atoms - schultz915
... a. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. b. Some but not all elements are composed of atoms. c. Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of protons. d. Atoms are divisible. ...
... a. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. b. Some but not all elements are composed of atoms. c. Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of protons. d. Atoms are divisible. ...
Structure of the Atom
... Aristotle (384-322 BC)- rejected Democritus’ view and that atoms existed -since Democritus could not prove his theory, Aristotle’s view become widely known John Dalton (1803)-revised Democritus’ view based on scientific research ...
... Aristotle (384-322 BC)- rejected Democritus’ view and that atoms existed -since Democritus could not prove his theory, Aristotle’s view become widely known John Dalton (1803)-revised Democritus’ view based on scientific research ...
The Atom - dsapresents.org
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole numbe ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole numbe ...
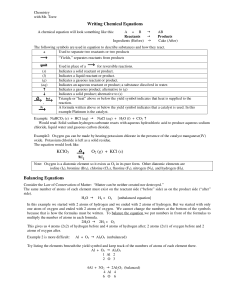
Writing Chemical Equations KClO3 O2 (g) + KCl (s) Balancing
... chloride, liquid water and gaseous carbon dioxide. Example2: Oxygen gas can be made by heating potassium chlorate in the presence of the catalyst manganese(IV) oxide. Potassium chloride is left as a solid residue. The equation would look like: ...
... chloride, liquid water and gaseous carbon dioxide. Example2: Oxygen gas can be made by heating potassium chlorate in the presence of the catalyst manganese(IV) oxide. Potassium chloride is left as a solid residue. The equation would look like: ...
Unit 4 PowerPoint
... differ in the number of neutrons. Scientists did not at this time know about isotopes. – In point #5, atoms are not indivisible. Atoms are made of even smaller particles (protons, neutrons, electrons). Atoms can be broken down, but only in a nuclear reaction, which Dalton was unfamiliar with. ...
... differ in the number of neutrons. Scientists did not at this time know about isotopes. – In point #5, atoms are not indivisible. Atoms are made of even smaller particles (protons, neutrons, electrons). Atoms can be broken down, but only in a nuclear reaction, which Dalton was unfamiliar with. ...
All you need to know about Additional Science
... • Calculate the approximate radius of its nucleus (in nm), given that it will be about one ten thousandth the radius of the boron atom. Give your answer in standard form. ...
... • Calculate the approximate radius of its nucleus (in nm), given that it will be about one ten thousandth the radius of the boron atom. Give your answer in standard form. ...
atoms
... have about the same number of protons and neutrons. Some nuclei are unstable because they have too many or too few neutrons. This is especially true for heavier elements such as uranium and plutonium. • The release of nuclear particles and energy is called radioactive decay. • In these nuclei, repul ...
... have about the same number of protons and neutrons. Some nuclei are unstable because they have too many or too few neutrons. This is especially true for heavier elements such as uranium and plutonium. • The release of nuclear particles and energy is called radioactive decay. • In these nuclei, repul ...
THE ATOM: THE BASIC BUILDING BLOCK OF MATTER 12
... Various models of how atoms are structured have developed over time. Greeks used the word “atom” which means indivisible. Note the work of Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr and Chadwick. Current understanding is that atoms are made up of a positively charged nucleus in the centre surrounded by negat ...
... Various models of how atoms are structured have developed over time. Greeks used the word “atom” which means indivisible. Note the work of Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr and Chadwick. Current understanding is that atoms are made up of a positively charged nucleus in the centre surrounded by negat ...
Science Class 9 Notes – Atoms and Molecules
... 2. Law of constant proportions (or constant com-position) : This law was first stated by Proust in 1797. According to the law “a chemical compound is always found to be made up of the same elements combined together in the same proportions by weight” e.g. the ratio of hydrogen and oxygen in pure wat ...
... 2. Law of constant proportions (or constant com-position) : This law was first stated by Proust in 1797. According to the law “a chemical compound is always found to be made up of the same elements combined together in the same proportions by weight” e.g. the ratio of hydrogen and oxygen in pure wat ...
1.2 Atomic Structure
... • Atoms must have equal numbers of protons and electrons. In our example, an atom of krypton must contain 36 electrons since it contains 36 protons. ...
... • Atoms must have equal numbers of protons and electrons. In our example, an atom of krypton must contain 36 electrons since it contains 36 protons. ...
Unit 7: Chemical Equations & Reactions
... 1. Identify the most complex substance. 2. Beginning with that substance, choose an element that appears in only one reactant and one product. • Adjust the coefficients to obtain the same number of atoms of this element on both sides. • Balance polyatomic ions as a unit (if possible). • Re-write H2 ...
... 1. Identify the most complex substance. 2. Beginning with that substance, choose an element that appears in only one reactant and one product. • Adjust the coefficients to obtain the same number of atoms of this element on both sides. • Balance polyatomic ions as a unit (if possible). • Re-write H2 ...
Defining the Atom Guided Reading WS
... Early Models of the Atom The scientific study of the atom began with John Dalton in the early 1800s. The ancient Greek Democritus first proposed that matter is made up of small, indivisible particles that he called atoms. John Dalton made the first accepted theory on atoms almost 2000 years after th ...
... Early Models of the Atom The scientific study of the atom began with John Dalton in the early 1800s. The ancient Greek Democritus first proposed that matter is made up of small, indivisible particles that he called atoms. John Dalton made the first accepted theory on atoms almost 2000 years after th ...
History of Atomic Theories (No Videos)
... b. Electron cloud- region where you have a 90% chance of finding an electron ...
... b. Electron cloud- region where you have a 90% chance of finding an electron ...
Parts Of An Atom
... Substances that contain only one kind of atom are called elements. Some familiar elements are oxygen, gold, silver, and helium. An atom is the smallest part of an element that can be broken down and still have the characteristics of that element. All atoms are basically the same. All atoms of the sa ...
... Substances that contain only one kind of atom are called elements. Some familiar elements are oxygen, gold, silver, and helium. An atom is the smallest part of an element that can be broken down and still have the characteristics of that element. All atoms are basically the same. All atoms of the sa ...
Subatomic Particles
... • We can find the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons of an isotope as we would with a standard atom. – Just have to note the mass and that mass change is due to neutrons ...
... • We can find the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons of an isotope as we would with a standard atom. – Just have to note the mass and that mass change is due to neutrons ...
Yr11 Chemistry Title Page:TourismContents
... Since each isotope has the same number of electrons (8) and since the electrons around the nucleus determine the chemical properties it can be seen that each isotope of oxygen has the same chemical properties. Since each isotope has a different number of neutrons they have slightly differing masses ...
... Since each isotope has the same number of electrons (8) and since the electrons around the nucleus determine the chemical properties it can be seen that each isotope of oxygen has the same chemical properties. Since each isotope has a different number of neutrons they have slightly differing masses ...
Chapter 1 Chemistry: The Study of Matter
... hydrogen and oxygen), methane (made of carbon and hydrogen) and sugar (made from carbon, hydrogen and oxygen). H2O, CH4 and CxHxOx ...
... hydrogen and oxygen), methane (made of carbon and hydrogen) and sugar (made from carbon, hydrogen and oxygen). H2O, CH4 and CxHxOx ...
The Development of Atomic Theory
... substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by physical or chemical means ...
... substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by physical or chemical means ...
Dalton introduced a theory that proposed that elements
... Proust had studied tin oxides and found that their masses were either 88.1% tin and 11.9% oxygen or 78.7% tin and 21.3% oxygen (these were tin(II) oxide and tin dioxide respectively). Dalton noted from these percentages that 100g of tin will combine either with 13.5g or 27g of oxygen; 13.5 and 27 fo ...
... Proust had studied tin oxides and found that their masses were either 88.1% tin and 11.9% oxygen or 78.7% tin and 21.3% oxygen (these were tin(II) oxide and tin dioxide respectively). Dalton noted from these percentages that 100g of tin will combine either with 13.5g or 27g of oxygen; 13.5 and 27 fo ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... – A carbon atom has 6 protons in its nucleus – A neutral carbon atom has 6 electrons • A carbon atom also contains neutrons, but unlike electrons and protons the number of neutrons can change from carbon atom to carbon atom • Some carbon atoms have 6 neutrons, others have 7 neutrons and still others ...
... – A carbon atom has 6 protons in its nucleus – A neutral carbon atom has 6 electrons • A carbon atom also contains neutrons, but unlike electrons and protons the number of neutrons can change from carbon atom to carbon atom • Some carbon atoms have 6 neutrons, others have 7 neutrons and still others ...
History leading to the creation of the atomic bomb
... History leading to the creation of the atomic bomb Atomic science began many centuries ago with experimenting and probing into the nature and structure of matter. This began with ancient philosophers and alchemists. Science began emerging with Thales of Miletus (634-546 BC), the Ionian Greek, who de ...
... History leading to the creation of the atomic bomb Atomic science began many centuries ago with experimenting and probing into the nature and structure of matter. This began with ancient philosophers and alchemists. Science began emerging with Thales of Miletus (634-546 BC), the Ionian Greek, who de ...
atoms
... have about the same number of protons and neutrons. Some nuclei are unstable because they have too many or too few neutrons. This is especially true for heavier elements such as uranium and plutonium. • The release of nuclear particles and energy is called radioactive decay. • In these nuclei, repul ...
... have about the same number of protons and neutrons. Some nuclei are unstable because they have too many or too few neutrons. This is especially true for heavier elements such as uranium and plutonium. • The release of nuclear particles and energy is called radioactive decay. • In these nuclei, repul ...
CHAPTER 2 - HCC Learning Web
... • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions • A compound is a substance consisting of two or more elements in a fixed ratio • A compound has characteristics different from those of its elements ...
... • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions • A compound is a substance consisting of two or more elements in a fixed ratio • A compound has characteristics different from those of its elements ...
Academic Chemistry Chapter 3 Review Activity
... List the three subatomic particles, their symbols, charges and explain where they are located at in the structure of the atom. Proton, p+1, +1 charge, located in the nucleus Neutron, n0, no charge, located in the nucleus Electron, e-1, -1 charge, located in energy levels surrounding the nucleus ...
... List the three subatomic particles, their symbols, charges and explain where they are located at in the structure of the atom. Proton, p+1, +1 charge, located in the nucleus Neutron, n0, no charge, located in the nucleus Electron, e-1, -1 charge, located in energy levels surrounding the nucleus ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.