Week 9 Concept Summary - UC Berkeley Astronomy w
... intrinsic luminosity and the mass: L ∝ M 4 , and the main sequence lifetime goes as t ∝ M −3 . Knowing the color of a main sequence star tells you the temperature, and uminosity, which in turn tells you the radius of the star and how far away it is. 3. Stellar Birth: Stars form out of giant gas clou ...
... intrinsic luminosity and the mass: L ∝ M 4 , and the main sequence lifetime goes as t ∝ M −3 . Knowing the color of a main sequence star tells you the temperature, and uminosity, which in turn tells you the radius of the star and how far away it is. 3. Stellar Birth: Stars form out of giant gas clou ...
File
... Definition of Life • The following are, in general, the characteristics of living organisms: 1.They can react to their environment. 2.They can grow by taking in nourishment and processing it into energy. 3.They can reproduce, passing along their characteristics to their offspring. 4.They have the c ...
... Definition of Life • The following are, in general, the characteristics of living organisms: 1.They can react to their environment. 2.They can grow by taking in nourishment and processing it into energy. 3.They can reproduce, passing along their characteristics to their offspring. 4.They have the c ...
The Closest New Stars To Earth
... from galaxies originates from nebulae like this one. But its great luminosity and relative proximity makes it easy to overlook the fact that there are a slew of much closer starforming regions than the Orion Nebula; they're just much, much fainter. If you get a collapsing molecular cloud many hundre ...
... from galaxies originates from nebulae like this one. But its great luminosity and relative proximity makes it easy to overlook the fact that there are a slew of much closer starforming regions than the Orion Nebula; they're just much, much fainter. If you get a collapsing molecular cloud many hundre ...
Measuring Distances: Mph (miles per hour): miles traveled per hour
... universe, and is supported by observa;onal evidence. A Belgian priest named Georges Lemaitre first suggested the Big Bang Theory when he theorized that the universe began from a single atom. Suppor;ng ...
... universe, and is supported by observa;onal evidence. A Belgian priest named Georges Lemaitre first suggested the Big Bang Theory when he theorized that the universe began from a single atom. Suppor;ng ...
File
... Stars Stars radiate energy through the process of fusion in which two hydrogen atoms are combined to form a helium atom, and large amounts of energy are released. Some of the energy generated by the star is in the form of visible light. ...
... Stars Stars radiate energy through the process of fusion in which two hydrogen atoms are combined to form a helium atom, and large amounts of energy are released. Some of the energy generated by the star is in the form of visible light. ...
Stellar and Atomic Spectra
... electrons is not true? A) Electrons orbit the nucleus rather like planets orbiting the Sun. B) Within an atom, an electron can have only particular energies. C) Electrons can jump between energy levels in an atom only if they receive or give up an amount of energy equal to the difference in energy b ...
... electrons is not true? A) Electrons orbit the nucleus rather like planets orbiting the Sun. B) Within an atom, an electron can have only particular energies. C) Electrons can jump between energy levels in an atom only if they receive or give up an amount of energy equal to the difference in energy b ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... formed iron, no more reactions can occur, and the core violently collapses in on itself Supernova ...
... formed iron, no more reactions can occur, and the core violently collapses in on itself Supernova ...
Nuclear Reactions
... This appears mostly in the form of gamma radiation, γ (some produced by the annihilation of positrons e+ ) A very small amount is effectively “wasted” in the neutrino ν But just how much energy is that? ...
... This appears mostly in the form of gamma radiation, γ (some produced by the annihilation of positrons e+ ) A very small amount is effectively “wasted” in the neutrino ν But just how much energy is that? ...
astr100_finalexam
... In the year 15,000 BCE d. In the year 37,000 BCE e. In the year 15, 000 CE [38] A blue spaceship is moving TOWARD you at an extremely fast rate. It would appear a., red b. orange c. yellow d. blue e. violet [39] About how many times will the solar system have orbited the center of the galaxy? a. ...
... In the year 15,000 BCE d. In the year 37,000 BCE e. In the year 15, 000 CE [38] A blue spaceship is moving TOWARD you at an extremely fast rate. It would appear a., red b. orange c. yellow d. blue e. violet [39] About how many times will the solar system have orbited the center of the galaxy? a. ...
Benchmark lesson
... gas and the helium gas that makes up the Sun. During the reaction, called nuclear fusion, large amounts of energy are given off in the form of light and heat. Many schools and community buildings in Florida use this energy to heat water. The energy from the heated water is used to make electricity. ...
... gas and the helium gas that makes up the Sun. During the reaction, called nuclear fusion, large amounts of energy are given off in the form of light and heat. Many schools and community buildings in Florida use this energy to heat water. The energy from the heated water is used to make electricity. ...
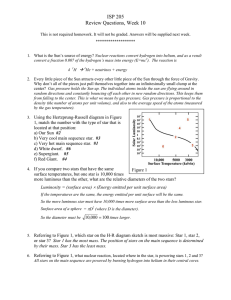
ISP 205 Review Questions, Week 10
... 4 1H 4He + neutrinos + energy 2. Every little piece of the Sun attracts every other little piece of the Sun through the force of Gravity. Why don’t all of the pieces just pull themselves together into an infinitesimally small clump at the center? Gas pressure holds the Sun up. The individual atoms ...
... 4 1H 4He + neutrinos + energy 2. Every little piece of the Sun attracts every other little piece of the Sun through the force of Gravity. Why don’t all of the pieces just pull themselves together into an infinitesimally small clump at the center? Gas pressure holds the Sun up. The individual atoms ...
BlackHoles - Montgomery College
... G, Newtonian universal gravitational constant, 6.67259x10-11m3/(kg s2) • M, mass of object in kg • R, radius of object in m ...
... G, Newtonian universal gravitational constant, 6.67259x10-11m3/(kg s2) • M, mass of object in kg • R, radius of object in m ...
From the Everett and Seattle Astronomical
... temperature gas. The atoms in the cloud are energized by ultraviolet light from a nearby star and emit radiation as they fall back into lower energy states. Emission nebulae are sites of recent and ongoing star formation. The Orion nebulae, also know as M42, is a good example of an emission nebulae. ...
... temperature gas. The atoms in the cloud are energized by ultraviolet light from a nearby star and emit radiation as they fall back into lower energy states. Emission nebulae are sites of recent and ongoing star formation. The Orion nebulae, also know as M42, is a good example of an emission nebulae. ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... Life Cycle of Stars by Dr. O’Brian 1. Away out there in space there’s huge clouds of dust and gas - nebula 2. If one of those clouds of dust and gas is massive enough, it’s own gravity causes it to start to collapse so it folds in on itself towards the center of that cloud it gets denser and denser ...
... Life Cycle of Stars by Dr. O’Brian 1. Away out there in space there’s huge clouds of dust and gas - nebula 2. If one of those clouds of dust and gas is massive enough, it’s own gravity causes it to start to collapse so it folds in on itself towards the center of that cloud it gets denser and denser ...
CST Prep- 8th Grade Astronomy
... 1. The theory of how the universe was created is called the ____________________. 2. Which equation states that matter and energy are interchangeable? __________________ 3. All matter in the Universe today came from an original pin prick of limitless __________________. 4. Is the universe contractin ...
... 1. The theory of how the universe was created is called the ____________________. 2. Which equation states that matter and energy are interchangeable? __________________ 3. All matter in the Universe today came from an original pin prick of limitless __________________. 4. Is the universe contractin ...
1 - TeacherWeb
... 33. List 4 forms of light or particles that come from the sun. 50. Give an example of an unstable metal. 34. How does solar energy reach the Earth? 51. Draw and label the modern version of an atom. 35. What happens to a super giant star at the end of its life cycle? 36. What is a black hole? 37. Wh ...
... 33. List 4 forms of light or particles that come from the sun. 50. Give an example of an unstable metal. 34. How does solar energy reach the Earth? 51. Draw and label the modern version of an atom. 35. What happens to a super giant star at the end of its life cycle? 36. What is a black hole? 37. Wh ...
Astronomy 114 Problem Set # 5 Due: 04 Apr 2007 SOLUTIONS 1 1
... Use this fact to explain why a relation between a star’s mass and its luminosity should exist, and why it is not surprising that L ∝ M 3.5 rather than just L ∝ M. One’s first guess might be that the L ∝ M since a larger star will have proportionately more mass available for fusion reactions. However ...
... Use this fact to explain why a relation between a star’s mass and its luminosity should exist, and why it is not surprising that L ∝ M 3.5 rather than just L ∝ M. One’s first guess might be that the L ∝ M since a larger star will have proportionately more mass available for fusion reactions. However ...
Slide 1 - Physics @ IUPUI
... somewhere. • Where does the energy the pulsars emit come from? • A) heat • B) nuclear fusion • C) gravity • D) Spin ...
... somewhere. • Where does the energy the pulsars emit come from? • A) heat • B) nuclear fusion • C) gravity • D) Spin ...
Sample Midterm - IUPUI Physics
... does the energy that a star needs to survive come from (before it starts to fuse Helium) and how does that affect the size and temperature of the surface of the star? B) What is the process by which Helium (also known as alpha particles) are fused into another element and what element is created fro ...
... does the energy that a star needs to survive come from (before it starts to fuse Helium) and how does that affect the size and temperature of the surface of the star? B) What is the process by which Helium (also known as alpha particles) are fused into another element and what element is created fro ...
Page 1 Astronomy 110 Homework #08 Assigned: 03/13/2007 Due
... A) to dim and redden distant stars by preferentially scattering their blue light. B) to scatter the red light from stars preferentially, making them appear more blue than expected. C) almost nonexistent, because light does not interact with dust. D) to make stars appear less bright than expected by ...
... A) to dim and redden distant stars by preferentially scattering their blue light. B) to scatter the red light from stars preferentially, making them appear more blue than expected. C) almost nonexistent, because light does not interact with dust. D) to make stars appear less bright than expected by ...