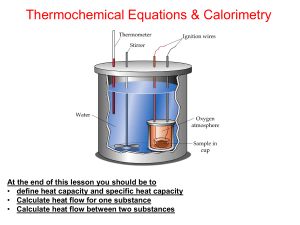
1 - mrfiust
... In the demonstration, a heated 0.06 kg copper pipe was dropped into a beaker of water. Students in the class were asked to predict the final temperature of the beaker of water when it reached equilibrium with the copper pipe. a. If this demonstration took place in a closed insulated beaker, instead ...
... In the demonstration, a heated 0.06 kg copper pipe was dropped into a beaker of water. Students in the class were asked to predict the final temperature of the beaker of water when it reached equilibrium with the copper pipe. a. If this demonstration took place in a closed insulated beaker, instead ...
6 Physical Properties and Principles I. Review of Fundamental
... Why? Because the crystal structure of ice takes up more space (greater volume) than the structure of liquid water molecules ...
... Why? Because the crystal structure of ice takes up more space (greater volume) than the structure of liquid water molecules ...
1 Analytical model for Stirling cycle machine design Corresponding
... as a function of fluid flow rates are added. Though it is not a free piston type engine, the GPU-3, it is one of the most documented Stirling engine and its data are therefore used to compare the model results to the experimental ones. For a wide range of different pressures and frequencies, the mod ...
... as a function of fluid flow rates are added. Though it is not a free piston type engine, the GPU-3, it is one of the most documented Stirling engine and its data are therefore used to compare the model results to the experimental ones. For a wide range of different pressures and frequencies, the mod ...
heat vs temp student sheet
... moves from hot to cold. It has units of Joules, calories or Calories (kcal). The symbols used for heat are ΔH or q. Heat is not directly measureable. It must be calculated using the following formula q = mCΔT. 10. Are heat and temperature the same? ...
... moves from hot to cold. It has units of Joules, calories or Calories (kcal). The symbols used for heat are ΔH or q. Heat is not directly measureable. It must be calculated using the following formula q = mCΔT. 10. Are heat and temperature the same? ...
ME 410 Day 15 Topics • Properties of Gas Mixtures - Rose
... 3. Exercise 2 (This is Problem 4.13) Further Practice in Using EES A diesel engine has a compression ratio of 22:1. The conditions in the cylinder at the start of compression are p=101.3 kPa and T=325 K. Calculate the pressure and temperature at the end of compression, assuming that compression is ...
... 3. Exercise 2 (This is Problem 4.13) Further Practice in Using EES A diesel engine has a compression ratio of 22:1. The conditions in the cylinder at the start of compression are p=101.3 kPa and T=325 K. Calculate the pressure and temperature at the end of compression, assuming that compression is ...
doc heat conversion
... Temperature can be defined as the degree to which a body is hot or cold. In simple terms, temperature is a means of detecting the existence of heat energy in a substance (What is Heat, 2010). The effect of heat energy of a substance gives the temperature of that particular substance. For example, wh ...
... Temperature can be defined as the degree to which a body is hot or cold. In simple terms, temperature is a means of detecting the existence of heat energy in a substance (What is Heat, 2010). The effect of heat energy of a substance gives the temperature of that particular substance. For example, wh ...
Heat - Ms. Bergman`s Classes at DCIS Montbello
... d) Heat is caused by the sun, and temperature is caused by conditions in the atmosphere ...
... d) Heat is caused by the sun, and temperature is caused by conditions in the atmosphere ...
ICEST2015 Paper Template
... rather than to its conversion to electrical energy. The primary forms of direct use include heating and cooling. Geothermal energy could be used to supply hot water or could be used with a special equipment (radiators) to make buildings warmer during winter seasons. In general, the geothermal fluid ...
... rather than to its conversion to electrical energy. The primary forms of direct use include heating and cooling. Geothermal energy could be used to supply hot water or could be used with a special equipment (radiators) to make buildings warmer during winter seasons. In general, the geothermal fluid ...
Heat Transfer Equipment Wort kettle – External calandria
... Energy Balance Example The power goes out at your brewery due to an overheated transformer, shutting down your fermentation cooling mechanism. Consider a 25 m3 cylindroconical vessel that is full with a product at 10oC, specific heat of 3.4 kJ/kg.K, and density of 1025 kg/m3. Assuming that the sum ...
... Energy Balance Example The power goes out at your brewery due to an overheated transformer, shutting down your fermentation cooling mechanism. Consider a 25 m3 cylindroconical vessel that is full with a product at 10oC, specific heat of 3.4 kJ/kg.K, and density of 1025 kg/m3. Assuming that the sum ...
Heat Sinks and Component Temperature Control
... • Pconv = convective heat loss to surrounding air from a vertical surface at sea level having a height dvert [in meters] less than one meter. ...
... • Pconv = convective heat loss to surrounding air from a vertical surface at sea level having a height dvert [in meters] less than one meter. ...
Ventilation: The System Stabilizer
... Intake vents are best installed in or near the roof eaves wherever they occur on a home. This helps protect against rain and snow infiltration and provides a more equal distribution of positive and negative pressure areas. ...
... Intake vents are best installed in or near the roof eaves wherever they occur on a home. This helps protect against rain and snow infiltration and provides a more equal distribution of positive and negative pressure areas. ...
Heat wave: Caring for babies and young children
... as quickly as an adult, even though they have been affected. They rely on others to control their environment and keep them from getting dehydrated or overheated and it is vey important to watch them closely Signs of heat stress and what to do Babies and young children may not show early signs and s ...
... as quickly as an adult, even though they have been affected. They rely on others to control their environment and keep them from getting dehydrated or overheated and it is vey important to watch them closely Signs of heat stress and what to do Babies and young children may not show early signs and s ...
Thermoregulation
... The animal actually has considerable control over many facets of this equation. – The animal can control surface area to some extent – The animal can control view factor. – The animal can control absorptivity. – S can be modified through position. ...
... The animal actually has considerable control over many facets of this equation. – The animal can control surface area to some extent – The animal can control view factor. – The animal can control absorptivity. – S can be modified through position. ...
appendecies
... temperature of the wire and ambient respectively, ∆H is the latent heat associated with the phase transformation [71]. This equation presents the effect of the Joule heating, convection heat transfer, and latent heat on the internal energy of the wire. ...
... temperature of the wire and ambient respectively, ∆H is the latent heat associated with the phase transformation [71]. This equation presents the effect of the Joule heating, convection heat transfer, and latent heat on the internal energy of the wire. ...
energy recovery ventilation
... Heat pumps are not ERV units. They are reversed heat engine or reversible vapor-compression refrigeration devices. Heat pumps are optimized for high efficiency in both directions of thermal energy transfer and can be an efficient way of heating or cooling a building. Just like the heat pipe and the ...
... Heat pumps are not ERV units. They are reversed heat engine or reversible vapor-compression refrigeration devices. Heat pumps are optimized for high efficiency in both directions of thermal energy transfer and can be an efficient way of heating or cooling a building. Just like the heat pipe and the ...
8. Temperature and Heat - City, University of London
... The aim is to find the final temperature of the block and water, assuming the calorimeter is light enough for it to be ignored, and that no heat is transferred from the calorimeter to its surroundings Remember that the final temperature of the block and water will be equal, and that the total energy ...
... The aim is to find the final temperature of the block and water, assuming the calorimeter is light enough for it to be ignored, and that no heat is transferred from the calorimeter to its surroundings Remember that the final temperature of the block and water will be equal, and that the total energy ...
Currents experiment
... What are the three types of heat transfer? How is heat transferred through space? What is a convection current? In general, what happens to the density of a fluid as it ...
... What are the three types of heat transfer? How is heat transferred through space? What is a convection current? In general, what happens to the density of a fluid as it ...
Thermochemistry Lesson 2
... (solution/water and calorimeter) absorb heat. • Temperature increase Solution absorbs heat therefore the reaction is exothermic • Temperature decrease solution releases heat therefore the reaction is endothermic. • (ΔHrxn = Qrxn/n) • Assumptions - For dilute acid or bases the density is close to ...
... (solution/water and calorimeter) absorb heat. • Temperature increase Solution absorbs heat therefore the reaction is exothermic • Temperature decrease solution releases heat therefore the reaction is endothermic. • (ΔHrxn = Qrxn/n) • Assumptions - For dilute acid or bases the density is close to ...
q - webhosting.au.edu
... DE is the change in internal energy of a system q is the heat exchange between the system and the surroundings w is the work done on (or by) the system w = -PDV when a gas expands against a constant external pressure ...
... DE is the change in internal energy of a system q is the heat exchange between the system and the surroundings w is the work done on (or by) the system w = -PDV when a gas expands against a constant external pressure ...
calorimetry
... neutralization for an acid-base reaction; and the heat of solution for a salt dissolving in water. SPECIFIC HEAT OF A METAL: THE LAW OF DULONG AND PETIT The quantity of heat required to change the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 oC is the specific heat of that substance. The specific heat ...
... neutralization for an acid-base reaction; and the heat of solution for a salt dissolving in water. SPECIFIC HEAT OF A METAL: THE LAW OF DULONG AND PETIT The quantity of heat required to change the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 oC is the specific heat of that substance. The specific heat ...
Basic Modes of Heat Transfer
... ambient air. This equation is a bit tricky because h, heat transfer coefficient, encompasses several parameters, namely airflow. It is extremely important to understand air flow and making proper design considerations for airflow since it plays a major role in convection. To give the reader an idea ...
... ambient air. This equation is a bit tricky because h, heat transfer coefficient, encompasses several parameters, namely airflow. It is extremely important to understand air flow and making proper design considerations for airflow since it plays a major role in convection. To give the reader an idea ...
Heat is energy transferring in a system and its surroundings.
... (c) the amount of energy transferred between objects as a result of a difference in temperature. (d) an invisible, odorless, weightless substance. (e) the total kinetic energy of an ideal gas. ...
... (c) the amount of energy transferred between objects as a result of a difference in temperature. (d) an invisible, odorless, weightless substance. (e) the total kinetic energy of an ideal gas. ...
AGU Fall Meeting 08 - Global Heat Flow Database
... In a conductive thermal regime, heat flow is predictable. Diagram 2a shows temperature and heat flow curves for conductive continental and oceanic thermal regimes. Continental heat flow decreases with depth as radiogenic heat decreases, but with radiogenic heat two orders of magnitude less than that ...
... In a conductive thermal regime, heat flow is predictable. Diagram 2a shows temperature and heat flow curves for conductive continental and oceanic thermal regimes. Continental heat flow decreases with depth as radiogenic heat decreases, but with radiogenic heat two orders of magnitude less than that ...
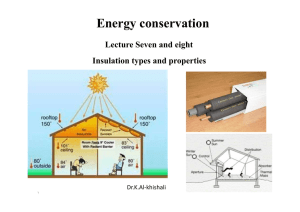
Why insulate?
... There is no set definition of super insulation, but super insulated buildings typically include: •Very high levels of insulation (typically Rip40 walls and Rip60 roof, corresponding to SI Uvalues of 0.15 and 0.1 W/(m²·K) respectively) •Details to ensure insulation continuity where walls meet roofs, ...
... There is no set definition of super insulation, but super insulated buildings typically include: •Very high levels of insulation (typically Rip40 walls and Rip60 roof, corresponding to SI Uvalues of 0.15 and 0.1 W/(m²·K) respectively) •Details to ensure insulation continuity where walls meet roofs, ...
A Mathematical Analysis of Two Dimensional Steady State Heat
... problems in 2-Dimentional (2-D) and in 3Dimentional (3-D) also. After considering some geometrical restrictions, we get the solution almost equal to the original values and hence this method is advantageous, hence is used here ...
... problems in 2-Dimentional (2-D) and in 3Dimentional (3-D) also. After considering some geometrical restrictions, we get the solution almost equal to the original values and hence this method is advantageous, hence is used here ...
Intercooler

An intercooler is any mechanical device used to cool a fluid, including liquids or gases, between stages of a multi-stage heating process, typically a heat exchanger that removes waste heat in a gas compressor. They are used in many applications, including air compressors, air conditioners, refrigerators, and gas turbines, and are widely known in automotive use as an air-to-air or air-to-liquid cooler for forced induction (turbocharged or supercharged) internal combustion engines to improve their volumetric efficiency by increasing intake air charge density through nearly isobaric (constant pressure) cooling.