The Chain of Infection
... mode of transmission. Every form of direct and indirect human contact provides an opportunity for disease-producing organisms to be transmitted. Contact Transmission: Contact transmission is the most common route of transmission of organisms in health care settings. It may be direct (e.g contaminate ...
... mode of transmission. Every form of direct and indirect human contact provides an opportunity for disease-producing organisms to be transmitted. Contact Transmission: Contact transmission is the most common route of transmission of organisms in health care settings. It may be direct (e.g contaminate ...
Helminths (Parasitic worms) Monogeneans
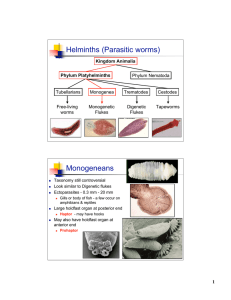
... Pathology: Generally very little. Attachment sites can ulcerate, and worms may obstruct small intestines and interfere with food absorption. Absorption of worm waste results in verminous intoxication similar to tapeworms. Symptoms: Depends on the number of worms (worm burden). Can include ...
... Pathology: Generally very little. Attachment sites can ulcerate, and worms may obstruct small intestines and interfere with food absorption. Absorption of worm waste results in verminous intoxication similar to tapeworms. Symptoms: Depends on the number of worms (worm burden). Can include ...
Americares Medical Outreach Health Worker Safety Pre and Post
... 3) In 2000, the WHO estimated that _______ % of the 16 billion injections given were done with re-used equipment.* _________________________________________________ 4) Unsafe management of sharps waste includes:* True ...
... 3) In 2000, the WHO estimated that _______ % of the 16 billion injections given were done with re-used equipment.* _________________________________________________ 4) Unsafe management of sharps waste includes:* True ...
260
... • Communicable disease: A disease that is spread from one host to another • Contagious disease: A disease that is easily spread from one host to another • Noncommunicable disease: A disease that is not transmitted from one host to another – SUCH AS?? ...
... • Communicable disease: A disease that is spread from one host to another • Contagious disease: A disease that is easily spread from one host to another • Noncommunicable disease: A disease that is not transmitted from one host to another – SUCH AS?? ...
PDF
... Furthermore, when there is complex migration of the pathogen within the host, rather than a linear infection “pathway,” direct counting of individual infectious agents may not be feasible. An alternative way to measure bottleneck sizes makes use of the stochastic changes in the genetic composition ...
... Furthermore, when there is complex migration of the pathogen within the host, rather than a linear infection “pathway,” direct counting of individual infectious agents may not be feasible. An alternative way to measure bottleneck sizes makes use of the stochastic changes in the genetic composition ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... When a person has a disease, his or her normal body functions are disrupted. Some diseases, such as diabetes and most cancers, are not spread from one person to another. But other diseases, such as the flu and strep throat, can be spread. These diseases are known as infectious diseases. Infectious d ...
... When a person has a disease, his or her normal body functions are disrupted. Some diseases, such as diabetes and most cancers, are not spread from one person to another. But other diseases, such as the flu and strep throat, can be spread. These diseases are known as infectious diseases. Infectious d ...
Lecture notes
... Average number of new infections per infected individual, in an otherwise totally susceptible population. ...
... Average number of new infections per infected individual, in an otherwise totally susceptible population. ...
Molluscum Contagiosum
... • Orf is a disease of sheep and goats transmitted to human beings by contact. • It is an occupational disease of sheep handlers. • In humans, the disease occurs as a single papulovesicular lesion with a central ulcer usually on the hand, forearm, or face. ...
... • Orf is a disease of sheep and goats transmitted to human beings by contact. • It is an occupational disease of sheep handlers. • In humans, the disease occurs as a single papulovesicular lesion with a central ulcer usually on the hand, forearm, or face. ...
Evolutionary Control of Infectious Disease: Prospects for
... to reproduce, and thereby contribute more copies of the instructions for that exploitation into future generations. These fitness benefits of exploitation are weighed against the costs. The illness caused by intense levels of exploitation may make the host immobile, host mobility may be necessary fo ...
... to reproduce, and thereby contribute more copies of the instructions for that exploitation into future generations. These fitness benefits of exploitation are weighed against the costs. The illness caused by intense levels of exploitation may make the host immobile, host mobility may be necessary fo ...
Data analysis studies on the HIV infection
... provided insights into the epidemiology and pathogenesis of the virus. Through multiple rounds of selection and escape, host and pathogen genomes are imprinted with signatures of evolutionary changes. Due to its rapid and error-prone replication HIV exhibits fast with-in host evolution which permits ...
... provided insights into the epidemiology and pathogenesis of the virus. Through multiple rounds of selection and escape, host and pathogen genomes are imprinted with signatures of evolutionary changes. Due to its rapid and error-prone replication HIV exhibits fast with-in host evolution which permits ...
Chapter 13
... science to society. This provides a good opportunity to present case studies for students. There are a number of excellent video documentaries that illustrate the epidemiological process. Students can also discuss the criteria for designating diseases as reportable to the CDC. This chapter lends its ...
... science to society. This provides a good opportunity to present case studies for students. There are a number of excellent video documentaries that illustrate the epidemiological process. Students can also discuss the criteria for designating diseases as reportable to the CDC. This chapter lends its ...
sti lab update_ 2015_sk.cdr
... to the identification of infected people. STIs are often asymptomatic or cause non-specific symptoms and are known to increase the infectiousness of HIV. The syndromic management approach misses infections that do not demonstrate clear symptoms. Up to 70% of men and women with gonococcal and/or chla ...
... to the identification of infected people. STIs are often asymptomatic or cause non-specific symptoms and are known to increase the infectiousness of HIV. The syndromic management approach misses infections that do not demonstrate clear symptoms. Up to 70% of men and women with gonococcal and/or chla ...
Disease Spread Simulation Worksheet
... When a person has a disease, his or her normal body functions are disrupted. Some diseases, such as diabetes and most cancers, are not spread from one person to another. But other diseases, such as the flu and strep throat, can be spread. These diseases are known as infectious diseases. Infectious d ...
... When a person has a disease, his or her normal body functions are disrupted. Some diseases, such as diabetes and most cancers, are not spread from one person to another. But other diseases, such as the flu and strep throat, can be spread. These diseases are known as infectious diseases. Infectious d ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... When a person has a disease, his or her normal body functions are disrupted. Some diseases, such as diabetes and most cancers, are not spread from one person to another. But other diseases, such as the flu and strep throat, can be spread. These diseases are known as infectious diseases. Infectious d ...
... When a person has a disease, his or her normal body functions are disrupted. Some diseases, such as diabetes and most cancers, are not spread from one person to another. But other diseases, such as the flu and strep throat, can be spread. These diseases are known as infectious diseases. Infectious d ...
Wild great apes as sentinels and sources of infectious disease
... Consequently, the characterization of microorganisms infecting wildlife in the tropics is central to the development of global health surveillance systems that are capable of identifying putative pathogens before they enter the human population [1,2]. However, where should we start? Technically, it ...
... Consequently, the characterization of microorganisms infecting wildlife in the tropics is central to the development of global health surveillance systems that are capable of identifying putative pathogens before they enter the human population [1,2]. However, where should we start? Technically, it ...
INFECTIOUS DISEASE MODELLING
... SOME QUESTIONS MODELS TRY TO ANSWER • What is current and future scope of epidemic? • Under what conditions does an epidemic take off? • What interventions will reduce transmission and by how much? ...
... SOME QUESTIONS MODELS TRY TO ANSWER • What is current and future scope of epidemic? • Under what conditions does an epidemic take off? • What interventions will reduce transmission and by how much? ...
unit5hbacteriaprotist fungi
... micrometers (um) and nanometers(nm). • A micrometer is equivalent to a millionth of a meter, while a nanometer is a billionth of a meter. • Bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and unicellular algae are normally measured in micrometers, while viruses are commonly measured in nanometers. • A typical bacterium ...
... micrometers (um) and nanometers(nm). • A micrometer is equivalent to a millionth of a meter, while a nanometer is a billionth of a meter. • Bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and unicellular algae are normally measured in micrometers, while viruses are commonly measured in nanometers. • A typical bacterium ...
BAPR 13_4_Oct00 - Baylorhealth.edu
... by degenerative changes in muscle, eye, and central nervous system. Mitochondrial diseases are maternally inherited because most human mitochondria are transmitted only in the cytoplasm of the egg. There is preliminary evidence of limited paternal transmission of mtDNA, and nuclear mitochondrial gen ...
... by degenerative changes in muscle, eye, and central nervous system. Mitochondrial diseases are maternally inherited because most human mitochondria are transmitted only in the cytoplasm of the egg. There is preliminary evidence of limited paternal transmission of mtDNA, and nuclear mitochondrial gen ...
Harmonizing methods for sampling and diagnosing
... Current system provides insufficient level of vigilance ...
... Current system provides insufficient level of vigilance ...
Invasive pathogens threaten amphibian diversity
... Lips et al PloS Biol 2008 Martel et al Science 2014 Van Rooij et al Vet Res 2015 Cunningham et al Vet Rec 2015 Sabino-Pinto et al AR 2015 Picco & Collins Cons Biol 2008 ...
... Lips et al PloS Biol 2008 Martel et al Science 2014 Van Rooij et al Vet Res 2015 Cunningham et al Vet Rec 2015 Sabino-Pinto et al AR 2015 Picco & Collins Cons Biol 2008 ...
INFECTIOUS DISEASE IN SCHOOLS
... Some infections are transmitted when a cut or mucous membranes (linings of various body parts and internal organs) comes in contact with an infected person's blood or other body secretions like saliva, urine, and seminal and cervical fluids. This type of transmission is very rare in school settings. ...
... Some infections are transmitted when a cut or mucous membranes (linings of various body parts and internal organs) comes in contact with an infected person's blood or other body secretions like saliva, urine, and seminal and cervical fluids. This type of transmission is very rare in school settings. ...
Standard Precautions Communicable Diseases
... Any used or contaminated supplies containing blood or body fluids (except sharps) should be placed in a plastic bag, securely fastened and disposed of in the regular school garbage dumpster. ...
... Any used or contaminated supplies containing blood or body fluids (except sharps) should be placed in a plastic bag, securely fastened and disposed of in the regular school garbage dumpster. ...
Chapter 2 * NORMAL FLORA
... *microorganism in perianal area enter the urinary tract (UT) causing infection in internal UT Can prevent infection by: Medical asepsis – personnel and hospital environment should be clean from pathogens Surgical asepsis – instrument used should be sterile and including the surgical room Wha ...
... *microorganism in perianal area enter the urinary tract (UT) causing infection in internal UT Can prevent infection by: Medical asepsis – personnel and hospital environment should be clean from pathogens Surgical asepsis – instrument used should be sterile and including the surgical room Wha ...