* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cosmology and Astrophysics II
Dark matter wikipedia , lookup
Hawking radiation wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
First observation of gravitational waves wikipedia , lookup
Standard solar model wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Weakly-interacting massive particles wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Flatness problem wikipedia , lookup
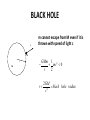
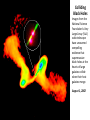
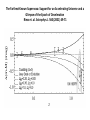
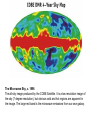
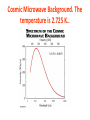
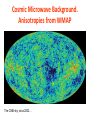
Expansion of Universe is governed by the FRIEDMAN EQUATION 1 2 GmM Flat Universe mv energy 0 2 r v M v r M m v dr v r dt r 2 2 r 4 3 r 2 3 c 8G 2 3c and the CONTINUITY EQUATION dE pdV TdS 0 4 3 E r 3 r 3( p) 0 r 4 3 V r 3 Reversible Expansion Types of matter energy in our universe p 0, p , matterhas, 1 ~ 3, r dark energy, ~ 1, a~t 2 3 a ~ et Dark energy contribution to energy density in rhs of Einstein-Friedman equation cannot be differentiated from cosmological constant on lhs. kind of matter equation of state ρ = ρ(a) a = a(t) Hagedorn p=ρ 1/a**6 t**(1/3) Radiation p = ρ/3 1/a**4 t**(1/2) Matter/Dust p=0 1/a**3 t**(2/3) Cosmic Strings p = -ρ/3 1/a**2 t 1/a**2 t Space Curvature Cosmic Walls p = -2ρ/3 1/a t**2 Dark Energy or p = -ρ 1 exp(t) 1 exp(t) Cosmological Constant Dark Matter = Matter in the universe which we cannot see. Black holes Brown dwarfs Massive Neutrinos Axions WIMP Gravitinos BLACK HOLE c m cannot escape from M even if it is thrown with speed of light c m r M GMm 1 2 mc 0 r 2 r 2GM black hole radius 2 c Colliding Black Holes Images from the National Science Foundation's Very Large Array (VLA) radio telescope have uncovered compelling evidence that supermassive black holes at the hearts of large galaxies collide when their host galaxies merge. August 1, 2002 11 pointings from September 21, 1999 through June 04, 2002 Lobes of hot gas (red) surround the Milky Way center. The black hole is located inside the white region of inte X-ray emission. (energy uncertainity)x(time uncertainity) = h speed of light = c = 300 Mm/s conversion factor c2 = 1017 J/kg conversion factor hc = 1240 eV.nm 1eV = (1240nm) -1 eV = -1 (μm) A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter, contains 107 to 1012 stars A star is a massive, luminous ball of plasma that is held together by gravity, ½ to 20 times the mass of sun. A supernova (plural supernovae) is a stellar explosion. A white dwarf, is a small star composed mostly of electrondegenerate matter. They are very dense; a white dwarf's mass is comparable to that of the Sun and its volume is comparable to that of the Earth. The Crab Nebula is a pulsar wind nebula associated with the 1054 supernova. SN 1994D in the NGC 4526 galaxy (bright spot on the lower left). Image by NASA, ESA, The Hubble Key Project Team, and The High-Z Supernova Search Team A Type Ia supernova results from the violent explosion of a white dwarf star when it reaches 1.4 times the sun’s mass. These supernova always explode with fixed luminosity and thus are the standard candles of the universe. By measuring their redshift and brigtness we conclude how universe has expanded in the past and how it is expanding now. A neutron star is a type of remnant that can result from the gravitational collapse of a massive star during a supernova event. Such stars are composed almost entirely of neutrons. If the exploding star leaves a core remnant between 1.4 to 2 solar masses the remnant is a neutron star. If the remnant is more than 5 times the mass of the sun it becomes a black hole. In between it may be a quark star which are yet hypothetical. Süpernova SN1997ff The Farthest Known Supernova: Support for an Accelerating Universe and a Glimpse of the Epoch of Deceleration Riess et. al. Astrophys.J. 560 (2001) 49-71 Karanlık madde: Yıldızların içinde bulundukları galaksinin merkezi etrafında dönüş hızlarını ölçerek varlığını bulduğumuz ama şu anda gözlemleyemediğimiz madde. Bugünkü evrendeki toplam madde-enerji’nin %22 si karanlık maddedir. Karanlık enerji: Evren genişledikçe yoğunluğu sabit kalan bir “madde-enerji” türü. Bugünkü evrendeki toplam madde-enerji’nin %75 ii karanlık enerjidir. Görünen madde: %3 The Microwave Sky, c. 1996 The all-sky image produced by the COBE Satellite. It is a low resolution image of the sky (7 degree resolution), but obvious cold and hot regions are apparent in the image. The large red band is the microwave emissions from our own galaxy. • Empirical foundations of the Big Bang theory. – Cosmic Microwave Background. – Physical and chemical composition of the Universe. Cosmic Microwave Background • • • The cosmic microwave background was discovered as a background “noise” a real problem for telecommunication satellites (1965) Wherever Penzias and Wilson pointed their antenna they would detect a microwave signal, very uniform across the sky This signal is now called the cosmic microwave background… Cosmic Microwave Background • • • The CMB was already visible in the data taken by Dunham and Adams of the properties of CN in the interstellar medium …back in 1937 The saw that CN was excited as if it was immersed in a thermal bath of radiation of temperature T~3K… But nobody realized it.. So the Nobel Prize went to Penzias & Wilson… and not to Dunham and Adams.. Such is life.. Cosmic Microwave Background • • A group of physicist (initially Gamow (1948) and then Alpher and Hermann (1950) and then Dicke and his group at Princeton) had predicted such radiation, from the so-called big bang nucleosynthesis theory (later in the class..) The CMB was predicted to be: – – – Thermal At a temperature of about 5K Isotropic Dicke was devising a CMB search when the discovery was made. His paper with Peebles, Roll, and Wilkinson presented the cosmological interpretation along-side the Penzias and Wilson paper. Cosmic Microwave Background. Thermal “Blackbody” Radiation • • • We know Penzias and Wilson detected isotropic radiation, so that was consistent with the Big Bang model and the copernican principle The theory predicted it to be thermal, i.e. a blackbody. But what is really a blackbody? 1. Matter and radiation in equilibrium 2. Characteristic spectral shape 3. Wien’s Law - hotter body produces higher energy photons Is the Microwave Background Radiation a Blackbody? COBE got the answer Cosmic Microwave Background. The temperature is 2.725 K.. Cosmic Microwave Background. Anisotropies from WMAP The CMB sky, circa 2002… What is the universe made of? “normal” matter • • • • Ordinary matter is made for the most part of protons and neutrons, i.e. quarks up and down. For this reason we refer to ordinary matter as baryonic matter Neutrinos should not have mass in the standard model, but they do (neutrino oscillations) No antimatter is observed! What baryons? Chemical composition of stars. • • • • • • The sun is made of: Hydrogen (74% by mass) Helium (25%) Heavier elements (1%) commonly referred to as “metals” by astrophysicists This is way more He than expected from a universe initially made of Hydrogen where Helium is produced in stars… This is a common problem: Helium abundance is always ~25% Helium abundance. The Big Bang solution • • • He is produced in the early Universe when T was high enough (above ~109 K) to allow for nuclear fusion. Why do you need high temperature to do fusion? The Big Bang theory predicts exactly the abundance of all heavy elements. Big Bang nucleosynthesis predicts a primordial abundance of about 25% helium-4 by mass, irrespective of the initial conditions of the universe. As long as the universe was hot enough for protons and neutrons to transform into each other easily, their ratio, determined solely by their relative masses, was about 1 neutron to 7 protons (allowing for some decay of neutrons into protons). Once it was cool enough, the neutrons quickly bound with an equal number of protons to form helium-4. Helium-4 is very stable and neither decays nor combines easily to form heavier nuclei. So out of every 16 nucleons (2 neutrons and 14 protons), 4 of these (25%) combined into one helium-4 nucleus. One analogy is to think of helium-4 as ash, and the amount of ash that one forms when one completely burns a piece of wood is insensitive to how one burns it. The helium-4 abundance is important because there is far more helium-4 in the universe than can be explained by stellar nucleosynthesis. In addition, it provides an important test for the Big Bang theory. If the observed helium abundance is much different from 25%, then this would pose a serious challenge to the theory. This would particularly be the case if the early helium-4 abundance was much smaller than 25% because it is hard to destroy helium-4. For a few years during the mid-1990s, observations suggested that this might be the case, causing astrophysicists to talk about a Big Bang nucleosynthetic crisis, but further observations were consistent with the Big Bang theory.[ Theories which govern Particles and Cosmology: Special Relativity depends on the absoluteness of light velocity. In simple terms velocity of light “added to” any other velocity still gives velocity of light. Quantum Field Theory unifies quantum physics whose basis is the uncertainity principle with special relativity. Standard Model incorporates the known particles: leptons, quarks and the electromagnetic, weak and strong force carriers in a consistent Quantum Field Theory . General Relativity generalizes Newtoniain Gravity such that it is consistent with Special Relativity. Both Newtonian Gravity and Special Relativity are noncoinciding special cases of General Relativity. General Relativity depends on the principle that matter-energy curves space-time. As yet no Quantum Field Theory which is consistent with General Relativity exists. A solution to this problem may be that basic entities are not point particles but are strings. Cosmology Astrophysics and Particles: a Postlude 1 : a closing piece of music; especially : an organ voluntary at the end of a church service 2 : a closing phase (as of an epoch or a literary work) God and Physics Newton, in his book “Principia mathemetica” explicitly refers to God and says his work is proof that god exists: God and the Universe This most beautiful system of the sun, planets, and comets could only proceed from the counsel and dominion of an intelligent and powerful Being. And if the fixed stars are the centers of other like systems, these, being formed by the like wise counsel, must be all subject to the dominion of One, especially since the light of the fixed stars is of the same nature with the light of the sun and from every system light passes into all the other systems; and lest the systems of the fixed stars should, by their gravity, fall on each other mutually, he hath placed those systems at immense distances from one another. This Being governs all things not as the soul of the world, but as Lord over all; and on account of his dominion he is wont to be called "Lord God" . . . or "Universal Ruler." . . . It is the dominion of a spiritual being which constitutes a God. . . And from his true dominion it follows that the true God is a living, intelligent and powerful Being. . . he governs all things, and knows all things that are or can be done. . . He endures forever, and is everywhere present; and by existing always and everywhere, he constitutes duration and space. . . In him are all things contained and moved; yet neither affects the other: God suffers nothing from the motion of bodies; bodies find no resistance from the omnipresence of God. . . As a blind man has no idea of colors so we have no idea of the manner by which the all-wise God preserves and understands all things. He is utterly void of all body and bodily figure, and can therefore neither be seen, nor heard, nor touched; nor ought to be worshipped under the representation of any corporeal thing. We have ideas of his attributes, but what the real substance of any thing is we know not.... Much less, then, have we any idea of the substance of God. We know him only by his most wise and excellent contrivances of things. . . We reverence and adore him as his servants, and a god without dominion, providence, and final causes, is nothing else but Fate and Nature. Blind metaphysical necessity, which is certainly the same always and everywhere, could produce no variety of things. All that diversity of natural things which we find suited to different times and places could arise from nothing but the ideas and will of a Being necessarily existing. . . And thus much concerning God, to discourse of whom from the appearances of things does certainly belong to Natural Philosophy. On the other hand Newton’s belief in an eternal nonchanging heaven may have prevented him from discovering the Big Bang model. The Friedman equation which governs the expansion of universe was first derived using General Relativity but we have seen that they can be derived from Newton’s equations. After the discovery of expansion of the universe but before the discovery of CMBR there were two competing theories: 1. The Big Bang model 2. The Steady State model which depended on the perfect cosmological principle. The perfect cosmological principle states that the univerese looks the same at all times as well as it looks the same when observed from different points in all directions. In this model to make up for the expanding univerese matter was constantly created to repair the decreasing density. Some Steady State believers accused the Big Bang believers by being influenced by their belief that God created the universe at Big Bang. CMBR proved that The Big Bang theory was the correct one. Although the Steady State believers accused the Big Bang believers of being too religous, it is a fact that Steady State model is more in concordance with Newton’s ideas.