ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars and Galaxies
... about 13 Billion Years ago Formed Galaxies from gas ...
... about 13 Billion Years ago Formed Galaxies from gas ...
Ch 20-21 Review
... B) is, in terms of the star's gravity, its "zone of influence." C) is the part of a rapidly rotating star that will eventually spin away to form planets. D) is the accretion disk around the companion star. E) leads to formation of rings, like around the jovian planets. ...
... B) is, in terms of the star's gravity, its "zone of influence." C) is the part of a rapidly rotating star that will eventually spin away to form planets. D) is the accretion disk around the companion star. E) leads to formation of rings, like around the jovian planets. ...
1. The distances to the most remote galaxies can be
... a) have all their stars on the main sequence. b) Have only their high mass stars on the main sequence while the low-mass protostars are still contracting (and hence are not on the main sequence yet). c) Have only their low mass stars on the main sequence while the high-mass protostars are still cont ...
... a) have all their stars on the main sequence. b) Have only their high mass stars on the main sequence while the low-mass protostars are still contracting (and hence are not on the main sequence yet). c) Have only their low mass stars on the main sequence while the high-mass protostars are still cont ...
Dwarf novae
... where Z is the number of protons and A is the number of nucleons (~0.5 for white dwarfs) ...
... where Z is the number of protons and A is the number of nucleons (~0.5 for white dwarfs) ...
supplemental materials.
... evolution. For white dwarfs, however, energy transport is dominated by conduction which changes the implementation of the numerical solution. We use the white dwarf evolution models of Wood (1992) and the white dwarf atmosphere models of Bergeron et al. (1995) to convert the surface luminosity and t ...
... evolution. For white dwarfs, however, energy transport is dominated by conduction which changes the implementation of the numerical solution. We use the white dwarf evolution models of Wood (1992) and the white dwarf atmosphere models of Bergeron et al. (1995) to convert the surface luminosity and t ...
Power Point - Solar System
... Orbital path crosses Pluto’s Faint rings made of dust particles Composed of H, He, & Methane & a core of molten ...
... Orbital path crosses Pluto’s Faint rings made of dust particles Composed of H, He, & Methane & a core of molten ...
digital book, stars and planets
... Our calendars and clocks are based on the movement of the Earth and Moon. One year is measured by the time it takes Earth to travel completely around the Sun. One month is about equal to the time it takes the Moon to orbit Earth. One day is the length of time it takes for Earth to rotate once around ...
... Our calendars and clocks are based on the movement of the Earth and Moon. One year is measured by the time it takes Earth to travel completely around the Sun. One month is about equal to the time it takes the Moon to orbit Earth. One day is the length of time it takes for Earth to rotate once around ...
Deep Time: Earth`s History and Future
... by the Sun shrinking Sun is 10 times its current diameter, luminosity 20-50% current value. Helium burning in core. Sun burning carbon and oxygen in core, expands to red giant again. Diameter 240 million km, luminosity 3000 times current value. Sun goes through series of helium flashes (3 or 4), swe ...
... by the Sun shrinking Sun is 10 times its current diameter, luminosity 20-50% current value. Helium burning in core. Sun burning carbon and oxygen in core, expands to red giant again. Diameter 240 million km, luminosity 3000 times current value. Sun goes through series of helium flashes (3 or 4), swe ...
N.2 Formation of Mass
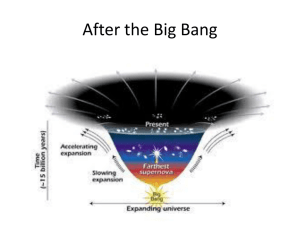
... • After the Big Bang the Universe expanded rapidly. • As it expanded it cooled. • As it cooled, matter began attracted to each other and the four forces of the Universe ...
... • After the Big Bang the Universe expanded rapidly. • As it expanded it cooled. • As it cooled, matter began attracted to each other and the four forces of the Universe ...
Notes: Star Formation
... • If a protostar gains enough mass: – The temperature & pressure keeps increasing – Hydrogen begins to fuse together – The protostar officially becomes a star once fusion begins. • The star is now in the Main Sequence –90% of stars are in the main sequence –All main sequence stars fuse hydrogen ...
... • If a protostar gains enough mass: – The temperature & pressure keeps increasing – Hydrogen begins to fuse together – The protostar officially becomes a star once fusion begins. • The star is now in the Main Sequence –90% of stars are in the main sequence –All main sequence stars fuse hydrogen ...
123mt13-2a
... Confine your answers to the space provided and write legibly for the last 3 questions. There are a total of 120 points on this exam. Part I: True or False: Circle your answer. 2 pts each ...
... Confine your answers to the space provided and write legibly for the last 3 questions. There are a total of 120 points on this exam. Part I: True or False: Circle your answer. 2 pts each ...
Presentation - Science in the News
... A giant ball of gas that is gravitationally attracted to itself but supported by thermal pressure given off from nucleosynthetic processes in its core. ...
... A giant ball of gas that is gravitationally attracted to itself but supported by thermal pressure given off from nucleosynthetic processes in its core. ...
Lecture 6-1: Schematic Evolution of Stars as seen from the core
... Stars start their life on the Hayashi track at low central density and temperature (Lecture 5-3 slides 14–19). As the star contracts, the core heats up (virial theorem, lecture 2) and eventually reaches H-burning conditions. At that point contraction will halt, as nuclear energy generation can suppl ...
... Stars start their life on the Hayashi track at low central density and temperature (Lecture 5-3 slides 14–19). As the star contracts, the core heats up (virial theorem, lecture 2) and eventually reaches H-burning conditions. At that point contraction will halt, as nuclear energy generation can suppl ...
How Bright is that star?
... Luminosity is the amount of energy a star gives off as light. Measured in Watts or Solar Units or “Sols” However for all practical purposes Absolute magnitude and Luminosity of a star measure the same thing. Absolute Magnitude Approximate Luminosity ...
... Luminosity is the amount of energy a star gives off as light. Measured in Watts or Solar Units or “Sols” However for all practical purposes Absolute magnitude and Luminosity of a star measure the same thing. Absolute Magnitude Approximate Luminosity ...
Physics@Brock - Brock University
... (a) About 50% hydrogen, about 50% helium, and less than 2% heavier elements. (b) About 60% hydrogen, about 40% helium, and less than 2% heavier elements. (c) About 75% hydrogen, about 25% helium, and less than 2% heavier elements. (d) About 90% hydrogen, about 10% helium, and less than 2% heavier el ...
... (a) About 50% hydrogen, about 50% helium, and less than 2% heavier elements. (b) About 60% hydrogen, about 40% helium, and less than 2% heavier elements. (c) About 75% hydrogen, about 25% helium, and less than 2% heavier elements. (d) About 90% hydrogen, about 10% helium, and less than 2% heavier el ...
Star and Planet Formation - Homepages of UvA/FNWI staff
... should actually stay behind because of the movement of the Earth on its orbit. 2. If the Earth rotates around its axis (as required to explain day and night), things should fly off the spinning planet. 3. If the Earth rotates around the Sun, we should observe parallaxes for the fixed stars. While th ...
... should actually stay behind because of the movement of the Earth on its orbit. 2. If the Earth rotates around its axis (as required to explain day and night), things should fly off the spinning planet. 3. If the Earth rotates around the Sun, we should observe parallaxes for the fixed stars. While th ...