Electron orbitals imaginary
... call the “closing of the periods”—that is why the periods end, in the sense of achieving a full-shell configuration, at atomic numbers 2, 10, 18, 36, 54, and so forth. This is a separate question from the closing of the shells. For example, if the shells were to fill sequentially, Pauli’s scheme wou ...
... call the “closing of the periods”—that is why the periods end, in the sense of achieving a full-shell configuration, at atomic numbers 2, 10, 18, 36, 54, and so forth. This is a separate question from the closing of the shells. For example, if the shells were to fill sequentially, Pauli’s scheme wou ...
ch.4 - Chemistry
... positively charged particles in the nucleus called protons. • James Chadwick received the Nobel Prize in 1935 for discovering the existence of neutrons, neutral particles in the nucleus which accounts for the remainder of an atom’s mass. ...
... positively charged particles in the nucleus called protons. • James Chadwick received the Nobel Prize in 1935 for discovering the existence of neutrons, neutral particles in the nucleus which accounts for the remainder of an atom’s mass. ...
pdf.format - San Diego Mesa College
... Elements are made from atoms having the same atomic number, protons Are all atoms of one particular atom the same or are they mixtures? 1) All atom nuclei for an element have the same number of protons. 2) Every atom in an element has the same number of protons & electrons. 3) However, elements are ...
... Elements are made from atoms having the same atomic number, protons Are all atoms of one particular atom the same or are they mixtures? 1) All atom nuclei for an element have the same number of protons. 2) Every atom in an element has the same number of protons & electrons. 3) However, elements are ...
Chapter 2 - Bruder Chemistry
... Atomic Weight & Decimals Atomic Weight- of an element is a weighted average mass of the atoms in a naturally occurring sample of an element Atomic Weights use decimal points because it is an average of an element ...
... Atomic Weight & Decimals Atomic Weight- of an element is a weighted average mass of the atoms in a naturally occurring sample of an element Atomic Weights use decimal points because it is an average of an element ...
The Atom
... _________ by E. Goldstein. (3) The neutron does not have a charge. In other words, it is neutral It was discovered in 1932 ________. ____ by James Chadwick. The neutron has about the same _________ mass as the proton. visible matter • These three particles make up all the ____________________ in the ...
... _________ by E. Goldstein. (3) The neutron does not have a charge. In other words, it is neutral It was discovered in 1932 ________. ____ by James Chadwick. The neutron has about the same _________ mass as the proton. visible matter • These three particles make up all the ____________________ in the ...
Defining the Atom
... A. teaching that all matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms B. theorizing that all atoms of the same element are identical C. using experimental methods to establish a scientific theory D. not relating atoms to chemical change ...
... A. teaching that all matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms B. theorizing that all atoms of the same element are identical C. using experimental methods to establish a scientific theory D. not relating atoms to chemical change ...
Chap 4 Review with answers
... When scientists wanted to find out what an atom was, they were not able to look directly at what the atom was made of. They had to make inferences from the results of many different experiments. It was like trying to describe a picture, such as the one on the next slide, with only small portions vis ...
... When scientists wanted to find out what an atom was, they were not able to look directly at what the atom was made of. They had to make inferences from the results of many different experiments. It was like trying to describe a picture, such as the one on the next slide, with only small portions vis ...
mass number - KCPE-KCSE
... Subatomic particles Atoms are composed of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. The two important properties of these particles are mass and charge: Particle ...
... Subatomic particles Atoms are composed of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. The two important properties of these particles are mass and charge: Particle ...
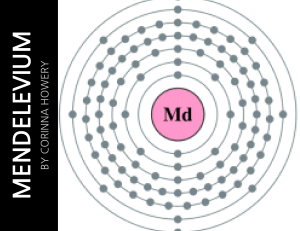
Mendelevium
... table so its atomic number is 101. There are 101 protons/electrons in the nucleus and 157 neutrons. It also has 2 valence electrons. Mendelevium has 7 shells. On the periodic table, mendelevium is in the group actinide and it is radioactive. Mendeleviums state of matter is radioactive. ...
... table so its atomic number is 101. There are 101 protons/electrons in the nucleus and 157 neutrons. It also has 2 valence electrons. Mendelevium has 7 shells. On the periodic table, mendelevium is in the group actinide and it is radioactive. Mendeleviums state of matter is radioactive. ...
Hydrogen Models 1
... one neutron in its nucleus is called Deuterium. Deuterium is not radioactive. Water made from deuterium is called heavy water because the extra neutron makes it heavier. It is used in nuclear reactors. The third isotope of hydrogen is known as Tritium. It has one proton and two neutrons in its nucle ...
... one neutron in its nucleus is called Deuterium. Deuterium is not radioactive. Water made from deuterium is called heavy water because the extra neutron makes it heavier. It is used in nuclear reactors. The third isotope of hydrogen is known as Tritium. It has one proton and two neutrons in its nucle ...
Chem Ch4,25
... He called them atoms. 2. Pictured atoms as tiny, solid spheres. 3. All atoms of the same element are identical atoms of different elements are different. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in whole number ratios. 5. Chemical reactions occur when atoms separate from each other, join with others, ...
... He called them atoms. 2. Pictured atoms as tiny, solid spheres. 3. All atoms of the same element are identical atoms of different elements are different. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in whole number ratios. 5. Chemical reactions occur when atoms separate from each other, join with others, ...
Topic 1 – Atomic structure and the periodic table
... E.g he left two gaps between zinc and arsenic Based on the known elements around them, Mendeleev predicted the properties of the elements which should go in the gaps In the modern periodic table, these gaps have been filled by gallium and germanium – they have very similar properties to those ...
... E.g he left two gaps between zinc and arsenic Based on the known elements around them, Mendeleev predicted the properties of the elements which should go in the gaps In the modern periodic table, these gaps have been filled by gallium and germanium – they have very similar properties to those ...
CHEMISTRY OLYMPICS 2nd 6 weeks What particles form the
... other two • B) Two electrons in one orbital, one in another, none in the third • C) One electron in each orbital ...
... other two • B) Two electrons in one orbital, one in another, none in the third • C) One electron in each orbital ...
Name
... chemical symbol, atomic number, atomic mass number, and physical and chemical properties is called the ______________________________ of elements. P. 82, VCR: Atoms and Molecules 50. The periodic table of elements was originally created by a Russian chemist named ____________________________________ ...
... chemical symbol, atomic number, atomic mass number, and physical and chemical properties is called the ______________________________ of elements. P. 82, VCR: Atoms and Molecules 50. The periodic table of elements was originally created by a Russian chemist named ____________________________________ ...
OCR AS LEVEL CHEMISTRY A 1.1.1 ATOMS 1.2.1 ELECTRON
... State which two elements from the first twenty elements of the modern Periodic Table are not arranged in order of increasing atomic mass. ...
... State which two elements from the first twenty elements of the modern Periodic Table are not arranged in order of increasing atomic mass. ...
Period:______ Table Number
... 83. The number and arrangement of the electrons found in the electron cloud of an atom determines nearly all of an element’s _____________________________ properties. P. 125, VCR: Atoms and Molecules 84. The total number of electrons found in the electron cloud of an atom adds very little to the mas ...
... 83. The number and arrangement of the electrons found in the electron cloud of an atom determines nearly all of an element’s _____________________________ properties. P. 125, VCR: Atoms and Molecules 84. The total number of electrons found in the electron cloud of an atom adds very little to the mas ...
Elements Compounds
... Ionic bond – electron from Na is transferred to Cl, this causes a charge imbalance in each atom. The Na becomes (Na+) and the Cl becomes (Cl-), charged particles or ions. ...
... Ionic bond – electron from Na is transferred to Cl, this causes a charge imbalance in each atom. The Na becomes (Na+) and the Cl becomes (Cl-), charged particles or ions. ...
Atoms, Elements, and Compounds
... If you look at a periodic table, you will notice that the atomic number increases by one whole number at a time. This is because you add one proton at a time for each element. The atomic mass however, increases by amounts greater than one. This difference is due to the neutrons in the nucleus. The v ...
... If you look at a periodic table, you will notice that the atomic number increases by one whole number at a time. This is because you add one proton at a time for each element. The atomic mass however, increases by amounts greater than one. This difference is due to the neutrons in the nucleus. The v ...
atomic number = ZE = Element symbol
... Radioactivity, Decay, Dating, and Other Hazards There is no prelab assignment this week I. Radioactive Isotopes and Nuclear Equations Atoms are composed of three main subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. The total number of ...
... Radioactivity, Decay, Dating, and Other Hazards There is no prelab assignment this week I. Radioactive Isotopes and Nuclear Equations Atoms are composed of three main subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. The total number of ...
IT IS ELEMENTARY - the OLLI at UCI Blog
... “All things are poison and nothing is without poison; only the dose makes a thing not a ...
... “All things are poison and nothing is without poison; only the dose makes a thing not a ...
Chapter 3
... electrons. Protons have a positive charge, neutrons are neutral, and electrons have a negative charge. ▶ Protons and neutrons are present in a dense, positively charged region called the nucleus. Electrons are a relatively large distance away from the nucleus. ▶The number of protons an element conta ...
... electrons. Protons have a positive charge, neutrons are neutral, and electrons have a negative charge. ▶ Protons and neutrons are present in a dense, positively charged region called the nucleus. Electrons are a relatively large distance away from the nucleus. ▶The number of protons an element conta ...
Mystery Isotopes
... "Atoms are the smallest unit of matter...but what are the parts of an atom? How are they arranged? Let's draw a Bohr's model of the isotope Oxygen-18." Teacher will model how to a Bohr's diagram model of Oxygen-18. (The 18 of Oxygen-18 represents the mass.) While modeling how to draw a Bohr's diagra ...
... "Atoms are the smallest unit of matter...but what are the parts of an atom? How are they arranged? Let's draw a Bohr's model of the isotope Oxygen-18." Teacher will model how to a Bohr's diagram model of Oxygen-18. (The 18 of Oxygen-18 represents the mass.) While modeling how to draw a Bohr's diagra ...