Document
... • After the supernova explosion, a high mass star will become a neutron star. • After a supernova explosion, in a very high mass star the core that remains will be so massive, that without the energy created by nuclear fusion to support it, the core is swallowed by its own gravity. • The gravity of ...
... • After the supernova explosion, a high mass star will become a neutron star. • After a supernova explosion, in a very high mass star the core that remains will be so massive, that without the energy created by nuclear fusion to support it, the core is swallowed by its own gravity. • The gravity of ...
- hoganshomepage
... chemical composition of the stars. (also temperature and direction the star is moving in relation to the Earth.) How? Set up a spectroscope with different tubes; each gas has different spectras – light patterns. ...
... chemical composition of the stars. (also temperature and direction the star is moving in relation to the Earth.) How? Set up a spectroscope with different tubes; each gas has different spectras – light patterns. ...
Stars
... •With Newton’s modifications to Kepler’s laws, the period and size of the orbits yield the sum of the masses, while the relative distance of each star from the center of mass yields the ratio of the masses. •The ratio and sum provide each mass individually. ...
... •With Newton’s modifications to Kepler’s laws, the period and size of the orbits yield the sum of the masses, while the relative distance of each star from the center of mass yields the ratio of the masses. •The ratio and sum provide each mass individually. ...
Star Properties and Stellar Evolution
... different distances be compared? Use their brightness if they were all an equal distance from Earth = 32 ly. Absolute Magnitude ...
... different distances be compared? Use their brightness if they were all an equal distance from Earth = 32 ly. Absolute Magnitude ...
(AU): Average distance from Earth to Sun
... if all stars same distance from Earth. Apparent Magnitude: How bright a star appears to be to an observer on Earth. - Depends on distance. Closer = brighter ...
... if all stars same distance from Earth. Apparent Magnitude: How bright a star appears to be to an observer on Earth. - Depends on distance. Closer = brighter ...
Morning Announcements
... neatly. You can draw it or create a model out of pipe cleaners and construction paper. Every page must be titled with the stage of the life cycle Sign the back of each card you create. Each team r will create pages individually or together and sign that it is there work for verification. This is ...
... neatly. You can draw it or create a model out of pipe cleaners and construction paper. Every page must be titled with the stage of the life cycle Sign the back of each card you create. Each team r will create pages individually or together and sign that it is there work for verification. This is ...
Stellar Evolution and the HR Diagram – Study Guide
... 10. Draw the evolutionary path of our Sun. Start by locating it’s present position on the graph and then indicate where it will be as it ages, and finally what part of the graph it ends in. It would start above Red Dwarfs, but below Giants; it would move down and left to the main sequence (where it ...
... 10. Draw the evolutionary path of our Sun. Start by locating it’s present position on the graph and then indicate where it will be as it ages, and finally what part of the graph it ends in. It would start above Red Dwarfs, but below Giants; it would move down and left to the main sequence (where it ...
Can you write numbers in scientific notation
... How well you understand what processes are going on during the proto-star stage of a star’s life? What needs to happen for a proto-star to become a main sequence star? What are the properties of a main sequence star? How does a star’s mass affect the Luminosity, Temperature, Size, and lifespan of a ...
... How well you understand what processes are going on during the proto-star stage of a star’s life? What needs to happen for a proto-star to become a main sequence star? What are the properties of a main sequence star? How does a star’s mass affect the Luminosity, Temperature, Size, and lifespan of a ...
neutron star - The University of Chicago
... In the first lecture we learned that the fate of stars with masses more than 8 times the mass of the sun is different than that of sun-line stars. ...
... In the first lecture we learned that the fate of stars with masses more than 8 times the mass of the sun is different than that of sun-line stars. ...
The most important questions to study for the exam
... • Our eyes are mounted horizontally about 10 cm apart in our heads, and the brain uses the relative look angles of these eyes to estimate distance to the object viewed. • We are always moving our heads slightly from side to side, and the brain compares look angles from each of these positions to obt ...
... • Our eyes are mounted horizontally about 10 cm apart in our heads, and the brain uses the relative look angles of these eyes to estimate distance to the object viewed. • We are always moving our heads slightly from side to side, and the brain compares look angles from each of these positions to obt ...
Stefan-Boltzmann Law Problems
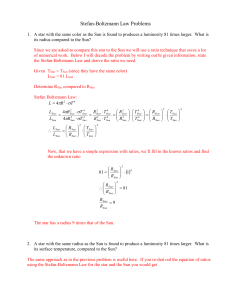
... 1. A star with the same color as the Sun is found to produces a luminosity 81 times larger. What is its radius compared to the Sun? Since we are asked to compare this star to the Sun we will use a ratio technique that saves a lot of numerical work. Below I will decode the problem by writing out ht g ...
... 1. A star with the same color as the Sun is found to produces a luminosity 81 times larger. What is its radius compared to the Sun? Since we are asked to compare this star to the Sun we will use a ratio technique that saves a lot of numerical work. Below I will decode the problem by writing out ht g ...
astr221lect2x
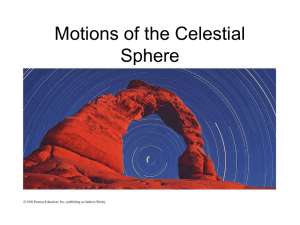
... day changes during the year because Earth’s orbit is slightly elliptical. • Mean solar time is based on the average length of a day. • Noon is average time at which Sun crosses meridian • It is a local definition of time ...
... day changes during the year because Earth’s orbit is slightly elliptical. • Mean solar time is based on the average length of a day. • Noon is average time at which Sun crosses meridian • It is a local definition of time ...