the case of electron capture decays, ...
... It is well known that decay rate of radioactive nuclides is usually independent on external conditions such as chemical structures of sample materials. However, there are some exceptions in the electron capture decay and the internal conversion processes [1]. In the case of electron capture decays, ...
Chemistry Of Life
... • Two or more elements together • Fixed ratio (always the same ratio) • Emergent properties – behavior of compound may be drastically different than the behavior of the individual ...
... • Two or more elements together • Fixed ratio (always the same ratio) • Emergent properties – behavior of compound may be drastically different than the behavior of the individual ...
Another look at chemical reactions HYDROGEN PEROXIDE WATER
... - a small particle that carries an overall unit NEGATIVE CHARGE - about 2000 times LESS massive than either protons or neutrons ...
... - a small particle that carries an overall unit NEGATIVE CHARGE - about 2000 times LESS massive than either protons or neutrons ...
Early Greek Philosophers determined that atoms are the building
... Located on either side of the zigzag line separating metals and nonmetals Most common is Silicon ...
... Located on either side of the zigzag line separating metals and nonmetals Most common is Silicon ...
The periodic table is the most significant tool that chemist use for
... Many properties of molecules depend on the distances between the atoms in the molecule. Atomic radii allow one to estimated the bond lengths between different elements in molecules. The C--C bond length is 1.54 Å, implying a radius of 0.77 Å for a carbon atom. The radial-electron-density distributio ...
... Many properties of molecules depend on the distances between the atoms in the molecule. Atomic radii allow one to estimated the bond lengths between different elements in molecules. The C--C bond length is 1.54 Å, implying a radius of 0.77 Å for a carbon atom. The radial-electron-density distributio ...
FIREWORKS EMC summary notes
... In a chemical reaction a new substance is always formed. Most chemical changes are not easily reversed; they are irreversible. In a physical change no new substance is formed. Melting and evaporation are examples of physical changes. Physical changes are usually reversible. You can tell that a react ...
... In a chemical reaction a new substance is always formed. Most chemical changes are not easily reversed; they are irreversible. In a physical change no new substance is formed. Melting and evaporation are examples of physical changes. Physical changes are usually reversible. You can tell that a react ...
atoms and elements
... An atom is the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still maintain the properties of that element. All elements are made of atoms. So what’s an element? What makes one element different from another? Let’s find out! Vocabulary: First things first, let’s look at the structure of ...
... An atom is the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still maintain the properties of that element. All elements are made of atoms. So what’s an element? What makes one element different from another? Let’s find out! Vocabulary: First things first, let’s look at the structure of ...
What does the Periodic Table tell us?
... are vertical (up and down) elements in the same group/family ________________________________ there are ____of them on the periodic table o Ex) Li, Na, K all have a similar ____________________ with water (H2O). They all create an explosion that releases hydrogen gas (H2). Therefore, they are ...
... are vertical (up and down) elements in the same group/family ________________________________ there are ____of them on the periodic table o Ex) Li, Na, K all have a similar ____________________ with water (H2O). They all create an explosion that releases hydrogen gas (H2). Therefore, they are ...
Chapter 4: Atomic Structure
... the region the nucleus. (a tiny central core of an atom and is composed of protons and neutrons) Rutherford’s atomic model is known as the nuclear atom. In the nuclear atom, the protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. The electrons are distributed around the nucleus and occupy almost all of ...
... the region the nucleus. (a tiny central core of an atom and is composed of protons and neutrons) Rutherford’s atomic model is known as the nuclear atom. In the nuclear atom, the protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. The electrons are distributed around the nucleus and occupy almost all of ...
Fall Semester Review Packet
... variable and a control. Describe how these variables relate to one another during an experiment. 12. Explain the difference between accuracy and precision when describing scientific measurements. 13. Explain how atoms of the same element may differ. Include all of the following terms in your explana ...
... variable and a control. Describe how these variables relate to one another during an experiment. 12. Explain the difference between accuracy and precision when describing scientific measurements. 13. Explain how atoms of the same element may differ. Include all of the following terms in your explana ...
Classification of Matter
... Chemical Properties - Characteristics of a substance that do change the chemical makeup of the substance. How a material reacts or fails to react in the presence of another material to form a ...
... Chemical Properties - Characteristics of a substance that do change the chemical makeup of the substance. How a material reacts or fails to react in the presence of another material to form a ...
atoms
... Element X contains three naturally occurring isotopes with masses of 78.0, 79.0, and 80.0 amu. What data is needed to calculate its average atomic mass? The natural abundance in percent of each isotope (Can you do these calculations?) ...
... Element X contains three naturally occurring isotopes with masses of 78.0, 79.0, and 80.0 amu. What data is needed to calculate its average atomic mass? The natural abundance in percent of each isotope (Can you do these calculations?) ...
ATOMIC THEORY
... The modern atomic theory states that atoms of one element are the same, while atoms of different elements are different. What makes atoms of different elements different? The fundamental characteristic that all atoms of the same element share is the number of protons . All atoms of hydrogen have on ...
... The modern atomic theory states that atoms of one element are the same, while atoms of different elements are different. What makes atoms of different elements different? The fundamental characteristic that all atoms of the same element share is the number of protons . All atoms of hydrogen have on ...
Course Syllabus - Honors Chemistry
... f.* The lanthanide, actinide, and transactinide elements and that the transuranium elements were synthesized and identified in laboratory experiments. g.* The position of an element in the periodic table relates to its quantum electron configuration and to its reactivity with other elements in the t ...
... f.* The lanthanide, actinide, and transactinide elements and that the transuranium elements were synthesized and identified in laboratory experiments. g.* The position of an element in the periodic table relates to its quantum electron configuration and to its reactivity with other elements in the t ...
Atomic Structure: SOL Review #1 Name: Historical Developments 1
... The electrons are not “singly before pairing.” Electrons repel each other, so they do want not pair until there is no more “space” left in the sublevel. Periodic Table and Periodic Trends 27) Which elements would have similar properties to Na? ...
... The electrons are not “singly before pairing.” Electrons repel each other, so they do want not pair until there is no more “space” left in the sublevel. Periodic Table and Periodic Trends 27) Which elements would have similar properties to Na? ...
Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... • Like forces repel, normally • BUT when protons are really close there is a strong attractive force • Same with neutrons • Called nuclear forces (energy, bombs) ...
... • Like forces repel, normally • BUT when protons are really close there is a strong attractive force • Same with neutrons • Called nuclear forces (energy, bombs) ...
Unit 3 Note Outline
... Atoms that have the same number of Most elements have more than one isotope - Hydrogen has Hydrogen-1 has Hydrogen-2 has Hydrogen-3 has ...
... Atoms that have the same number of Most elements have more than one isotope - Hydrogen has Hydrogen-1 has Hydrogen-2 has Hydrogen-3 has ...
Chapter 5: Atomic Structure
... concluded that they must be positive particles, which are now called protons. • In 1932, James Chadwick confirmed the existence of yet another subatomic particle: the neutron. Neutrons are subatomic particles with no charge but with a mass nearly equal to that of a proton. See simulation ...
... concluded that they must be positive particles, which are now called protons. • In 1932, James Chadwick confirmed the existence of yet another subatomic particle: the neutron. Neutrons are subatomic particles with no charge but with a mass nearly equal to that of a proton. See simulation ...
Atomic structure and periodic table notes sheet
... Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Notes 1. What are Atoms? ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ 2. 400 BC- _________________ was the first scientist to suggest that all matter is composed of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. (Atomos) 3. El ...
... Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Notes 1. What are Atoms? ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ 2. 400 BC- _________________ was the first scientist to suggest that all matter is composed of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. (Atomos) 3. El ...
Electron Configuration, Noble Gas Configuration
... electrons. If an atom changes its number of electrons and the atom has an unequal number of protons and electrons then the atom will be charged. Charged atoms are called Ions. Even though atoms of the same element may have different numbers of neutrons or electrons we need to remember that they are ...
... electrons. If an atom changes its number of electrons and the atom has an unequal number of protons and electrons then the atom will be charged. Charged atoms are called Ions. Even though atoms of the same element may have different numbers of neutrons or electrons we need to remember that they are ...
File - Ingolstadt Academy
... Density (definition and equation) Dimensional analysis Instruments that measure mass, volume, pressure, etc. (lab stuff!) The Scientific Method Atomic Structure: ...
... Density (definition and equation) Dimensional analysis Instruments that measure mass, volume, pressure, etc. (lab stuff!) The Scientific Method Atomic Structure: ...
Chapter 3 Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms, and Ions
... the same composition regardless of where it comes from ...
... the same composition regardless of where it comes from ...
Atomic History
... nucleus could only be located in specific paths called orbitals. This was supported by the line spectra of atoms His model is called the planetary model ...
... nucleus could only be located in specific paths called orbitals. This was supported by the line spectra of atoms His model is called the planetary model ...