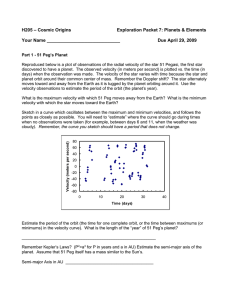
Where Did All The Elements Come From??
... In the very beginning, both space and time were created in the Big Bang. It happened 13.7 billion years ago. Afterwards, the universe was a very hot, expanding soup of fundamental particles. The universe expanded rapidly during inflation and expands at a more or less constant rate now. As it grows, ...
... In the very beginning, both space and time were created in the Big Bang. It happened 13.7 billion years ago. Afterwards, the universe was a very hot, expanding soup of fundamental particles. The universe expanded rapidly during inflation and expands at a more or less constant rate now. As it grows, ...
Unit8TheUniverse
... A. 13-15 b.y.a. the Universe came into being and began to expand at an incredible rate (Inflation). B. Evidence for the Big Bang: The BBT is not designed to explain the origins of the universe only how it developed. 1). Expanding Universe 2). Background radiation that was predicted and later found. ...
... A. 13-15 b.y.a. the Universe came into being and began to expand at an incredible rate (Inflation). B. Evidence for the Big Bang: The BBT is not designed to explain the origins of the universe only how it developed. 1). Expanding Universe 2). Background radiation that was predicted and later found. ...
Celestial Objects
... 1) the farther away the galaxy, the greater the red shift 2) almost all galaxies show a red shiftshiftproof that the universe is expanding (Edwin Hubble was the first to realize this!) ...
... 1) the farther away the galaxy, the greater the red shift 2) almost all galaxies show a red shiftshiftproof that the universe is expanding (Edwin Hubble was the first to realize this!) ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) ISSN: 2278-4861.
... After the super-explosion (The Big-Bang), according to the nebula hypothesis [1], the solar system began as a nebula, an area in the Milky Way Galaxy that was a swirling concentration of cold gas and dust. Due to some perturbation, possibly from the nearby supernova this cloud of gas and dust began ...
... After the super-explosion (The Big-Bang), according to the nebula hypothesis [1], the solar system began as a nebula, an area in the Milky Way Galaxy that was a swirling concentration of cold gas and dust. Due to some perturbation, possibly from the nearby supernova this cloud of gas and dust began ...
Planets and Life - Indiana University Astronomy
... The universe is roughly 1/4 helium and 3/4 hydrogen by mass, but very little of this helium was made in stars. Early in the Big Bang the Universe was hot and dense (like the core of a star) and protons could fuse together to make some helium. The fact that the Universe is 1/4 helium is evidence for ...
... The universe is roughly 1/4 helium and 3/4 hydrogen by mass, but very little of this helium was made in stars. Early in the Big Bang the Universe was hot and dense (like the core of a star) and protons could fuse together to make some helium. The fact that the Universe is 1/4 helium is evidence for ...
Astronomy and Cosmology Exam Review
... the universe? It is expanding 3) What is currently the most accepted theory about the origin of the universe called? Big Bang 4) What can I tell about a star based on its color? What elements are present 5) What is the most common unit for measuring the distance of cosmic objects? Light Years 6) Who ...
... the universe? It is expanding 3) What is currently the most accepted theory about the origin of the universe called? Big Bang 4) What can I tell about a star based on its color? What elements are present 5) What is the most common unit for measuring the distance of cosmic objects? Light Years 6) Who ...
10.1 PPT
... galaxies which are further away from Earth are moving apart faster than those closer to Earth. He used the analogy comparing an uncooked loaf of raisin bread to one that is put into the oven. As the dough rises the raisins (galaxies) are moving further away from each other. ...
... galaxies which are further away from Earth are moving apart faster than those closer to Earth. He used the analogy comparing an uncooked loaf of raisin bread to one that is put into the oven. As the dough rises the raisins (galaxies) are moving further away from each other. ...
The Big Bang!
... taken every galaxy the same amount of time to move from a common starting position to its current position ...
... taken every galaxy the same amount of time to move from a common starting position to its current position ...
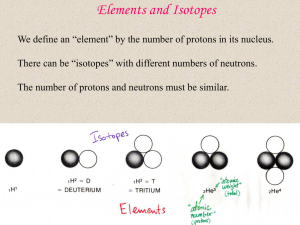
Elements and Isotopes - University of California, Berkeley
... You can do this by having high density (lots of particles) and high temperature (particles moving very quickly). But actually, you must also have both a proton and a neutron. ...
... You can do this by having high density (lots of particles) and high temperature (particles moving very quickly). But actually, you must also have both a proton and a neutron. ...
Big Bang Theory
... • Hubble found that most galaxies had redshifted (meaning…) • They are moving away from the observer • This means that the universe is expanding • In honour of this discovery: the first large space telescope was named after Hubble ...
... • Hubble found that most galaxies had redshifted (meaning…) • They are moving away from the observer • This means that the universe is expanding • In honour of this discovery: the first large space telescope was named after Hubble ...
Vocabulary Terms - Dayton Independent Schools
... the theory that the universe started with a big bang, or explosion, and has been expanding ever since ...
... the theory that the universe started with a big bang, or explosion, and has been expanding ever since ...
Children of the stars, children of the Universe…
... rays made matter opaque for photons After 1 million years, the Universe became cool enough for neutral atoms to form. The gas became transparent for radiation in this recombination phase At this time, the temperature of the Universe was ~3000 K. We observe photons from this epoch as the CBR After re ...
... rays made matter opaque for photons After 1 million years, the Universe became cool enough for neutral atoms to form. The gas became transparent for radiation in this recombination phase At this time, the temperature of the Universe was ~3000 K. We observe photons from this epoch as the CBR After re ...
origins powerpoint
... •This radiation can be detected by common radio and television antennae. (ex: “snow” on old televisions is made up of a small percent of radiation from the formation of the universe!) ...
... •This radiation can be detected by common radio and television antennae. (ex: “snow” on old televisions is made up of a small percent of radiation from the formation of the universe!) ...
here
... (a) The Special Theory of Relativity. (b) The Big Bang. (c) The theory of Inflation. (d) Both (b) and (c). 2. Astronomers use the fact that atoms have quantized energy levels to: (a) Determine the elemental abundances of stars and other astrophysical bodies. (b) Measure the mass of stars and other a ...
... (a) The Special Theory of Relativity. (b) The Big Bang. (c) The theory of Inflation. (d) Both (b) and (c). 2. Astronomers use the fact that atoms have quantized energy levels to: (a) Determine the elemental abundances of stars and other astrophysical bodies. (b) Measure the mass of stars and other a ...
1 The Big Bang • The Big Bang Theory postulates that the universe
... In 1948 it was suggested that if the Big Bang did happen then it would be the biggest single emission of energy in the universe and there should be a measurable peak wavelength associated with it. The universe has cooled considerably since the Big Bang. It was predicted to be at a current temperatur ...
... In 1948 it was suggested that if the Big Bang did happen then it would be the biggest single emission of energy in the universe and there should be a measurable peak wavelength associated with it. The universe has cooled considerably since the Big Bang. It was predicted to be at a current temperatur ...
A time travel of 14 billion years
... big bang’s remainders that we are not (yet) able to detect: -The background neutrinos that provide a picture of the universe a second after its birth. - The gravitational waves that provide a picture of the universe at 10-43 seconds after the Big Bang. ...
... big bang’s remainders that we are not (yet) able to detect: -The background neutrinos that provide a picture of the universe a second after its birth. - The gravitational waves that provide a picture of the universe at 10-43 seconds after the Big Bang. ...
The “Big Bang” Theory
... So what’s the deal with Stars? • Stars are giant balls of mostly gas (usually _________ and ________) that give off huge amounts of _______ through nuclear _______. • Nuclear _________ is a process that joins two nuclei together and gives off a lot of ________ in the process. • ________________ is ...
... So what’s the deal with Stars? • Stars are giant balls of mostly gas (usually _________ and ________) that give off huge amounts of _______ through nuclear _______. • Nuclear _________ is a process that joins two nuclei together and gives off a lot of ________ in the process. • ________________ is ...
Quiz
... big bang theory cosmic background radiation Doppler effect big crunch red-shift galaxy dark matter general theory relativity ...
... big bang theory cosmic background radiation Doppler effect big crunch red-shift galaxy dark matter general theory relativity ...
BBN + Inflation
... Big Bang Nucleosynthesis • Around 10-9 s, quarks froze out into protons and neutrons, note neutrons are unstable, but lifetime is long enough, 15 minutes. • When did nuclei form? Simplest nucleus is deuterium, D, consists of p+n. Energy to dissociate D is 2.2 MeV, which is 160,000 that needed to di ...
... Big Bang Nucleosynthesis • Around 10-9 s, quarks froze out into protons and neutrons, note neutrons are unstable, but lifetime is long enough, 15 minutes. • When did nuclei form? Simplest nucleus is deuterium, D, consists of p+n. Energy to dissociate D is 2.2 MeV, which is 160,000 that needed to di ...
The Universe - The Ohio State University
... freely through space. The expansion of the universe had caused the temperature to drop when photons no longer had the energy to create proton anti-proton pairs. Protons and neutrons are now frozen out of thermal equilibrium with radiation. By 4-10 seconds, the temperature had fallen further to the p ...
... freely through space. The expansion of the universe had caused the temperature to drop when photons no longer had the energy to create proton anti-proton pairs. Protons and neutrons are now frozen out of thermal equilibrium with radiation. By 4-10 seconds, the temperature had fallen further to the p ...
Big Bang PPT
... The WMAP satellite gave a better resolution of the small fluctuations of temperature ...
... The WMAP satellite gave a better resolution of the small fluctuations of temperature ...
We Are All Stardust: Nuclear Physics in the Cosmos
... nuclear force can be felt Probability of a reaction depends very strongly on temperature Only at very high temperatures of a few million K or higher can fusion occur, for typical pressures ...
... nuclear force can be felt Probability of a reaction depends very strongly on temperature Only at very high temperatures of a few million K or higher can fusion occur, for typical pressures ...
Lecture 24 Early Universe
... point where deuterium can survive • Deuterium formation is the first step in a whole sequence of nuclear reactions: – e.g. Helium-4 (4He) formation: ...
... point where deuterium can survive • Deuterium formation is the first step in a whole sequence of nuclear reactions: – e.g. Helium-4 (4He) formation: ...