Uniqueness of the Earth, Lebo, 7-30
... Must be near, but not in, a spiral arm. We are at a corotation point far from our galactic center. Note: At the co-rotation point the Sun remains stationary and out of a spiral arm. Most all stars in the Milky Way are in the central bulge, a globular cluster or a spiral arm. In each of these locatio ...
... Must be near, but not in, a spiral arm. We are at a corotation point far from our galactic center. Note: At the co-rotation point the Sun remains stationary and out of a spiral arm. Most all stars in the Milky Way are in the central bulge, a globular cluster or a spiral arm. In each of these locatio ...
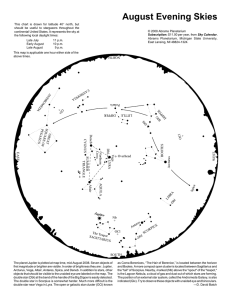
August Evening Skies
... double star (Dbl) at the bend of the handle of the Big Dipper is easily detected. The double star in Scorpius is somewhat harder. Much more difficult is the double star near Vega in Lyra. The open or galactic star cluster (OCl) known ...
... double star (Dbl) at the bend of the handle of the Big Dipper is easily detected. The double star in Scorpius is somewhat harder. Much more difficult is the double star near Vega in Lyra. The open or galactic star cluster (OCl) known ...
a Supernova!
... to halt the collapse and support the star) resulting in lots of very energetic radiation (gamma rays). ...
... to halt the collapse and support the star) resulting in lots of very energetic radiation (gamma rays). ...
He fusion
... But a deeper understanding of astrophysics suggests that fusions at the core will die out when just over 0.0003 of its mass has been lost. lifetime of Sun as a star doing fusion ...
... But a deeper understanding of astrophysics suggests that fusions at the core will die out when just over 0.0003 of its mass has been lost. lifetime of Sun as a star doing fusion ...
ASTR 200 : Lecture 15 Ensemble Properties of Stars
... • So, a large cloud (1000s to ~million solar masses) gets cold enough that many cores collapse into stars, giving a cluster • Each star clears gas disk away, but the cluster as a whole also blows out all the remaining interstellar gas, shutting down star formation • The stars settle onto the main se ...
... • So, a large cloud (1000s to ~million solar masses) gets cold enough that many cores collapse into stars, giving a cluster • Each star clears gas disk away, but the cluster as a whole also blows out all the remaining interstellar gas, shutting down star formation • The stars settle onto the main se ...
Lecture 14 - Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy CASA
... We now see a dozen or so every year in distant galaxies. ...
... We now see a dozen or so every year in distant galaxies. ...
astro20 chap27 - Las Positas College
... – need to remove fraction of binary stars ~ 0.5 – need to remove stars that don’t live long enough ( ~ 1 billion years : 0.5 – need to remove all stars whose zones are small enough so that a planet is not likely to orbit within ~ 0.2 - 0.3 – alltogether this should be ~ 0.1 ...
... – need to remove fraction of binary stars ~ 0.5 – need to remove stars that don’t live long enough ( ~ 1 billion years : 0.5 – need to remove all stars whose zones are small enough so that a planet is not likely to orbit within ~ 0.2 - 0.3 – alltogether this should be ~ 0.1 ...
Stellar Classification and Evolution What is a star? A cloud of gas
... (which actually has nothing to do with planets, but we didn’t know that in the 18th century when Herschel coined the term) The core _____________________ to form a White Dwarf ...
... (which actually has nothing to do with planets, but we didn’t know that in the 18th century when Herschel coined the term) The core _____________________ to form a White Dwarf ...
MAUI STARGAZING MAY OBSERVING LIST DEEP SPACE
... CONSTELLATIONS - A constellation is a specific area of the celestial sphere as defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). There are 88 officially recognized constellations, covering the entire sky. GALAXIES A galaxy is a gravitationally bound system of stars, stellar remnants, interstell ...
... CONSTELLATIONS - A constellation is a specific area of the celestial sphere as defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). There are 88 officially recognized constellations, covering the entire sky. GALAXIES A galaxy is a gravitationally bound system of stars, stellar remnants, interstell ...
Geocentric vs. Heliocentric
... At the time his theory was a complete disaster at “predicting” the positions of the planets in the sky. Ptolemy’s model “worked” much better. ...
... At the time his theory was a complete disaster at “predicting” the positions of the planets in the sky. Ptolemy’s model “worked” much better. ...
Star Game Cards
... Before being engulfed, matter that is pulled into a black hole should become very hot and emit ____. ...
... Before being engulfed, matter that is pulled into a black hole should become very hot and emit ____. ...
Dim Stars - granthamkuehl
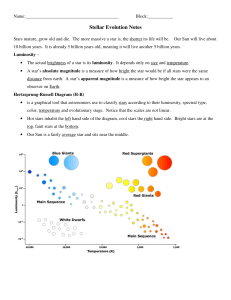
... In our study of Stars The students will be able to Determine color, temp., brightness and Size of a star And show what they learned by Interpreting the HR Diagram ...
... In our study of Stars The students will be able to Determine color, temp., brightness and Size of a star And show what they learned by Interpreting the HR Diagram ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... A galaxy is a group of hundreds of billions of stars that are relatively close to each other. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, contains over 100 billion stars. The universe has more than 100 billion galaxies with each galaxy containing an average of 100 billion stars. ...
... A galaxy is a group of hundreds of billions of stars that are relatively close to each other. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, contains over 100 billion stars. The universe has more than 100 billion galaxies with each galaxy containing an average of 100 billion stars. ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... A galaxy is a group of hundreds of billions of stars that are relatively close to each other. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, contains over 100 billion stars. The universe has more than 100 billion galaxies with each galaxy containing an average of 100 billion stars. ...
... A galaxy is a group of hundreds of billions of stars that are relatively close to each other. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, contains over 100 billion stars. The universe has more than 100 billion galaxies with each galaxy containing an average of 100 billion stars. ...
Pretest
... than low beams do. Also, the closer an oncoming car is to you, the greater the apparent brightness of its headlights (on low or high). 21. Low-mass stars have longer lifetimes than do high-mass stars because low-mass stars use up their fuel much more slowly. 22. Because of high temperatures in the i ...
... than low beams do. Also, the closer an oncoming car is to you, the greater the apparent brightness of its headlights (on low or high). 21. Low-mass stars have longer lifetimes than do high-mass stars because low-mass stars use up their fuel much more slowly. 22. Because of high temperatures in the i ...
Stars - Red, Blue, Old, New pt.3
... core, there is a zone of H to He fusion surrounding the core • When the core is all C, further changes occur and C to O fusion starts (with zones of He to C and H to He surrounding) • Stars get an “onion” structure ...
... core, there is a zone of H to He fusion surrounding the core • When the core is all C, further changes occur and C to O fusion starts (with zones of He to C and H to He surrounding) • Stars get an “onion” structure ...
Day 1212
... Its core contracts and increases in temperature. The outer layers expand and cool. In this late stage of its life cycle, an average star like our Sun is called a giant. ...
... Its core contracts and increases in temperature. The outer layers expand and cool. In this late stage of its life cycle, an average star like our Sun is called a giant. ...