Today`s Powerpoint
... Ionized helium. Requires extreme UV photons. Only hottest stars produce many of these. ...
... Ionized helium. Requires extreme UV photons. Only hottest stars produce many of these. ...
Introduction to the Celestial Sphere
... with one axis above the northern horizon and the other axis below the southern horizon? Now everyone should know their directions, north, south, east and west. Facing north, what direction is to your right? Facing west, which direction is to your left? ...
... with one axis above the northern horizon and the other axis below the southern horizon? Now everyone should know their directions, north, south, east and west. Facing north, what direction is to your right? Facing west, which direction is to your left? ...
LESSON 4, STARS
... red giant, and finally, a white dwarf. A more-massive star: begins as a nebula, becomes a protostar, a main-sequence star, a very massive star, a supergiant, a supernova, and finally, either a neutron star (pulsar) or a black hole. ...
... red giant, and finally, a white dwarf. A more-massive star: begins as a nebula, becomes a protostar, a main-sequence star, a very massive star, a supergiant, a supernova, and finally, either a neutron star (pulsar) or a black hole. ...
Pulsars - Chabot College
... overcome electron degeneracy pressure if white dwarf mass greater than 1.4 M Chandrasekhar Limit Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar ...
... overcome electron degeneracy pressure if white dwarf mass greater than 1.4 M Chandrasekhar Limit Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar ...
The Application of Forbidden Line X-Ray Diagnostics to the Hot Star
... X-Ray Diagnostics to the Hot Star Tau Sco ...
... X-Ray Diagnostics to the Hot Star Tau Sco ...
Chapter 19 Star Formation
... Star formation happens when part of a dust cloud begins to contract under its own gravitational force; as it collapses, the center becomes hotter and hotter until nuclear fusion begins in the core. ...
... Star formation happens when part of a dust cloud begins to contract under its own gravitational force; as it collapses, the center becomes hotter and hotter until nuclear fusion begins in the core. ...
Life Cycle of a Star - Intervention Worksheet
... After the star explodes, some of the materials from the star are left behind. This material may form a neutron star. Neutron stars are the remains of high-mass stars. The most massive stars become black holes when they die. After a large mass star explodes, a large amount of mass may remain. The gra ...
... After the star explodes, some of the materials from the star are left behind. This material may form a neutron star. Neutron stars are the remains of high-mass stars. The most massive stars become black holes when they die. After a large mass star explodes, a large amount of mass may remain. The gra ...
Wien`s Law and Temperature
... 1. Go to the website http://astro.unl.edu/naap/blackbody/animations/blackbody.html. This site generates graphs simulating the blackbody spectra of stars of varying temperatures. It has a default of a star that is 6,000 K which is just slightly hotter than our sun. What is the peak wavelength for a s ...
... 1. Go to the website http://astro.unl.edu/naap/blackbody/animations/blackbody.html. This site generates graphs simulating the blackbody spectra of stars of varying temperatures. It has a default of a star that is 6,000 K which is just slightly hotter than our sun. What is the peak wavelength for a s ...
The Life Cycle of Stars Webquest
... 1. In this webquest, you will learn how to identify stars by their magnitude, color, temperature, and spectral class. 2. You will investigate the process of nuclear fusion explained by Einstein's famous equation E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and caus ...
... 1. In this webquest, you will learn how to identify stars by their magnitude, color, temperature, and spectral class. 2. You will investigate the process of nuclear fusion explained by Einstein's famous equation E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and caus ...
The Life Cycle of Stars Webquest
... 1. In this webquest, you will learn how to identify stars by their magnitude, color, temperature, and spectral class. 2. You will investigate the process of nuclear fusion explained by Einstein's famous equation E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and caus ...
... 1. In this webquest, you will learn how to identify stars by their magnitude, color, temperature, and spectral class. 2. You will investigate the process of nuclear fusion explained by Einstein's famous equation E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and caus ...
Today`s Objectives - RanelaghALevelPhysics
... • If the Sun has a radius of 6.96 x 108 m and a surface temperature of about 6000 K, what is its total power output? • What is the power per unit area? • What is the peak wavelength? ...
... • If the Sun has a radius of 6.96 x 108 m and a surface temperature of about 6000 K, what is its total power output? • What is the power per unit area? • What is the peak wavelength? ...
Space Science Unit
... star and the absolute magnitude (brightness) of the star to help astronomers decide which phase of the star’s life cycle the star is in and other important information about the star. • Most stars are what we consider main sequence (including our sun). They make up 90% of the stars in our sky. These ...
... star and the absolute magnitude (brightness) of the star to help astronomers decide which phase of the star’s life cycle the star is in and other important information about the star. • Most stars are what we consider main sequence (including our sun). They make up 90% of the stars in our sky. These ...
Exercises
... i-iii. Answer question (a) iii, iv and v for the dynamical timescale. iv. In stellar evolution models one often assumes that stars evolve quasi-statically, i.e. that the star remains in hydrostatic equilibrium throughout. Why can we make this assumption? v. Rapid changes that are sometimes observed ...
... i-iii. Answer question (a) iii, iv and v for the dynamical timescale. iv. In stellar evolution models one often assumes that stars evolve quasi-statically, i.e. that the star remains in hydrostatic equilibrium throughout. Why can we make this assumption? v. Rapid changes that are sometimes observed ...
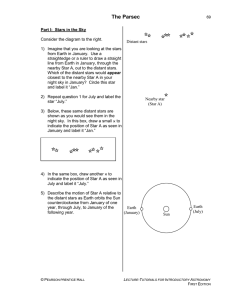
The Parsec
... line through Star A to the top of the page. 8) There is now a narrow triangle with the Earth-Sun distance as its base. The small angle, just below Star A, formed by the two longest sides of this triangle is called the parallax angle for Star A. Label this angle “pA.” Knowing a star’s parallax angle ...
... line through Star A to the top of the page. 8) There is now a narrow triangle with the Earth-Sun distance as its base. The small angle, just below Star A, formed by the two longest sides of this triangle is called the parallax angle for Star A. Label this angle “pA.” Knowing a star’s parallax angle ...
File - Science with Mrs. Schmidt
... b. some of the colors and some black lines. c. all the colors. d. all the colors and some black lines. _____ 11. What instrument breaks a star’s light into a spectrum? a. a continuous spectrum b. a telescope c. a spectrometer d. a spectrograph _____ 12. What can scientists tell about a star from its ...
... b. some of the colors and some black lines. c. all the colors. d. all the colors and some black lines. _____ 11. What instrument breaks a star’s light into a spectrum? a. a continuous spectrum b. a telescope c. a spectrometer d. a spectrograph _____ 12. What can scientists tell about a star from its ...
Astronomy 122 mid Term Exam
... Here is an example that got ½ credit – again even though it’s not even close to correct: “You determine the age by looking at the stars around it. Since they are in a stellar cluster they are the same age. The age of the star is 2 times the age of the Sun.” Or “The most massive star still on the mai ...
... Here is an example that got ½ credit – again even though it’s not even close to correct: “You determine the age by looking at the stars around it. Since they are in a stellar cluster they are the same age. The age of the star is 2 times the age of the Sun.” Or “The most massive star still on the mai ...