Anticipation Guide: Electricity from Magnetism
... Before Reading: In the space to the left of each statement, place a check mark () if you agree or think the statement is true or an (X) if you disagree or think the statement is false. During or After Reading: Add new check marks or cross-through the X’s for which you have changed your mind. Keep i ...
... Before Reading: In the space to the left of each statement, place a check mark () if you agree or think the statement is true or an (X) if you disagree or think the statement is false. During or After Reading: Add new check marks or cross-through the X’s for which you have changed your mind. Keep i ...
Magnetism - Miss Toole
... made of cobalt, iron or nickel can be magnetized by lining up its domains. ...
... made of cobalt, iron or nickel can be magnetized by lining up its domains. ...
docx: Geo Magnetic Journal
... 2. Draw and describe the following: When two magnets have the same poles (north/north or south/south) toward each other what happens? Why? (label: poles and magnetic field) ...
... 2. Draw and describe the following: When two magnets have the same poles (north/north or south/south) toward each other what happens? Why? (label: poles and magnetic field) ...
2.1.4 magnetic fields
... (North and & South). More correctly they should be referred to as the “North seeking pole” and “South seeking pole” Like poles repel each other Unlike poles attract each other ...
... (North and & South). More correctly they should be referred to as the “North seeking pole” and “South seeking pole” Like poles repel each other Unlike poles attract each other ...
File - Lanier Bureau of Investigation
... 1. Compass – b) a magnetic navigational device that points toward magnetic north 2. Electromagnet – e) a magnet made from electricity 3. Magnetic field – c) the area in which magnets will feel magnetic force. More arrows show a stronger one. 4. Core – a) the center of an electromagnet 5. Iron – d) ...
... 1. Compass – b) a magnetic navigational device that points toward magnetic north 2. Electromagnet – e) a magnet made from electricity 3. Magnetic field – c) the area in which magnets will feel magnetic force. More arrows show a stronger one. 4. Core – a) the center of an electromagnet 5. Iron – d) ...
It must have domains (north and south poles) The
... Inside the Earth’s surface there is a huge amount of ferromagnetic liquids. These liquids are constantly in motion around a solid iron core and produce a massive magnetic field which can be felt anywhere around the ...
... Inside the Earth’s surface there is a huge amount of ferromagnetic liquids. These liquids are constantly in motion around a solid iron core and produce a massive magnetic field which can be felt anywhere around the ...
Modelling of the magnetic field By M. Kruglanski The Earth`s
... The Earth's magnetic field results from the superposition of the internal field, the crustal field and a magnetospheric field. The internal magnetic field originates in the magmatic flows inside the terrestrial core. It is generally modeled by a spherical harmonics expansion, the first term of which ...
... The Earth's magnetic field results from the superposition of the internal field, the crustal field and a magnetospheric field. The internal magnetic field originates in the magmatic flows inside the terrestrial core. It is generally modeled by a spherical harmonics expansion, the first term of which ...
Open PhD and Post-Doc Positions on permanent magnet
... Open PhD and Post-Doc Positions on permanent magnet research We are looking for some more excellent and highly motivated candidates who aspire to work in a challenging and international research environment. You should possess a degree in Physics, Materials Science, Inorganic Chemistry or Mechanical ...
... Open PhD and Post-Doc Positions on permanent magnet research We are looking for some more excellent and highly motivated candidates who aspire to work in a challenging and international research environment. You should possess a degree in Physics, Materials Science, Inorganic Chemistry or Mechanical ...
t=0
... When a charged particle has velocity components both perpendicular and parallel to a uniform magnetic field, the particle moves in a helical path. The magnetic field does no work on the particle, so its speed and kinetic energy remain constant. ...
... When a charged particle has velocity components both perpendicular and parallel to a uniform magnetic field, the particle moves in a helical path. The magnetic field does no work on the particle, so its speed and kinetic energy remain constant. ...
Plate Tectonics - University of Hawaii at Hilo
... What causes the magnetic field of the earth? How is paleomagnetism useful for determining age of rocks. Magnetic field reversals. What is magnetic inclination? What are the main types of crust-What are the main differences between them? Plate boundary types For each main type, know the types of asso ...
... What causes the magnetic field of the earth? How is paleomagnetism useful for determining age of rocks. Magnetic field reversals. What is magnetic inclination? What are the main types of crust-What are the main differences between them? Plate boundary types For each main type, know the types of asso ...
Magnetism Summary - Don`t Trust Atoms
... The magnetic force becomes weaker the farther away you are from the magnet. The magnetic force is strongest at the poles. Magnetic materials can be magnetised to make temporary magnets by slowing stroking a magnets pole against a magnetic material in the same direction many times. The magnetic field ...
... The magnetic force becomes weaker the farther away you are from the magnet. The magnetic force is strongest at the poles. Magnetic materials can be magnetised to make temporary magnets by slowing stroking a magnets pole against a magnetic material in the same direction many times. The magnetic field ...
Earth`s Magnetic Field
... The magnetic field protects us by channeling super-fast, high energy charged particles from the Sun away from the Earth. They flow around the field This causes electrons to flow along the field lines to the poles where they rain down energizing the molecules of the atmosphere making them glow … The ...
... The magnetic field protects us by channeling super-fast, high energy charged particles from the Sun away from the Earth. They flow around the field This causes electrons to flow along the field lines to the poles where they rain down energizing the molecules of the atmosphere making them glow … The ...
Magnetism Webquest - Mrs. Blevins` Science
... http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2004/09/0909_040909_earthmagfield.html 1) How long have scientists been recording the strength of the Earth’s magnetic field? 2) What is happening to the Earth’s field right now? ...
... http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2004/09/0909_040909_earthmagfield.html 1) How long have scientists been recording the strength of the Earth’s magnetic field? 2) What is happening to the Earth’s field right now? ...
Slide 1
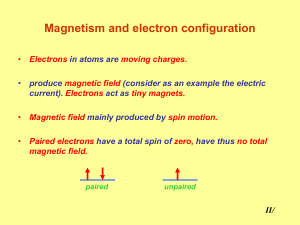
... Usually, opposite direction spinning electrons pair up, and cancel the magnetic field. ...
... Usually, opposite direction spinning electrons pair up, and cancel the magnetic field. ...
18-1 Magnetism - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... Magnetism 18-1 Fill-In Notes (Use pages 518-523 to fill-in the notes below.) 1. Magnets attract objects that contain ___________________________________. 2. All magnets have two ends. What are these ends called? ______________________ ________________________________________________________________ ...
... Magnetism 18-1 Fill-In Notes (Use pages 518-523 to fill-in the notes below.) 1. Magnets attract objects that contain ___________________________________. 2. All magnets have two ends. What are these ends called? ______________________ ________________________________________________________________ ...
Magnetic Fields and Electromagnetic Induction --
... 20. Indicate graphically the direction of B generated by the two currents, respectively, and the direction of the magnetic forces exerted on the currents. ...
... 20. Indicate graphically the direction of B generated by the two currents, respectively, and the direction of the magnetic forces exerted on the currents. ...
Edward Sabine

General Sir Edward Sabine KCB FRS (14 October 1788 – 26 June 1883) was an Irish astronomer, geophysicist, ornithologist,explorer, soldier and the 30th President of the Royal Society.Two branches of Sabine's work are notable: Determination of the length of the seconds pendulum, a simple pendulum whose time period on the surface of the Earth is two seconds, that is, one second in each direction; and his research on the Earth's magnetic field. He led the effort to establish a system of magnetic observatories in various parts of British territory all over the globe, and much of his life was devoted to their direction, and to analyzing their observations.While most of his research bears on the subjects just mentioned, other research deals with the birds of Greenland (Sabine's gull is named for him), ocean temperatures, the Gulf Stream, barometric measurement of heights, arc of the meridian, glacial transport of rocks, the volcanoes of the Hawaiian Islands, and various points of meteorology.