PPT
... • The overall range of stellar masses runs from 0.08 times the mass of the Sun to about 150 times the mass of the Sun. • Masses are only known for stars that form binary systems, but about half of all stars are in fact in binary systems! – 0.08 MSun is approximately 80 MJupiter ...
... • The overall range of stellar masses runs from 0.08 times the mass of the Sun to about 150 times the mass of the Sun. • Masses are only known for stars that form binary systems, but about half of all stars are in fact in binary systems! – 0.08 MSun is approximately 80 MJupiter ...
1 - Quia
... 11. An "explosion" on the star that arcs its gases back onto the sun's surface is called a -. (2 points) A. solar flare B. solar prominence C. sunspot D. chromosphere 12. A light-year measures - (2 points) A. brightness B. distance C. radiation D. time 13. The layer of the sun with a red color is th ...
... 11. An "explosion" on the star that arcs its gases back onto the sun's surface is called a -. (2 points) A. solar flare B. solar prominence C. sunspot D. chromosphere 12. A light-year measures - (2 points) A. brightness B. distance C. radiation D. time 13. The layer of the sun with a red color is th ...
Lecture 19 - Stellar Lifecycles
... • Once neutrons are formed the collapse stops, the surrounding gas is heated and explodes off the core. This is a supernova explosion. • The explosion is so energetic that it can outshine the combined light of a galaxy! • Heavy elements are formed in the material blown off the star. These elements a ...
... • Once neutrons are formed the collapse stops, the surrounding gas is heated and explodes off the core. This is a supernova explosion. • The explosion is so energetic that it can outshine the combined light of a galaxy! • Heavy elements are formed in the material blown off the star. These elements a ...
Stellar Explosions
... High Mass Stars can continue to fuse elements in its core right up to iron (after which the fusion reaction is energetically unfavored) As heavier elements are fused, the reactions go faster and the stage is over more quickly 20-solar-mass star will burn carbon for about 10,000 years, but its iron c ...
... High Mass Stars can continue to fuse elements in its core right up to iron (after which the fusion reaction is energetically unfavored) As heavier elements are fused, the reactions go faster and the stage is over more quickly 20-solar-mass star will burn carbon for about 10,000 years, but its iron c ...
Planets beyond the solar system
... the total light from the star. Since the planet is much smaller than the stars, the total light is reduced only by a few percent, even less for Earth-like planets. ...
... the total light from the star. Since the planet is much smaller than the stars, the total light is reduced only by a few percent, even less for Earth-like planets. ...
Star evolution - El Camino College
... What should we observe as a result? CLICKER The light “gets stuck” and pushes the outer layers out. What happens to gas when you _______________? Color of outside? What kind of star do we have? What is the core made of? What is the structure? ...
... What should we observe as a result? CLICKER The light “gets stuck” and pushes the outer layers out. What happens to gas when you _______________? Color of outside? What kind of star do we have? What is the core made of? What is the structure? ...
Scientific Notation Worksheet
... 43. Explain how astronomers can use the inverse square law to determine the Luminosity of a near-by star. Explain how astronomers would get the information they need to calculate Luminosity. ...
... 43. Explain how astronomers can use the inverse square law to determine the Luminosity of a near-by star. Explain how astronomers would get the information they need to calculate Luminosity. ...
Chapter13
... dwarfs are found in the lower left corner of the HertzsprungRussell diagram. The more massive a white dwarf, the smaller it is! ...
... dwarfs are found in the lower left corner of the HertzsprungRussell diagram. The more massive a white dwarf, the smaller it is! ...
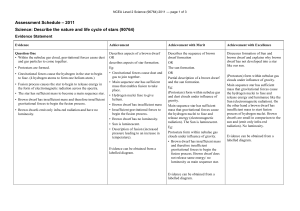
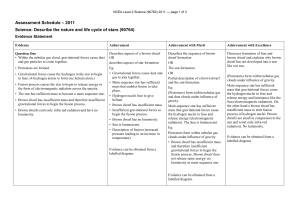
Level 2 Science (90764) 2011 Assessment Schedule
... Explains gas clouds are the birth places for new stars. Supernova gives out clouds of gases and plasma exploding off its surface. AND These gas clouds are the birth places for new stars. AND After this process ceases, a black hole or a dense neutron star remains (detail provided about the formation) ...
... Explains gas clouds are the birth places for new stars. Supernova gives out clouds of gases and plasma exploding off its surface. AND These gas clouds are the birth places for new stars. AND After this process ceases, a black hole or a dense neutron star remains (detail provided about the formation) ...
Foundation 1 - Discovering Astronomy
... When core hydrogen fusion ceases, a main-sequence star becomes a giant • When hydrogen fusion ceases in the core, the star will collapse inward – this causes the layer just outside the core to become so hot and dense that hydrogen fusion will begin in this outer layer. • The energy produced by hydr ...
... When core hydrogen fusion ceases, a main-sequence star becomes a giant • When hydrogen fusion ceases in the core, the star will collapse inward – this causes the layer just outside the core to become so hot and dense that hydrogen fusion will begin in this outer layer. • The energy produced by hydr ...
18. Formation of Stars.
... Gravity and energy are the keys to understanding star formation & evolution. ◦ Gravity is constantly trying to pull matter toward the center of mass of a gas cloud or a star. ◦ Since stars do not have an infinite supply of energy, they must readjust their structure in response to the energy supply ...
... Gravity and energy are the keys to understanding star formation & evolution. ◦ Gravity is constantly trying to pull matter toward the center of mass of a gas cloud or a star. ◦ Since stars do not have an infinite supply of energy, they must readjust their structure in response to the energy supply ...