Stellar Evolution and the HR Diagram – Study Guide
... 10. Draw the evolutionary path of our Sun. Start by locating it’s present position on the graph and then indicate where it will be as it ages, and finally what part of the graph it ends in. It would start above Red Dwarfs, but below Giants; it would move down and left to the main sequence (where it ...
... 10. Draw the evolutionary path of our Sun. Start by locating it’s present position on the graph and then indicate where it will be as it ages, and finally what part of the graph it ends in. It would start above Red Dwarfs, but below Giants; it would move down and left to the main sequence (where it ...
GRAVITY FIELD IN EXTERNAL PARTS OF THE SOLAR SYSTEM
... a length several thousand parsecs. The masses in the galaxy are concentrated toward the center. The Sun is located about 8000 pc from the galactic center (Binney & Merrifield, 1998). The size of the solar space is much smaller than the size of the galaxy. For this reason, gravitational perturbations ...
... a length several thousand parsecs. The masses in the galaxy are concentrated toward the center. The Sun is located about 8000 pc from the galactic center (Binney & Merrifield, 1998). The size of the solar space is much smaller than the size of the galaxy. For this reason, gravitational perturbations ...
WORD - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... c. the structure and evolution of the earth's crust. d. everything in the universe that lies above Earth's atmosphere. 02. Which of the following terms would not be associated with astronomy? a. horoscope b. telescope c. astrolabe d. celestial sphere 03. A planet is an object which a. occurs only in ...
... c. the structure and evolution of the earth's crust. d. everything in the universe that lies above Earth's atmosphere. 02. Which of the following terms would not be associated with astronomy? a. horoscope b. telescope c. astrolabe d. celestial sphere 03. A planet is an object which a. occurs only in ...
Stellar Evolution Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Hertzsprung
... when it stops emitting light end of many sun-like stars ...
... when it stops emitting light end of many sun-like stars ...
Neutron Stars
... The energy source for the repeated gamma-ray bursts (SGRs) from some neutron stars is what? A: fusion of hydrogen on the surface B: energy released by material accreting onto the surface. C: the result of reconfigurations of the strong magnetic fields ...
... The energy source for the repeated gamma-ray bursts (SGRs) from some neutron stars is what? A: fusion of hydrogen on the surface B: energy released by material accreting onto the surface. C: the result of reconfigurations of the strong magnetic fields ...
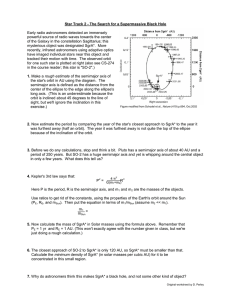
Star Track 2 - The Search for a Supermassive Black... Early radio astronomers detected an immensely
... Star Track 2 - The Search for a Supermassive Black Hole Early radio astronomers detected an immensely powerful source of radio waves towards the center of the Galaxy in the constellation Sagittarius; this mysterious object was designated SgrA*. More recently, infrared astronomers using adaptive opti ...
... Star Track 2 - The Search for a Supermassive Black Hole Early radio astronomers detected an immensely powerful source of radio waves towards the center of the Galaxy in the constellation Sagittarius; this mysterious object was designated SgrA*. More recently, infrared astronomers using adaptive opti ...
Astr604-Ch1
... to obtain the magnitudes. Detectors of electromagnetic radiation are sensitive only over given wavelength bands. Because the flux of star light varies with wavelength, the magnitude of a star depends on the wavelength interval at which we observe. Originally, photographic plates were sensitive only ...
... to obtain the magnitudes. Detectors of electromagnetic radiation are sensitive only over given wavelength bands. Because the flux of star light varies with wavelength, the magnitude of a star depends on the wavelength interval at which we observe. Originally, photographic plates were sensitive only ...
Exam # 2 – Tue 11/08/2011
... A. four times the energy of the emitted photon B. twice the energy of the emitted photon C. the same energy as the emitted photon D. half the energy of the emitted photon E. one fourth the energy of the emitted photon 24. The fusion of four hydrogen nuclei into a helium nucleus releases energy becau ...
... A. four times the energy of the emitted photon B. twice the energy of the emitted photon C. the same energy as the emitted photon D. half the energy of the emitted photon E. one fourth the energy of the emitted photon 24. The fusion of four hydrogen nuclei into a helium nucleus releases energy becau ...
Astronomy 103 Exam 2 Review
... Why are there no stars of less massive than approximately 0.08 solar masses? A. They are sLll contracLng and haven’t yet reached the main sequence B. They cannot compress their cores to hydrogen fusion temperatures C. Their mass is so small that deuterium fusion blasts them apart D. Non ...
... Why are there no stars of less massive than approximately 0.08 solar masses? A. They are sLll contracLng and haven’t yet reached the main sequence B. They cannot compress their cores to hydrogen fusion temperatures C. Their mass is so small that deuterium fusion blasts them apart D. Non ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... If initial star mass < 8 MSun or so. (and remember: Maximum WD mass is 1.4 MSun , radius is about that of the Earth) 2. Neutron Star If initial mass > 8 MSun and < 25 MSun . ...
... If initial star mass < 8 MSun or so. (and remember: Maximum WD mass is 1.4 MSun , radius is about that of the Earth) 2. Neutron Star If initial mass > 8 MSun and < 25 MSun . ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • The energy of the electron depends on orbit • When an electron jumps from one orbital to another, it emits (emission line) or absorbs (absorption line) a photon of a certain energy • The frequency of emitted or absorbed photon is related to its energy ...
... • The energy of the electron depends on orbit • When an electron jumps from one orbital to another, it emits (emission line) or absorbs (absorption line) a photon of a certain energy • The frequency of emitted or absorbed photon is related to its energy ...