* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 3: Chemistry. Introduction to Atoms. Atomic mass
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
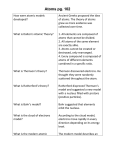
Bell Ringer THINK BACK TO LAST CLASS & The History of the Atom! WITHOUT using your notes match the scientist to the correct statement that describes his work. Ernest Rutherford John Dalton J.J. Thomson Democritus Schrodinger & Heisenberg Niels Bohr 1. _______________________________ proposed that all matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms (from the word that means "indivisible.") 2. _______________________________ suggested that electrons travel in well-defined paths. 3. _______________________________ discovered that atoms have electrons and thought that they were embedded in positively charged material. 4. _______________________________ proposed that matter is composed of atoms and the atoms of an element are identical. His Atomic Theory suggested that atoms can be thought of as being much like a small uniformly solid ball. 5. _______________________________ concluded that there is a small, dense, positively charged nucleus. 6. ______________________________ proposed that electrons travel in electron clouds. Unit 3: Chemistry. Introduction to Atoms. How big is an atom? On average the diameter is 0.00000003 cm! Unit 3: Chemistry. Introduction to Atoms. LET’S WATCH THE TED ED VIDEO! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yQP4UJhNn0I Unit 3: Chemistry. Introduction to Atoms. What is inside an atom? Electrons: are negatively charged particles found in electron clouds outside the nucleus. Protons: are positively charged particles in the nucleus if the atom. Neutrons: are particles in the nucleus of an atom that have no charge. The Nucleus: is the small, dense, positively charged center of the atom. It contains most of the atom’s mass. The diameter of the nucleus is 1/100,000 the diameter of the atom. Unit 3: Chemistry. Introduction to Atoms. Atomic mass unit (amu): the SI unit used to express the masses of particles in atoms Proton Neutron Electron Charge: positive Charge: none Charge: negative Mass: 1 amu Mass: 1 amu Mass: almost zero Location: nucleus Location: nucleus Location: electron clouds Unit 3: Chemistry. Introduction to Atoms. Fun Fact: If it were possible to have a nucleus the volume of an average grape, that nucleus would have a mass greater than 9 MILLION TONS! Unit 3: Chemistry. Introduction to Atoms. The atom is neutral when there are equal number protons and electrons. If the number of protons and electrons are not equal, the atoms becomes a charged particle called an ion. Unit 3: Chemistry. Introduction to Atoms. Stop and think… 1)What particles form the nucleus? 2)Explain why atoms are neutral. Unit 3: Chemistry. Introduction to Atoms. Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus. This # determines what type of element it is! Atomic mass: the sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom Unit 3: Chemistry. Introduction to Atoms. Isotopes are atoms that have the same number of protons but have different number of neutrons. Unit 3: Chemistry. Introduction to Atoms. Calculate the number of neutrons for these carbon isotopes!!! _____ neutrons _____ neutrons Atomic Mass -Number of protons Number of neutrons _____ neutrons