Structure of an Atom
... Atoms of a given element are identical but differ from the atoms of other elements. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds. Atoms take part in all chemical reactions. According to Dalton’s atom ...
... Atoms of a given element are identical but differ from the atoms of other elements. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds. Atoms take part in all chemical reactions. According to Dalton’s atom ...
Ch#4 Atoms and Elements
... • Compound – distinct substance that is composed of the atoms of two or more elements and always contains exactly the same whole number ratio of those elements. • Chemical Formulas – expresses the types of atoms and the number of each type in each formula unit, or molecule of a given compound. ...
... • Compound – distinct substance that is composed of the atoms of two or more elements and always contains exactly the same whole number ratio of those elements. • Chemical Formulas – expresses the types of atoms and the number of each type in each formula unit, or molecule of a given compound. ...
Chapter Excerpt
... quantum numbers (n, l, and ml) to describe an orbital and a fourth (ms) to describe an electron in an orbital. This model is useful for understanding the frequencies of radiation emitted and absorbed by atoms and chemical properties of atoms. The principal quantum number n may have positive integer ...
... quantum numbers (n, l, and ml) to describe an orbital and a fourth (ms) to describe an electron in an orbital. This model is useful for understanding the frequencies of radiation emitted and absorbed by atoms and chemical properties of atoms. The principal quantum number n may have positive integer ...
Study Guide: Elements, Compounds, Mixtures Physical Properties
... color & luster, conductivity Can be used to separate a mixture into its components ...
... color & luster, conductivity Can be used to separate a mixture into its components ...
Unit 3: Chemistry. Introduction to Atoms. Atomic mass
... 2. _______________________________ suggested that electrons travel in well-defined paths. 3. _______________________________ discovered that atoms have electrons and thought that they were embedded in positively charged material. 4. _______________________________ proposed that matter is composed of ...
... 2. _______________________________ suggested that electrons travel in well-defined paths. 3. _______________________________ discovered that atoms have electrons and thought that they were embedded in positively charged material. 4. _______________________________ proposed that matter is composed of ...
Chp 4 PPT final
... The atomic numbers gives the number of protons AND the number of electrons in a neutral atom of an element ...
... The atomic numbers gives the number of protons AND the number of electrons in a neutral atom of an element ...
atomic number
... called atoms, that cannot be destroyed or created. 2. Each element has atoms that are identical to each other in all of their properties, and these properties are different from the properties of all other atoms. 3. Chemical reactions are simple rearrangements of atoms from one combination to anothe ...
... called atoms, that cannot be destroyed or created. 2. Each element has atoms that are identical to each other in all of their properties, and these properties are different from the properties of all other atoms. 3. Chemical reactions are simple rearrangements of atoms from one combination to anothe ...
Chapter 05
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory All matter is made of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. Atoms of the same element are identical, those of different atoms are different. Atoms of different elements combine in whole number ratios to form compounds. Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement o ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory All matter is made of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. Atoms of the same element are identical, those of different atoms are different. Atoms of different elements combine in whole number ratios to form compounds. Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement o ...
electrons - River Dell Regional School District
... however, did bounce away from the gold sheet as if they had hit ...
... however, did bounce away from the gold sheet as if they had hit ...
DAY
... light. By crashing protons into antiprotons or into fixed targets, researchers can create new and different particles to study. Creating a new particle, however, requires an enormous amount of energy. The Tevatron is unique because it can accelerate particles to energies higher than those of any oth ...
... light. By crashing protons into antiprotons or into fixed targets, researchers can create new and different particles to study. Creating a new particle, however, requires an enormous amount of energy. The Tevatron is unique because it can accelerate particles to energies higher than those of any oth ...
Chapter 2
... atoms which carry a positive or negative electric charge. Common table salt (which has the chemical name of sodium chloride) is made of a large network of sodium ions, Na+ and chloride ions, Cl - ...
... atoms which carry a positive or negative electric charge. Common table salt (which has the chemical name of sodium chloride) is made of a large network of sodium ions, Na+ and chloride ions, Cl - ...
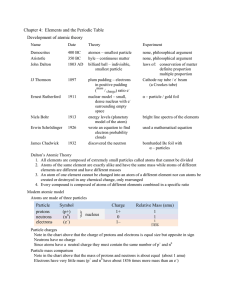
Chapter 4: Elements and the Periodic Table Development of atomic
... Conductivity – most metals are good conductors of heat and electricity Luster – most metals are very shiny or have high metallic luster Magnetic – many metals (but not all) are attracted to magnets Chemical properties of metals Reactivity – metals react by losing electrons to form positive ions Some ...
... Conductivity – most metals are good conductors of heat and electricity Luster – most metals are very shiny or have high metallic luster Magnetic – many metals (but not all) are attracted to magnets Chemical properties of metals Reactivity – metals react by losing electrons to form positive ions Some ...
atomic number Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
... • About 8 out of 10 chlorine atoms are chlorine-35. Two out of 10 are chlorine-37. ...
... • About 8 out of 10 chlorine atoms are chlorine-35. Two out of 10 are chlorine-37. ...
Ch#4 Atoms and Elements
... elements combine with each other. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. •Chemical changes involve reorganization of the atoms, to different ratios. ...
... elements combine with each other. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. •Chemical changes involve reorganization of the atoms, to different ratios. ...
Academic Chemistry Midterm Study Guide Chapters 1
... proton- positively charged subatomic particle neutron- subatomic particle with no charge electron- negatively charged subatomic particle atomic number- equal to the number of protons within an atom mass number- equal to the number of protons and neutrons found within the nucleus of an atom isotope- ...
... proton- positively charged subatomic particle neutron- subatomic particle with no charge electron- negatively charged subatomic particle atomic number- equal to the number of protons within an atom mass number- equal to the number of protons and neutrons found within the nucleus of an atom isotope- ...
The Atom
... • C. John Dalton (late 1700’s) – 1. Atoms cannot be created, divided or destroyed. – 2. Atoms of the same element are alike. – 3. Atoms join with other atoms to make new substances ...
... • C. John Dalton (late 1700’s) – 1. Atoms cannot be created, divided or destroyed. – 2. Atoms of the same element are alike. – 3. Atoms join with other atoms to make new substances ...
ATOMS: THE BUILDING BLOCKS OF MATTER from the
... Hund's Rule of Maximum Multiplicity Electrons fill the energy levels in regular patterns. They first fill the s orbitals, then the p, and so on. hydrogen - The element with the atomic number of one and symbol of H. Hydrogen is the most common element in the universe. ion - An atom with more or less ...
... Hund's Rule of Maximum Multiplicity Electrons fill the energy levels in regular patterns. They first fill the s orbitals, then the p, and so on. hydrogen - The element with the atomic number of one and symbol of H. Hydrogen is the most common element in the universe. ion - An atom with more or less ...
Welcome to Chemistry 1001
... The atoms can be from the same element (eg. N2) or different elements (eg. H2O). ...
... The atoms can be from the same element (eg. N2) or different elements (eg. H2O). ...
Chapter 2. The Chemical Context of Life
... Pair of electrons not shared equally by 2 atoms Water = O + H oxygen has stronger “attraction” for the shared electrons than hydrogen oxygen has higher ...
... Pair of electrons not shared equally by 2 atoms Water = O + H oxygen has stronger “attraction” for the shared electrons than hydrogen oxygen has higher ...
Study Guide-Chemistry Of Life
... 7. In an isotope of element X, what will change? 8. Describe how radioactive isotopes are beneficial. 9. Describe how radioactive isotopes can be harmful. 10. Describe how radioactive isotopes can be used as biological spies or tracers. 11. Why do isotopes of the same element have the same chemical ...
... 7. In an isotope of element X, what will change? 8. Describe how radioactive isotopes are beneficial. 9. Describe how radioactive isotopes can be harmful. 10. Describe how radioactive isotopes can be used as biological spies or tracers. 11. Why do isotopes of the same element have the same chemical ...
Chemistry Mid-Term Review Sheet
... 48. What are the following groups called: Group 1, 2, 3 – 12, 17, and 18? 49. List the properties of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. 50. What does each row on the periodic table represent? 51. How did Mendeleev arrange his periodic table? 52. How is the modern periodic table arranged? 53. What de ...
... 48. What are the following groups called: Group 1, 2, 3 – 12, 17, and 18? 49. List the properties of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. 50. What does each row on the periodic table represent? 51. How did Mendeleev arrange his periodic table? 52. How is the modern periodic table arranged? 53. What de ...
Chapter 2
... • Table salt (sodium chloride or NaCl) is a compound with equal numbers of chlorine and sodium atoms. • While pure sodium is a metal and chlorine is a gas, their combination forms an edible compound, an ...
... • Table salt (sodium chloride or NaCl) is a compound with equal numbers of chlorine and sodium atoms. • While pure sodium is a metal and chlorine is a gas, their combination forms an edible compound, an ...