Big Bang - schoolphysics
... time and space began at that moment. Before the Big Bang there was no space or time – a very difficult idea to grasp. Anyway we do have some idea of what happened after the Big Bang. The temperature in that explosion was unbelievably large – astrophysicists think it may have been as high as 1000 mil ...
... time and space began at that moment. Before the Big Bang there was no space or time – a very difficult idea to grasp. Anyway we do have some idea of what happened after the Big Bang. The temperature in that explosion was unbelievably large – astrophysicists think it may have been as high as 1000 mil ...
dark matter - Aurora City Schools
... microwave radiation all throughout the universe, but couldn’t explain where it came from • Only possible source is it’s left over from Big Bang • Later shown not to be “evenly spread” ...
... microwave radiation all throughout the universe, but couldn’t explain where it came from • Only possible source is it’s left over from Big Bang • Later shown not to be “evenly spread” ...
6 Big Bang Nucleosynthesis - Course Pages of Physics Department
... occurs at a higher temperature T4 ∼ 0.3 MeV. But we noted earlier that only deuterium stays close to its equilibrium abundance once it gets large. Helium begins to form only when there is sufficient deuterium available, in practice slightly above Td . Helium forms then rapidly. The available number ...
... occurs at a higher temperature T4 ∼ 0.3 MeV. But we noted earlier that only deuterium stays close to its equilibrium abundance once it gets large. Helium begins to form only when there is sufficient deuterium available, in practice slightly above Td . Helium forms then rapidly. The available number ...
Cosmology and Astrophysics II
... duration and space. . . In him are all things contained and moved; yet neither affects the other: God suffers nothing from the motion of bodies; bodies find no resistance from the omnipresence of God. . . As a blind man has no idea of colors so we have no idea of the manner by which the all-wise God ...
... duration and space. . . In him are all things contained and moved; yet neither affects the other: God suffers nothing from the motion of bodies; bodies find no resistance from the omnipresence of God. . . As a blind man has no idea of colors so we have no idea of the manner by which the all-wise God ...
The Origins of Physics, Chemistry, and Biology, or Big Bang is the
... and antimatter was the cause of present state of the Universe comprising of matter and radiation. Very simple chemistry started in proverbial first three minutes after the Big Bang when hydrogen and helium nuclei were created. After 380 thousand years the expanding Universe cooled down sufficiently ...
... and antimatter was the cause of present state of the Universe comprising of matter and radiation. Very simple chemistry started in proverbial first three minutes after the Big Bang when hydrogen and helium nuclei were created. After 380 thousand years the expanding Universe cooled down sufficiently ...
Name Origins: Back to the Beginning Video Questions http://www
... http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/space/origins-series-overview.html#origins-back-beginning 1. The Big Bang theory has been called the greatest discovery in cosmology. Describe it. ...
... http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/space/origins-series-overview.html#origins-back-beginning 1. The Big Bang theory has been called the greatest discovery in cosmology. Describe it. ...
Big Bang Theory
... Within the first minute, 98% of all matter in the universe was formed. It began cooling immediately. ...
... Within the first minute, 98% of all matter in the universe was formed. It began cooling immediately. ...
The Evolution of the Universe: from Cosmic Soup to Earth
... Big Bang: The initial point from which the universe began developing approximately 13.7 billion years ago. Cosmic Microwave Background: the leftover energy that can be detected from the initial Big Bang. Element: a pure chemical substance which is determined by the number of protons in its nu ...
... Big Bang: The initial point from which the universe began developing approximately 13.7 billion years ago. Cosmic Microwave Background: the leftover energy that can be detected from the initial Big Bang. Element: a pure chemical substance which is determined by the number of protons in its nu ...
Lecture 33
... • A few seconds after the Big Bang, the main particle species present were protons, neutrons, neutrinos, and photons ...
... • A few seconds after the Big Bang, the main particle species present were protons, neutrons, neutrinos, and photons ...
Elemental Abundances
... in the harsh environment of stellar interiors • Li abundance comes from measurements in meteorites; it is still lower in the solar photosphere because of destruction by mixing with hotter layers below. • Abundant in primary cosmic rays as a result of fusion and spallation reactions between p and (ma ...
... in the harsh environment of stellar interiors • Li abundance comes from measurements in meteorites; it is still lower in the solar photosphere because of destruction by mixing with hotter layers below. • Abundant in primary cosmic rays as a result of fusion and spallation reactions between p and (ma ...
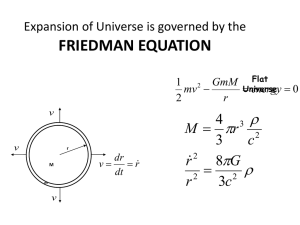
Helium Production in Big Bang Weighing a Galaxy12 Nov 11/12/2010
... • When T is between 10BK and 3BK, the density drops so that – number of collisions falls & neutrons and protons are no longer in equilibrium. – Protons no longer change into neutrons. Neutrons decay into protons. ...
... • When T is between 10BK and 3BK, the density drops so that – number of collisions falls & neutrons and protons are no longer in equilibrium. – Protons no longer change into neutrons. Neutrons decay into protons. ...
Lecture 9
... They all have large cross-sections and fast reaction rates ⇒ deuterium efficiently converts to 4 He. ...
... They all have large cross-sections and fast reaction rates ⇒ deuterium efficiently converts to 4 He. ...
Origin of Elements - Madison Public Schools
... concentrated in one point. The “Big Bang” refers to the extraordinary explosion from that infinitesimal point. ...
... concentrated in one point. The “Big Bang” refers to the extraordinary explosion from that infinitesimal point. ...