White Dwarf Stars Near The Earth
... Sirius B is the companion to Sirius, which is the brightest star in Earth’s sky. As can be seen from the chart, Sirius B is unusually hot, and that means it is unusually young, probably only 250 million years or thereabouts. It is also unusually massive, being the remnant of a giant B-class star tha ...
... Sirius B is the companion to Sirius, which is the brightest star in Earth’s sky. As can be seen from the chart, Sirius B is unusually hot, and that means it is unusually young, probably only 250 million years or thereabouts. It is also unusually massive, being the remnant of a giant B-class star tha ...
Properties of Stars
... same way as low-mass stars. • During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, mediummass stars are thought to cast off their bloated outer layer, creating an expanding round cloud of gas called planetary nebula. ...
... same way as low-mass stars. • During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, mediummass stars are thought to cast off their bloated outer layer, creating an expanding round cloud of gas called planetary nebula. ...
GEARS Workshop Monday - Georgia Southern University
... camera radius (from geometry and knowing distance) to get temperature of the sun as blackbody • We used Wien’s Law model for peak wavelength of blackbody emitter using the temperature ...
... camera radius (from geometry and knowing distance) to get temperature of the sun as blackbody • We used Wien’s Law model for peak wavelength of blackbody emitter using the temperature ...
L = σAT 4
... • The point of classifying the various types of stars is to see is any patterns exists. A useful way of making the comparison is the H-R diagram. Each dot on the diagram represents a different star. • The vertical axis is the luminosity of the star. It should be noted that the scale is not a linear ...
... • The point of classifying the various types of stars is to see is any patterns exists. A useful way of making the comparison is the H-R diagram. Each dot on the diagram represents a different star. • The vertical axis is the luminosity of the star. It should be noted that the scale is not a linear ...
HW #8 Stellar Evolution I Solutions
... star to collapse and heat. However, even though no hydrogen fusion is possible in the collapsing core (since there is no hydrogen in the core anymore, it being all converted into helium) a thin shell of hydrogen in a shell around the collapsing core is pushed deeper into the star as the core collaps ...
... star to collapse and heat. However, even though no hydrogen fusion is possible in the collapsing core (since there is no hydrogen in the core anymore, it being all converted into helium) a thin shell of hydrogen in a shell around the collapsing core is pushed deeper into the star as the core collaps ...
PDF version
... in our solar system that all revolve around the sun. Mercury is the closest planet to the sun, and it's the smallest of the eight. Venus is the second-closest to the sun, and it's the hottest planet because of its gaseous atmosphere. Sunlight gets trapped and heats up Venus. Earth, the third planet ...
... in our solar system that all revolve around the sun. Mercury is the closest planet to the sun, and it's the smallest of the eight. Venus is the second-closest to the sun, and it's the hottest planet because of its gaseous atmosphere. Sunlight gets trapped and heats up Venus. Earth, the third planet ...
chapter6
... • Electron orbits in the electron cloud are restricted to very specific radii and energies. • These characteristic electron energies are different ...
... • Electron orbits in the electron cloud are restricted to very specific radii and energies. • These characteristic electron energies are different ...
Lecture21
... If a degenerate core (or white dwarf) exceeds the Chandrasekhar mass limit (1.4MSun) it must collapse until neutron degeneracy pressure takes over. M 1.4M Sun R 10km ...
... If a degenerate core (or white dwarf) exceeds the Chandrasekhar mass limit (1.4MSun) it must collapse until neutron degeneracy pressure takes over. M 1.4M Sun R 10km ...
The Life Cycle of the Stars
... Like all stars, our Sun was formed from a cloud of hydrogen gas and dust that almost certainly included the ashes from an earlier star gone supernova. In its death throes, it created elements heavier than iron that our solar system inherited. Gravity pulled the cloud together into a giant ball. When ...
... Like all stars, our Sun was formed from a cloud of hydrogen gas and dust that almost certainly included the ashes from an earlier star gone supernova. In its death throes, it created elements heavier than iron that our solar system inherited. Gravity pulled the cloud together into a giant ball. When ...
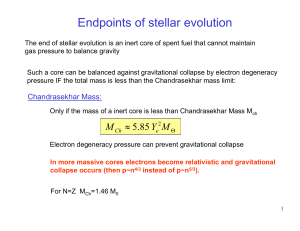
Endpoints of stellar evolution
... To explain the origin of the elements one needs to have • constant overproduction (then the pattern is solar) • sufficiently high overproduction to explain total amount of elements observed today ...
... To explain the origin of the elements one needs to have • constant overproduction (then the pattern is solar) • sufficiently high overproduction to explain total amount of elements observed today ...
Due: January 14, 2014 Name: White dwarfs are “has been
... The energy radiated from a protostar comes from gravitational potential energy that is converted to kinetic and then thermal energy when the matter within the protostar falls toward the core. The energy radiated by a main-sequence star comes from nuclear fusion. ...
... The energy radiated from a protostar comes from gravitational potential energy that is converted to kinetic and then thermal energy when the matter within the protostar falls toward the core. The energy radiated by a main-sequence star comes from nuclear fusion. ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... What is happening in the interior of a star that is on the main sequence on the HertzsprungRussell diagram? A: Stars that have reached the main sequence have ceased nuclear "burning" and are simply cooling down by emitting ...
... What is happening in the interior of a star that is on the main sequence on the HertzsprungRussell diagram? A: Stars that have reached the main sequence have ceased nuclear "burning" and are simply cooling down by emitting ...
Black Holes, Part 9, Star Eaters
... The solar action of the secondary star would be so intense thereby that the star's emission spectrum would be shifted upwards into the high-energy bands, way past the UV band, into the hard-x-rays band. The extreme energy emission takes the resulting spectrum far outside the visible band. ...
... The solar action of the secondary star would be so intense thereby that the star's emission spectrum would be shifted upwards into the high-energy bands, way past the UV band, into the hard-x-rays band. The extreme energy emission takes the resulting spectrum far outside the visible band. ...
Lecture 31
... sources) and found its distance from its redshift to be 2 billion light years--not a star, and L = 1040 watts--1,000 L (MW)!! .8 to 14(?) Billion years--distance range. L = 1038-1042 watts. Energy comes from a region solar system-sized. Radio Jets. A thermal (synchotron) and non-thermal (black-body) ...
... sources) and found its distance from its redshift to be 2 billion light years--not a star, and L = 1040 watts--1,000 L (MW)!! .8 to 14(?) Billion years--distance range. L = 1038-1042 watts. Energy comes from a region solar system-sized. Radio Jets. A thermal (synchotron) and non-thermal (black-body) ...
Black Hole
... It is a system of stars, dust, and gas held together by gravity. There are three basic types: spiral, elliptical, and irregular. A spiral galaxy is a flattened, discus-shaped collection of stars, having a central bulge. Examples include the Milky Way and Andromeda. An elliptical galaxy ranges in sha ...
... It is a system of stars, dust, and gas held together by gravity. There are three basic types: spiral, elliptical, and irregular. A spiral galaxy is a flattened, discus-shaped collection of stars, having a central bulge. Examples include the Milky Way and Andromeda. An elliptical galaxy ranges in sha ...
Earth Science Curriculum Unit 1 Maps and Measurements
... HSN.Q.A.1: Use units as a way to understand problems and to guide the solution of multistep problems; choose and interpret units consistently in formulas; choose and interpret the scale and the origin in graphs and data displays. HSN.Q.A.2: Define appropriate quantities for the purpose of descriptiv ...
... HSN.Q.A.1: Use units as a way to understand problems and to guide the solution of multistep problems; choose and interpret units consistently in formulas; choose and interpret the scale and the origin in graphs and data displays. HSN.Q.A.2: Define appropriate quantities for the purpose of descriptiv ...
Our Sun, Sol - Hobbs High School
... collapses, its powerful gravity takes it right through the white dwarf stage to produce one of two extremely bizarre objects—either a neutron star or a black hole. • In most cases, the rest of the star then blows up, in a gargantuan explosion called a supernova. ...
... collapses, its powerful gravity takes it right through the white dwarf stage to produce one of two extremely bizarre objects—either a neutron star or a black hole. • In most cases, the rest of the star then blows up, in a gargantuan explosion called a supernova. ...
a description of planets and stars you may see
... The Triangulum galaxy, Messier 33, is spiral galaxy approximately 3 million light years from Earth in the constellation Triangulum. The Triangulum Galaxy is the third-largest member of the Local Group of galaxies, which includes the Milky Way Galaxy, the Andromeda Galaxy. It is one of the most dista ...
... The Triangulum galaxy, Messier 33, is spiral galaxy approximately 3 million light years from Earth in the constellation Triangulum. The Triangulum Galaxy is the third-largest member of the Local Group of galaxies, which includes the Milky Way Galaxy, the Andromeda Galaxy. It is one of the most dista ...
Physics@Brock - Brock University
... Contemplating the stars, their enormous distances from us, their enormous sizes (some are so large that they would swallow up the entire orbit of the Earth!), their complex workings, and their interesting life stories, never fails to elicit a cosmic feeling. The universe is vast, and we are but a sm ...
... Contemplating the stars, their enormous distances from us, their enormous sizes (some are so large that they would swallow up the entire orbit of the Earth!), their complex workings, and their interesting life stories, never fails to elicit a cosmic feeling. The universe is vast, and we are but a sm ...