Atom - WCHS Physical Science
... • Other levels can hold more electrons but are considered stable with 8 electrons ...
... • Other levels can hold more electrons but are considered stable with 8 electrons ...
Chapter 2 Atoms and Molecules
... vary greatly in appearance over ½ are gases at RT some are solid one (bromine) is a liquid Poor conductors of heat or electricity not ductile or maleable do not have luster Common nonmetals shown in table 2.5 Note that several nonmetal elements have a subscript of 2 This means that the elemental uni ...
... vary greatly in appearance over ½ are gases at RT some are solid one (bromine) is a liquid Poor conductors of heat or electricity not ductile or maleable do not have luster Common nonmetals shown in table 2.5 Note that several nonmetal elements have a subscript of 2 This means that the elemental uni ...
Physical Science – Chapter 4 Study Guide
... Who provided evidence for the existence of a nucleus in an atom? Know and understand the atomic model and the nucleus. Know and understand neutrons, electrons, and protons of the elements. The number of protons in one atom of an element is that element’s what? Know how to find the number of neutrons ...
... Who provided evidence for the existence of a nucleus in an atom? Know and understand the atomic model and the nucleus. Know and understand neutrons, electrons, and protons of the elements. The number of protons in one atom of an element is that element’s what? Know how to find the number of neutrons ...
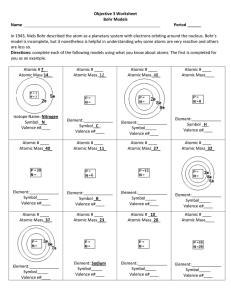
Objective 3 Worksheet Bohr Models Name Period In 1943, Niels
... Objective 3 Worksheet Bohr Models Name ...
... Objective 3 Worksheet Bohr Models Name ...
Atomic Structure Notepacket
... So instead they mass them(weigh them) Qt. What accounts for the mass of the atom? ...
... So instead they mass them(weigh them) Qt. What accounts for the mass of the atom? ...
Build an Atom
... – MAKE SURE THE # OF PROTONS AND # OF ELECTRONS ARE EQUAL Build a -3 ion and copy it into your notebook. ...
... – MAKE SURE THE # OF PROTONS AND # OF ELECTRONS ARE EQUAL Build a -3 ion and copy it into your notebook. ...
Build an Atom
... – MAKE SURE THE # OF PROTONS AND # OF ELECTRONS ARE EQUAL Build a -3 ion and copy it into your notebook. ...
... – MAKE SURE THE # OF PROTONS AND # OF ELECTRONS ARE EQUAL Build a -3 ion and copy it into your notebook. ...
CP Chemistry Final Exam Review Sheet
... 58. a) An atom with 7 valence electrons would most likely be in what state/phase of matter? solid/liquid/gas b) An atom with 2 valence electrons would most likely be in what state/phase of matter? solid c) An atom with 8 valence electrons would most likely be in what state/phase of matter? gas 59. W ...
... 58. a) An atom with 7 valence electrons would most likely be in what state/phase of matter? solid/liquid/gas b) An atom with 2 valence electrons would most likely be in what state/phase of matter? solid c) An atom with 8 valence electrons would most likely be in what state/phase of matter? gas 59. W ...
File - Science with Mr Thompson
... 6. Number of electrons = number of protons because an atom is always neutral! 7. Neutrons: Carry a neutral charge. Make atoms stable (or not). 8. Atomic number: The number of protons in the nucleus of the atom, which determines its chemical properties and its position in periodic table. Examples: Ox ...
... 6. Number of electrons = number of protons because an atom is always neutral! 7. Neutrons: Carry a neutral charge. Make atoms stable (or not). 8. Atomic number: The number of protons in the nucleus of the atom, which determines its chemical properties and its position in periodic table. Examples: Ox ...
Adventures in Chemistry Julie T. Millard, Colby College
... Electrons in the highest occupied energy level are the greatest stable distance from the nucleus. These outermost electrons are known as valence electrons. Shell is a principal energy level defined by a given value of n, where n can be 1,2,3,4 etc… and is capable of holding 2n2 electrons. An orbital ...
... Electrons in the highest occupied energy level are the greatest stable distance from the nucleus. These outermost electrons are known as valence electrons. Shell is a principal energy level defined by a given value of n, where n can be 1,2,3,4 etc… and is capable of holding 2n2 electrons. An orbital ...
Atomic structure packets
... a. Who was responsible for the concept of atoms? b. What does the word “atom” mean? c. What is the word origin for “atom?” ...
... a. Who was responsible for the concept of atoms? b. What does the word “atom” mean? c. What is the word origin for “atom?” ...
Study Guide Answer Key
... 2. Consider an element Z that has two naturally occurring isotopes with the following percent abundances: the isotope with a mass number of 19.0 is 55.0% abundant; the isotope with a mass number of 21.0 is 45.0% abundant. What is the average atomic mass for element Z? [(mass A) (%A)] + [(mass B) (%B ...
... 2. Consider an element Z that has two naturally occurring isotopes with the following percent abundances: the isotope with a mass number of 19.0 is 55.0% abundant; the isotope with a mass number of 21.0 is 45.0% abundant. What is the average atomic mass for element Z? [(mass A) (%A)] + [(mass B) (%B ...
Atomic Structure and Types of Atoms
... is the sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. The most common isotope of carbon has a mass number of 12 (6 protons + 6 neutrons) and may be written as “carbon-12.” Two other isotopes are carbon-13 and carbon-14. As shown in Figure 3, a symbol with the mass number above and the at ...
... is the sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. The most common isotope of carbon has a mass number of 12 (6 protons + 6 neutrons) and may be written as “carbon-12.” Two other isotopes are carbon-13 and carbon-14. As shown in Figure 3, a symbol with the mass number above and the at ...
The Structure of the Atom
... •His experimental results revealed something different. Most alpha particles paths were not affected by any charge when in contact with gold foil. (Red straight lines on left diagram). Just a few deflected back at large angles. Knew it had to be of the same charge, because repelled. ...
... •His experimental results revealed something different. Most alpha particles paths were not affected by any charge when in contact with gold foil. (Red straight lines on left diagram). Just a few deflected back at large angles. Knew it had to be of the same charge, because repelled. ...
Lesson 5: Current Atomic Model
... During the 1930’s protons and neutrons discovered. Charges are the same magnitude but opposite sign for protons and electrons, neutrons have no charge. ...
... During the 1930’s protons and neutrons discovered. Charges are the same magnitude but opposite sign for protons and electrons, neutrons have no charge. ...
Naming Compounds
... a change in matter in which NEW substances are produced with NEW properties. Clues that May Indicate a Chemical Change ...
... a change in matter in which NEW substances are produced with NEW properties. Clues that May Indicate a Chemical Change ...
Test! - Cobb Learning
... or the same atomic number, but having different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus, or different atomic weights. What is an ion? An ion (/ˈaɪən, -ɒn/) is an atom or a molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving the atom or molecule a net positi ...
... or the same atomic number, but having different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus, or different atomic weights. What is an ion? An ion (/ˈaɪən, -ɒn/) is an atom or a molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving the atom or molecule a net positi ...
Elements Combine to Form Compounds
... a change in matter in which NEW substances are produced with NEW properties. Clues that May Indicate a Chemical Change ...
... a change in matter in which NEW substances are produced with NEW properties. Clues that May Indicate a Chemical Change ...
Chemistry 1 Revision: Metals and their uses
... Complete the following using the periodic table to help: H2O: ........... atoms of h.......................... .......... atoms of o....................... ...
... Complete the following using the periodic table to help: H2O: ........... atoms of h.......................... .......... atoms of o....................... ...
по темі “Atoms and Molecules. The Periodic Table”
... 4. Mendeleev found he could arrange the elements in a grid so that each element had a lower atomic weight than the one on its left. 5. Adams and Le Verrier could be said to have discovered germanium, gallium and scandium on paper. 6. A group is a horizontal row in the periodic table. 7. There is a p ...
... 4. Mendeleev found he could arrange the elements in a grid so that each element had a lower atomic weight than the one on its left. 5. Adams and Le Verrier could be said to have discovered germanium, gallium and scandium on paper. 6. A group is a horizontal row in the periodic table. 7. There is a p ...
chapter 3 pp - Bridgewater
... I. Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms. II. All atoms of a given element are identical. III. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. IV. Atoms are indestructible. ...
... I. Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms. II. All atoms of a given element are identical. III. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. IV. Atoms are indestructible. ...
Elements, Atoms, Ions PPT
... I. Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms. II. All atoms of a given element are identical. III. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. IV. Atoms are indestructible. ...
... I. Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms. II. All atoms of a given element are identical. III. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. IV. Atoms are indestructible. ...
Intro to the Periodic Table
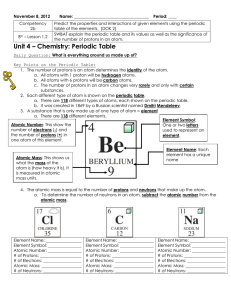
... c. How many protons are in one atom of this element? __________________ d. How many electrons are in one atom of this element? __________________ e. What is the atomic mass of this element? ______________________ f. How many neutrons are in one atom of this element? __________________ 8. Find the el ...
... c. How many protons are in one atom of this element? __________________ d. How many electrons are in one atom of this element? __________________ e. What is the atomic mass of this element? ______________________ f. How many neutrons are in one atom of this element? __________________ 8. Find the el ...
atoms - schultz915
... a. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. b. Some but not all elements are composed of atoms. c. Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of protons. d. Atoms are divisible. ...
... a. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. b. Some but not all elements are composed of atoms. c. Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of protons. d. Atoms are divisible. ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.