RIPL Radio Interferometric Planet Search
... with RV method Planet fraction of low mass stars poorly determined Detects planets that can be studied with extreme AO Ties radio and optical astrometric reference frame ...
... with RV method Planet fraction of low mass stars poorly determined Detects planets that can be studied with extreme AO Ties radio and optical astrometric reference frame ...
ref H-R Spectral types
... • how H-R diagrams were developed, and • why the temperature scale goes “the wrong way”. In the next Activity, we will study a real example by continuing the story of how a huge, cool molecular cloud can become a blazing star, and we’ll use H-R diagrams to help us. ...
... • how H-R diagrams were developed, and • why the temperature scale goes “the wrong way”. In the next Activity, we will study a real example by continuing the story of how a huge, cool molecular cloud can become a blazing star, and we’ll use H-R diagrams to help us. ...
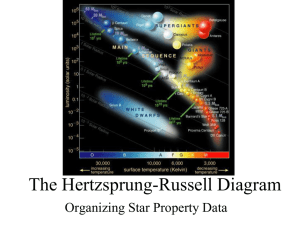
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
Star - AUSD Blogs
... and geophysics out of proportion to our numbers. Will my report on the Phoenix Nebula end our thousand years of history? It will end, I fear, much more than that. I do not know who gave the nebula its name, which seems to me a very bad one. If it contains a prophecy, it is one that cannot be verifie ...
... and geophysics out of proportion to our numbers. Will my report on the Phoenix Nebula end our thousand years of history? It will end, I fear, much more than that. I do not know who gave the nebula its name, which seems to me a very bad one. If it contains a prophecy, it is one that cannot be verifie ...
Astronomy 100—Exam 2
... E. Iron 11. A white dwarf is supported against collapse by A. thermal pressure. C. electron degeneracy pressure. B. gravity. D. neutron degeneracy pressure. ...
... E. Iron 11. A white dwarf is supported against collapse by A. thermal pressure. C. electron degeneracy pressure. B. gravity. D. neutron degeneracy pressure. ...
DYNAMICAL STABILITY OF SPHERICAL STARS
... by the same factor: r = r0 (1 + x), where x is a very small number that may vary with time, but not in space. Mass conservation expressed with eq. (d.1b) demands that ρ = ρ0 (1 − 3x). We shall assume that the change is adiabatic, with a constant adiabatic exponent γ : ...
... by the same factor: r = r0 (1 + x), where x is a very small number that may vary with time, but not in space. Mass conservation expressed with eq. (d.1b) demands that ρ = ρ0 (1 − 3x). We shall assume that the change is adiabatic, with a constant adiabatic exponent γ : ...
TF_final3 - Arecibo Observatory
... velocity width (W) of the lines is proportional to its luminosity (L) following an equation, L ∝ In a sample of 33 LIRGs the neutral hydrogen emission line width was measured. The luminosities of these galaxies from literature were found and a study was made of whether the Tully-Fisher law is mainta ...
... velocity width (W) of the lines is proportional to its luminosity (L) following an equation, L ∝ In a sample of 33 LIRGs the neutral hydrogen emission line width was measured. The luminosities of these galaxies from literature were found and a study was made of whether the Tully-Fisher law is mainta ...
William Paterson University Department of Physics General
... Every student at William Paterson has a student university e-mail address. Your university email address is attached to Blackboard, and that is the one that will be used to contact you about assignments and other matters related to the course. You should check it daily. AOL users: if you have AOL, y ...
... Every student at William Paterson has a student university e-mail address. Your university email address is attached to Blackboard, and that is the one that will be used to contact you about assignments and other matters related to the course. You should check it daily. AOL users: if you have AOL, y ...
the lives of stars
... star, has been a main sequence star for about 5 billion years. It will continue to shine without changing for about 5 billion more years. Really large stars burn through their supply of hydrogen very quickly, so they ‘live fast and die young’! These very large stars may only be on the main sequence ...
... star, has been a main sequence star for about 5 billion years. It will continue to shine without changing for about 5 billion more years. Really large stars burn through their supply of hydrogen very quickly, so they ‘live fast and die young’! These very large stars may only be on the main sequence ...
Properties of Stars in general
... • But its mass (= fuel supply) is only ~ 17 times that of our Sun. • So its life cannot be so long: ~ 17/45,000 that of our Sun ************* ...
... • But its mass (= fuel supply) is only ~ 17 times that of our Sun. • So its life cannot be so long: ~ 17/45,000 that of our Sun ************* ...
Exercise 8
... such a way that the apparent size of a galaxy is related to its distance from Earth. This is method similar to the main-sequence fitting we did in an earlier exercise for star clusters. Figure 8.1 shows the images and visible spectra of five elliptical galaxies. The spectrum of each galaxy is shown ...
... such a way that the apparent size of a galaxy is related to its distance from Earth. This is method similar to the main-sequence fitting we did in an earlier exercise for star clusters. Figure 8.1 shows the images and visible spectra of five elliptical galaxies. The spectrum of each galaxy is shown ...
Test 2, Nov. 17, 2015 - Physics@Brock
... 2. According to Kepler’s second law, a planet moves fastest when it is (a) closest to the Sun. (b) at the greatest distance from the Sun. (c) [The speed of the planet does not depend on its distance from the Sun.] 3. It is possible to determine the mass of a planet from the orbital data (the period ...
... 2. According to Kepler’s second law, a planet moves fastest when it is (a) closest to the Sun. (b) at the greatest distance from the Sun. (c) [The speed of the planet does not depend on its distance from the Sun.] 3. It is possible to determine the mass of a planet from the orbital data (the period ...
A stars
... Around Sirius (Spectral type A1: 26 times more luminous than the Sun), an Earth-sized planet would have to orbit at about the distance of Jupiter from the star. Around Epsilon Indi (Spectral type K5: about one-tenth the Sun's luminosity), an Earth-sized planet would have to orbit at about the distan ...
... Around Sirius (Spectral type A1: 26 times more luminous than the Sun), an Earth-sized planet would have to orbit at about the distance of Jupiter from the star. Around Epsilon Indi (Spectral type K5: about one-tenth the Sun's luminosity), an Earth-sized planet would have to orbit at about the distan ...
File
... The Solar System formed 4.568 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a region within a large molecular cloud. This initial cloud was likely several light-years across and probably birthed several stars. As is typical of molecular clouds, this one consisted mostly of hydrogen, with some ...
... The Solar System formed 4.568 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a region within a large molecular cloud. This initial cloud was likely several light-years across and probably birthed several stars. As is typical of molecular clouds, this one consisted mostly of hydrogen, with some ...
Lecture 9/10 Stellar evolution Ulf Torkelsson 1 Main sequence stars
... flash as a dimming of the star. Presumably these event are also related to significant mass loss events in the evolution of the star. Eventually the surface layers of the star are expelled, and a degenerate carbon-oxygen core remains at the centre of the star. This core becomes a white dwarf. On the ...
... flash as a dimming of the star. Presumably these event are also related to significant mass loss events in the evolution of the star. Eventually the surface layers of the star are expelled, and a degenerate carbon-oxygen core remains at the centre of the star. This core becomes a white dwarf. On the ...
Neutron Stars
... If initial star mass < 8 MSun or so. (and remember: Maximum WD mass is 1.4 MSun , radius is about that of the Earth) ...
... If initial star mass < 8 MSun or so. (and remember: Maximum WD mass is 1.4 MSun , radius is about that of the Earth) ...
Teacher Guide - Astronomy Outreach at UT Austin
... which these stars differ as they progress through their various stages of life and death. A star, like our Sun, is an enormous and complex system. In order to model and understand their properties and how they change with time, astronomers and astrophysicists apply the basic ideas in physics to math ...
... which these stars differ as they progress through their various stages of life and death. A star, like our Sun, is an enormous and complex system. In order to model and understand their properties and how they change with time, astronomers and astrophysicists apply the basic ideas in physics to math ...