Stars II. Stellar Physics
... uniqueness of the solution is claimed in the Russel-VogtTheorem: For a star of given chemical composition and mass there exists only one equilibrium configuration which solves the boundary problem of stellar structure. [In this generality, the theorem is not proven. Local uniqueness can be shown, ho ...
... uniqueness of the solution is claimed in the Russel-VogtTheorem: For a star of given chemical composition and mass there exists only one equilibrium configuration which solves the boundary problem of stellar structure. [In this generality, the theorem is not proven. Local uniqueness can be shown, ho ...
som1
... Statistical mechanics • If the gas is in thermal equilibrium with temperature T, the atoms have a range of velocities described by the MaxwellBoltzmann distribution function. • The number density of gas particles with speed between v and v+dv is: ...
... Statistical mechanics • If the gas is in thermal equilibrium with temperature T, the atoms have a range of velocities described by the MaxwellBoltzmann distribution function. • The number density of gas particles with speed between v and v+dv is: ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... diagonal” shows that larger mass ‘normal’ stars are hotter…and thus ‘burn’ fuel fast, and have short lives White Dwarfs are hot, but not that bright, so they must be small. Giants and Supergiants are cool, but bright so they must be very large. ...
... diagonal” shows that larger mass ‘normal’ stars are hotter…and thus ‘burn’ fuel fast, and have short lives White Dwarfs are hot, but not that bright, so they must be small. Giants and Supergiants are cool, but bright so they must be very large. ...
Astronomy Unit Test – Chapter 21
... 25. Predict what will happen when the sun runs out of fuel. 26. What is used to classify stars? 27. At which phase of the moon could a solar eclipse occur? 28. A star is twice as massive as the sun. How will its lifespan compare with the sun? 29. Some astronomers discover a galaxy that contains only ...
... 25. Predict what will happen when the sun runs out of fuel. 26. What is used to classify stars? 27. At which phase of the moon could a solar eclipse occur? 28. A star is twice as massive as the sun. How will its lifespan compare with the sun? 29. Some astronomers discover a galaxy that contains only ...
Star Life Cycle
... A Red Giant Star is a main sequence star that is not longer in equilibrium. There is a ...
... A Red Giant Star is a main sequence star that is not longer in equilibrium. There is a ...
The Universe Inside of You: Where do the atoms in your body come
... Another Way To Make Au: The r-Process Capture neutrons very quickly - “rapid” compared to the time it takes to beta-decay. So many neutrons are captured that we push the “path” far from the stable isotopes. No information on nuclear properties of thousands of nuclei that participate in this process ...
... Another Way To Make Au: The r-Process Capture neutrons very quickly - “rapid” compared to the time it takes to beta-decay. So many neutrons are captured that we push the “path” far from the stable isotopes. No information on nuclear properties of thousands of nuclei that participate in this process ...
HW10_Answers
... 4) State the two postulates of Special Relativity and explain what each means. 1) For objects moving at a constant velocity, all motion is relative. This means that there is no object that is at absolute rest. It is impossible to tell if one object is at rest and another is in motion. You can only ...
... 4) State the two postulates of Special Relativity and explain what each means. 1) For objects moving at a constant velocity, all motion is relative. This means that there is no object that is at absolute rest. It is impossible to tell if one object is at rest and another is in motion. You can only ...
Homework #8
... speed, and arrive back on earth 26 yr after they left. Assume that the time needed to accelerate and decelerate is negligible. (a) What is the speed of the starship? (b) How much time has elapsed on the astronauts' chronometers? 5. At what speed, as a fraction of c, will a moving rod have a length 7 ...
... speed, and arrive back on earth 26 yr after they left. Assume that the time needed to accelerate and decelerate is negligible. (a) What is the speed of the starship? (b) How much time has elapsed on the astronauts' chronometers? 5. At what speed, as a fraction of c, will a moving rod have a length 7 ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... Sun – you are here. This is what our Galaxy would look like if we were looking at it from another galaxy. ...
... Sun – you are here. This is what our Galaxy would look like if we were looking at it from another galaxy. ...
STARS
... • An enormous explosion when a large star dies. • When all the hydrogen is used up the core collapses • The absence of pressure causes a neutron star or a black hole. • The explosion can be bright enough to see during the day! ...
... • An enormous explosion when a large star dies. • When all the hydrogen is used up the core collapses • The absence of pressure causes a neutron star or a black hole. • The explosion can be bright enough to see during the day! ...
Quiz Chapter 10 Answers
... Quiz Chapter 10 Answers 10-1. Protostars are not seen in visible light telescopes because: a) they don’t emit any radiation b) they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust X c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are all moving away from Earth so fast that their visible light is Doppler shift ...
... Quiz Chapter 10 Answers 10-1. Protostars are not seen in visible light telescopes because: a) they don’t emit any radiation b) they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust X c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are all moving away from Earth so fast that their visible light is Doppler shift ...
ems 6 - LincolnLions.org
... present day Identify and explain the relevant space technologies invented Include pictures when possible Complete on paper provided ...
... present day Identify and explain the relevant space technologies invented Include pictures when possible Complete on paper provided ...
Test ticket - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]
... 2-2 the life cycle of stars the beginning and end of stars nuclear fusion different types of stars ...
... 2-2 the life cycle of stars the beginning and end of stars nuclear fusion different types of stars ...
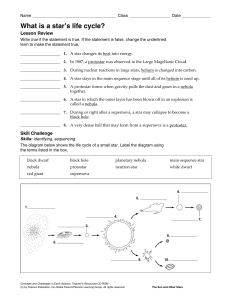
What is a star`s life cycle?
... ____________________ 1. A star changes its heat into energy. ____________________ 2. In 1987, a protostar was observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud. ____________________ 3. During nuclear reactions in large stars, helium is changed into carbon. ____________________ 4. A star stays in the main seque ...
... ____________________ 1. A star changes its heat into energy. ____________________ 2. In 1987, a protostar was observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud. ____________________ 3. During nuclear reactions in large stars, helium is changed into carbon. ____________________ 4. A star stays in the main seque ...



















![Test ticket - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010793453_1-3f96ef5ee7d4646c2142d92e4dc3c3f6-300x300.png)