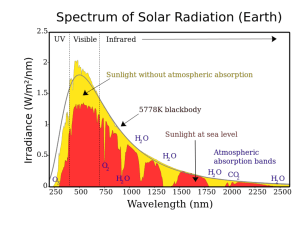
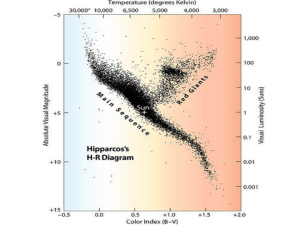
Astron 104 Laboratory #7 Nuclear Fusion and Stars
... You are intimately linked to the nuclear fusion that occurs in stars. Life on Earth thrives on sunlight, which originates as energy produced at the center of the Sun as hydrogen is fused to form helium. Even the very atoms and molecules of your body — iron in your blood, calcium in your bones, phosp ...
... You are intimately linked to the nuclear fusion that occurs in stars. Life on Earth thrives on sunlight, which originates as energy produced at the center of the Sun as hydrogen is fused to form helium. Even the very atoms and molecules of your body — iron in your blood, calcium in your bones, phosp ...
Neutron Star - Perry Local Schools
... • What natural cycles do stars go through? • In a way that is similar to other natural cycles, stars are born, go through various stages of development, and eventually die. • The sun formed from a cloud of gas and dust. – The sun formed about 5 billion years ago. – Stars do not last forever. – The s ...
... • What natural cycles do stars go through? • In a way that is similar to other natural cycles, stars are born, go through various stages of development, and eventually die. • The sun formed from a cloud of gas and dust. – The sun formed about 5 billion years ago. – Stars do not last forever. – The s ...
PHY111 Stellar Evolution
... unstable nuclei decay before next capture, so this makes nuclei close to line of maximum stability, and generally next to other stable nuclei makes very unstable neutron-rich nuclei which produce stable nuclei by β-decay, so can’t make nuclei where the β-decay path is blocked ...
... unstable nuclei decay before next capture, so this makes nuclei close to line of maximum stability, and generally next to other stable nuclei makes very unstable neutron-rich nuclei which produce stable nuclei by β-decay, so can’t make nuclei where the β-decay path is blocked ...
Stars - TeacherWeb
... – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
Einstein
... light is emitted by charged particles moving close to the speed of light around magnetic fields. • Emission (mostly radio) is concentrated at the magnetic poles and focused into a beam. • Whether we see a pulsar depends on the geometry. – if the polar beam sweeps by Earth’s direction once each rotat ...
... light is emitted by charged particles moving close to the speed of light around magnetic fields. • Emission (mostly radio) is concentrated at the magnetic poles and focused into a beam. • Whether we see a pulsar depends on the geometry. – if the polar beam sweeps by Earth’s direction once each rotat ...
Chapter 10 Measuring the Stars: Giants, Dwarfs, and the Main
... • Transverse - perpendicular to line of sight • Radial - along our line of sight * ___________________ - annual movement of a star across the sky as seen from Earth • _____________________ has the largest known proper motion of any star ...
... • Transverse - perpendicular to line of sight • Radial - along our line of sight * ___________________ - annual movement of a star across the sky as seen from Earth • _____________________ has the largest known proper motion of any star ...
Degeneracy pressure Normal/degeneracy pressure White dwarfs — Oct 10
... • End of the road: planetary nebula & white dwarf core ...
... • End of the road: planetary nebula & white dwarf core ...
1. Base your answer to the following question
... the standard spectrum to the spectrum produced from this distant star? (1) The star’s spectral lines have shifted toward the ultraviolet end of the spectrum and the star is moving toward Earth. (2) The star’s spectral lines have shifted toward the infrared end of the spectrum and the star is moving ...
... the standard spectrum to the spectrum produced from this distant star? (1) The star’s spectral lines have shifted toward the ultraviolet end of the spectrum and the star is moving toward Earth. (2) The star’s spectral lines have shifted toward the infrared end of the spectrum and the star is moving ...
Calculating Main Sequence Lifetimes
... ‘short’ period the stellar temperature decreases without a great change of luminosity. The star burns Hydrogen in shell (red giants) through the CNO cycle: as its radius increases so its luminosity raises. Helium flash: the star begins to burn Helium maintaining the combustion of Hydrogen in shells. ...
... ‘short’ period the stellar temperature decreases without a great change of luminosity. The star burns Hydrogen in shell (red giants) through the CNO cycle: as its radius increases so its luminosity raises. Helium flash: the star begins to burn Helium maintaining the combustion of Hydrogen in shells. ...
7a Properties of Stars.pptx
... • Measured in light-‐years – distance light travels in one year (9.5 x 1012 or 9.5 trillion kilometers) ...
... • Measured in light-‐years – distance light travels in one year (9.5 x 1012 or 9.5 trillion kilometers) ...
MSci Astrophysics 210PHY412 - Queen's University Belfast
... Students should be able to understand the basic physics underlying complex stellar evolution models Students will learn how to interpret observational characteristics of stars in terms of the underlying physical parameters You should gain an understanding of how stars of different mass evolve, and w ...
... Students should be able to understand the basic physics underlying complex stellar evolution models Students will learn how to interpret observational characteristics of stars in terms of the underlying physical parameters You should gain an understanding of how stars of different mass evolve, and w ...
jackie822 beanerbutt777 life cycle of a star
... http://solarsystem.nasa.gov/multimedia/gallery/prominence.gif ...
... http://solarsystem.nasa.gov/multimedia/gallery/prominence.gif ...
Astronomical Numbers
... flat earth under a domed sky. 3) From Earth, stars appear to move in circles around Polaris, the North Star. ...
... flat earth under a domed sky. 3) From Earth, stars appear to move in circles around Polaris, the North Star. ...
Chapter16
... absorption line — A dark line superimposed on a continuous spectrum when a gas absorbs light from a continuous source that is hotter than the absorbing gas. antapex — The direction in the sky away from which the Sun is moving. Because of the Sun’s motion, nearby stars appear to converge toward the a ...
... absorption line — A dark line superimposed on a continuous spectrum when a gas absorbs light from a continuous source that is hotter than the absorbing gas. antapex — The direction in the sky away from which the Sun is moving. Because of the Sun’s motion, nearby stars appear to converge toward the a ...
Slide 1
... which predicts an effect 8 times larger than a classical approach! Even so the angle with b as the solar radius is at most only 1.74” of arc, a difficult measurement which has been tested (Eddington 1914,1919) but with an error factor. Radio time delays via interplanetary satellites in the extra pat ...
... which predicts an effect 8 times larger than a classical approach! Even so the angle with b as the solar radius is at most only 1.74” of arc, a difficult measurement which has been tested (Eddington 1914,1919) but with an error factor. Radio time delays via interplanetary satellites in the extra pat ...
Phobos
... observations of galaxy clusters, distances have been estimated to 38 galaxy clusters ranging from 1.4 to 9.3 billion light-years. The results give a Hubble constant of 77 km/s per megaparsec, with an uncertainty of about 15%, thereby reinforcing other recent values. The implied age of the Universe i ...
... observations of galaxy clusters, distances have been estimated to 38 galaxy clusters ranging from 1.4 to 9.3 billion light-years. The results give a Hubble constant of 77 km/s per megaparsec, with an uncertainty of about 15%, thereby reinforcing other recent values. The implied age of the Universe i ...
pptx
... • A hydrogen atom consists of 1 proton and 1 electron. • Inside of a star, the protons and electrons are detached from each other, and move around freely by themselves. • At lower temperatures, protons move slowly, so they repel ...
... • A hydrogen atom consists of 1 proton and 1 electron. • Inside of a star, the protons and electrons are detached from each other, and move around freely by themselves. • At lower temperatures, protons move slowly, so they repel ...
RED GIANTS
... • The star can no longer support its weight • The enormous weight from the outer layers compresses hydrogen in the layers just outside the core enough to initiate shell hydrogen fusion. • This extra internal heat causes the outer layers to expand into a giant star. ...
... • The star can no longer support its weight • The enormous weight from the outer layers compresses hydrogen in the layers just outside the core enough to initiate shell hydrogen fusion. • This extra internal heat causes the outer layers to expand into a giant star. ...
Lecture 13 (pdf from the powerpoint)
... •Gravitational contraction reaches hot enough for fusion •0.08 M sun •88 M Jupiter • smaller > Brown dwarf •Upper limit ~ 100Msun ...
... •Gravitational contraction reaches hot enough for fusion •0.08 M sun •88 M Jupiter • smaller > Brown dwarf •Upper limit ~ 100Msun ...