ppt - SLAC
... A W-R star is “A hot (25,000 to 50,000 K), massive (more than 25 solar masses), luminous star in an advanced stage of evolution, which is losing mass in the form a powerful stellar wind. Wolf-Rayets are believed to be O stars that have lost their hydrogen envelopes, leaving their helium cores expose ...
... A W-R star is “A hot (25,000 to 50,000 K), massive (more than 25 solar masses), luminous star in an advanced stage of evolution, which is losing mass in the form a powerful stellar wind. Wolf-Rayets are believed to be O stars that have lost their hydrogen envelopes, leaving their helium cores expose ...
how the solar system works
... 1. To investigate how the world was formed. An astrologist studies star formations, whereas a cosmologist studies how the world was formed. 2. Yes, because new discoveries are made every day, which can change their current report. 3. A nebula is a large space cloud of gas and dust. 4. Gravity is the ...
... 1. To investigate how the world was formed. An astrologist studies star formations, whereas a cosmologist studies how the world was formed. 2. Yes, because new discoveries are made every day, which can change their current report. 3. A nebula is a large space cloud of gas and dust. 4. Gravity is the ...
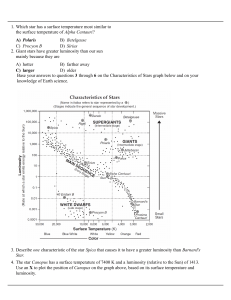
determining stellar parameters from star`s
... temperatures. The other is that the material in the star's atmosphere is not gray but may even be strongly colored; another way of saying this is that emissivity depends strongly on σ T 4 wavelength. [1] What then do we mean by the temperature of the star? One way is by making the best fit of the en ...
... temperatures. The other is that the material in the star's atmosphere is not gray but may even be strongly colored; another way of saying this is that emissivity depends strongly on σ T 4 wavelength. [1] What then do we mean by the temperature of the star? One way is by making the best fit of the en ...
Neutrino DS at ESGARD - GDR neutrino
... line with the strategy document and would enhance the EU role in this field. ...
... line with the strategy document and would enhance the EU role in this field. ...
Putting a Spin on the Solar System
... Jupiter, is more than ten times larger than Earth. Even though they are larger, the gas giants are less dense than the inner planets because they are made of gas. Gas giants all have visible rings around them. The rings are made from chunks of ice, rock, and dust in orbit around the planet. Gas gian ...
... Jupiter, is more than ten times larger than Earth. Even though they are larger, the gas giants are less dense than the inner planets because they are made of gas. Gas giants all have visible rings around them. The rings are made from chunks of ice, rock, and dust in orbit around the planet. Gas gian ...
THE LUYINOSITY VARIABILITY OF SOLAR
... The surface rotation rate of F- to K-type main-sequence stars several hundred Myr old shows some dependence on stellar mass, declining from ~7 km/sec to ~ 4 km/sec as mass decreases by 30% or so [Radick et al., 1987]. This trend in mean rotation rate is probably a relic of early evolution, because t ...
... The surface rotation rate of F- to K-type main-sequence stars several hundred Myr old shows some dependence on stellar mass, declining from ~7 km/sec to ~ 4 km/sec as mass decreases by 30% or so [Radick et al., 1987]. This trend in mean rotation rate is probably a relic of early evolution, because t ...
2010-02 LAAS Bulletin I - Los Angeles Astronomical Society
... But before they get exciting, they will get hot. Really hot. As the sun continuously eats up its hydrogen, the core becomes continuously polluted with the heavier helium, which causes the core to slowly & slightly compress under it own weight, so that the core is constantly heating up. And that, in ...
... But before they get exciting, they will get hot. Really hot. As the sun continuously eats up its hydrogen, the core becomes continuously polluted with the heavier helium, which causes the core to slowly & slightly compress under it own weight, so that the core is constantly heating up. And that, in ...
The Triple-Ring Nebula: Fingerprint of a Binary Merger
... 4 A Binary Merger Model for the Progenitor of SN 1987A The idea that the anomalous properties of the progenitor of SN 1987A are the result of the merger of two stars about 20,000 years before the explosion has long been the leading model for the progenitor8 . In this model, the system consisted init ...
... 4 A Binary Merger Model for the Progenitor of SN 1987A The idea that the anomalous properties of the progenitor of SN 1987A are the result of the merger of two stars about 20,000 years before the explosion has long been the leading model for the progenitor8 . In this model, the system consisted init ...
Planets and Life - Indiana University Astronomy
... Once the equilibrium reactions have stopped then neutrons simply decay: neutron -> proton + neutrino + electron The decay has a half life of 600 seconds. In 600 seconds, a neutron is as likely to turn into a proton as it is to stay a neutron. This can be simulated by tossing a coin. If it lands head ...
... Once the equilibrium reactions have stopped then neutrons simply decay: neutron -> proton + neutrino + electron The decay has a half life of 600 seconds. In 600 seconds, a neutron is as likely to turn into a proton as it is to stay a neutron. This can be simulated by tossing a coin. If it lands head ...
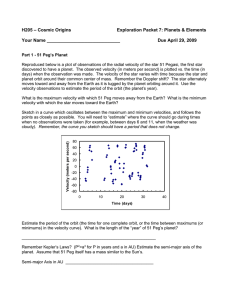
Kepler`s - Angelfire
... Table 1 'provides the heliocentric positions of Mercury over a period of several months. Selectthe set of data for October 1 and locate the given longitude on the polar graph paper. Measure.S out along the longitude line an appropriate distance, in your scale.forthe radius vector for this date. Make ...
... Table 1 'provides the heliocentric positions of Mercury over a period of several months. Selectthe set of data for October 1 and locate the given longitude on the polar graph paper. Measure.S out along the longitude line an appropriate distance, in your scale.forthe radius vector for this date. Make ...
Relativistic Third Kepler Law for Circular Orbits
... where the dot represents the derivative with respect to radial coordinate. By substituting for into the first integral for the angular coordinate in Eq.5 and considering that the coordinate orbital time, which is the observable quantity, is found when the angle is set to: 2 , the following re ...
... where the dot represents the derivative with respect to radial coordinate. By substituting for into the first integral for the angular coordinate in Eq.5 and considering that the coordinate orbital time, which is the observable quantity, is found when the angle is set to: 2 , the following re ...