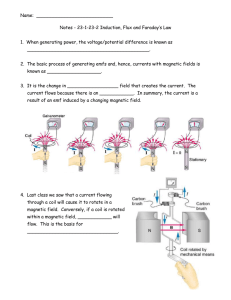
Name: Notes - 23-1-23-2 Induction, Flux and Faraday`s Law 1. When
... Name: ___________________________ Notes - 23-1-23-2 Induction, Flux and Faraday’s Law 1. When generating power, the voltage/potential difference is known as ___________________________________________. 2. The basic process of generating emfs and, hence, currents with magnetic fields is known as ____ ...
... Name: ___________________________ Notes - 23-1-23-2 Induction, Flux and Faraday’s Law 1. When generating power, the voltage/potential difference is known as ___________________________________________. 2. The basic process of generating emfs and, hence, currents with magnetic fields is known as ____ ...
W13.02 Conceptual Questions
... other. You have no other metal objects. Can you determine if both of the cylinders are magnets, or if one of them is a magnet and the other just a piece of iron? If so, how? If not, why not? 2. A current-carrying rectangular loop of wire is placed in a magnetic field with the direction of the curren ...
... other. You have no other metal objects. Can you determine if both of the cylinders are magnets, or if one of them is a magnet and the other just a piece of iron? If so, how? If not, why not? 2. A current-carrying rectangular loop of wire is placed in a magnetic field with the direction of the curren ...
VOICE OVER FOR TLM for Project 5 - Class CBSE
... CBSE;Class XII;Physics;Moving Charges and Magnetism;Biot - Savarts Law ...
... CBSE;Class XII;Physics;Moving Charges and Magnetism;Biot - Savarts Law ...
Magnetism Word List
... An object that attracts magnetic materials and attracts and repels other magnets Magnetic material A material that is attracted to a magnet Iron A magnetic element Cobalt A magnetic element Nickel A magnetic element Steel A material containing iron, which causes it to be a magnetic material Magnetis ...
... An object that attracts magnetic materials and attracts and repels other magnets Magnetic material A material that is attracted to a magnet Iron A magnetic element Cobalt A magnetic element Nickel A magnetic element Steel A material containing iron, which causes it to be a magnetic material Magnetis ...
Fun Facts about Earth`s Magnetism caused by the Dynamo Effect
... moves from the Earth’s spin axis. The magnetic North Pole keeps moving. Right now, the magnetic North Pole is very close to the Earth’s axis. One hundred years ago, it was in Arctic Canada. The magnetic South Pole also moves. The magnetosphere is the magnetic force that extends into space. This forc ...
... moves from the Earth’s spin axis. The magnetic North Pole keeps moving. Right now, the magnetic North Pole is very close to the Earth’s axis. One hundred years ago, it was in Arctic Canada. The magnetic South Pole also moves. The magnetosphere is the magnetic force that extends into space. This forc ...
paleomagnetism lab procedure
... *Have one of your group members see me to trade a shoe for a compass. 1. Draw a sketch of the model. It should have SIX (6) ridges and a central zone. 2. Place the compass in the middle on top of each of the six ridges so that N on the compass is toward the N side of the model (if you are not gettin ...
... *Have one of your group members see me to trade a shoe for a compass. 1. Draw a sketch of the model. It should have SIX (6) ridges and a central zone. 2. Place the compass in the middle on top of each of the six ridges so that N on the compass is toward the N side of the model (if you are not gettin ...
Magnets exert forces Magnets have two poles
... 6.3.1: State that moving charges give rise to magnetic fields. 6.3.2: Draw magnetic field patterns due to currents. 6.3.5: Define the magnitude and direction of a magnetic field. ...
... 6.3.1: State that moving charges give rise to magnetic fields. 6.3.2: Draw magnetic field patterns due to currents. 6.3.5: Define the magnitude and direction of a magnetic field. ...
Magnetic Materials
... The response of a material to a Magnetic Field H is called Magnetic Induction B The relationship between B and H is a property of the material In some materials and in free space B is a linear function of H but in general it is much more complicated and sometimes it is not even single valued ...
... The response of a material to a Magnetic Field H is called Magnetic Induction B The relationship between B and H is a property of the material In some materials and in free space B is a linear function of H but in general it is much more complicated and sometimes it is not even single valued ...
The mysteries of the Earth`s magnetic field and sunspots
... Professor Annraoi de Paor stumbled into this field in mid-1998, solving a mathematical problem posted on the Internet by Raymond Hide, Emeritus Professor of Geophysics at Oxford, ostensibly to do with proving absence of chaos in the dynamics of a particular self-excited dynamo driving a series-wound ...
... Professor Annraoi de Paor stumbled into this field in mid-1998, solving a mathematical problem posted on the Internet by Raymond Hide, Emeritus Professor of Geophysics at Oxford, ostensibly to do with proving absence of chaos in the dynamics of a particular self-excited dynamo driving a series-wound ...
Magnetism Conceptual Questions
... How are the magnetic and electric forces similar? How are they different. 2. electricity has positive and negative charges. What does a magnet have and how are they similar/different than electric charges? ...
... How are the magnetic and electric forces similar? How are they different. 2. electricity has positive and negative charges. What does a magnet have and how are they similar/different than electric charges? ...
bar magnets - jfindlay.ca
... Purpose: To see the effects of magnetic fields produced by magnets. ...
... Purpose: To see the effects of magnetic fields produced by magnets. ...
PHY-ZS-004 Electromagnetic Induction
... the same direction. Later, stones of magnetite called “lodestones” were used in navigation. ...
... the same direction. Later, stones of magnetite called “lodestones” were used in navigation. ...
Magnetic field pattern data analysis activity
... Students use magnetic field data and a map of the ocean floor around Iceland to observe how the direction of magnetisation of the ocean floor varies. This links the magnetization of rocks with the theory of tectonic plates. Students tackle the worksheet Magnetic patterns: ocean floor pattern plottin ...
... Students use magnetic field data and a map of the ocean floor around Iceland to observe how the direction of magnetisation of the ocean floor varies. This links the magnetization of rocks with the theory of tectonic plates. Students tackle the worksheet Magnetic patterns: ocean floor pattern plottin ...
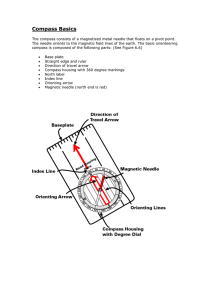
Compass Basics - NSW Public Schools
... True North: (also known as Geographic North or Map North - marked as H on a topographic map - see Figure 6.8) is the geographic north pole where all longitude lines meet. All maps are laid out with true north directly at the top. Unfortunately for the wilderness traveler, true north is not at the sa ...
... True North: (also known as Geographic North or Map North - marked as H on a topographic map - see Figure 6.8) is the geographic north pole where all longitude lines meet. All maps are laid out with true north directly at the top. Unfortunately for the wilderness traveler, true north is not at the sa ...
Edward Sabine

General Sir Edward Sabine KCB FRS (14 October 1788 – 26 June 1883) was an Irish astronomer, geophysicist, ornithologist,explorer, soldier and the 30th President of the Royal Society.Two branches of Sabine's work are notable: Determination of the length of the seconds pendulum, a simple pendulum whose time period on the surface of the Earth is two seconds, that is, one second in each direction; and his research on the Earth's magnetic field. He led the effort to establish a system of magnetic observatories in various parts of British territory all over the globe, and much of his life was devoted to their direction, and to analyzing their observations.While most of his research bears on the subjects just mentioned, other research deals with the birds of Greenland (Sabine's gull is named for him), ocean temperatures, the Gulf Stream, barometric measurement of heights, arc of the meridian, glacial transport of rocks, the volcanoes of the Hawaiian Islands, and various points of meteorology.