24.3 The Sun - Planet Earth
... of the solar atmosphere, the corona (corona ⫽ crown) is very weak and, as with the chromosphere, is visible only when the brilliant photosphere is covered. This envelope of ionized gases normally extends a million kilometers from the sun and produces a glow about half as bright as the full moon. At ...
... of the solar atmosphere, the corona (corona ⫽ crown) is very weak and, as with the chromosphere, is visible only when the brilliant photosphere is covered. This envelope of ionized gases normally extends a million kilometers from the sun and produces a glow about half as bright as the full moon. At ...
The Celestial Sphere
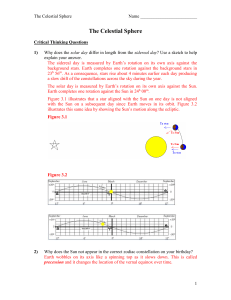
... Figure 3.1 illustrates that a star aligned with the Sun on one day is not aligned with the Sun on a subsequent day since Earth moves in its orbit. Figure 3.2 illustrates this same idea by showing the Sun’s motion along the ecliptic. Figure 3.1 ...
... Figure 3.1 illustrates that a star aligned with the Sun on one day is not aligned with the Sun on a subsequent day since Earth moves in its orbit. Figure 3.2 illustrates this same idea by showing the Sun’s motion along the ecliptic. Figure 3.1 ...
Night_Sky
... The sky is full of stars from night sky observation The moon is not a star from morning discussion The sun is a star from morning discussion The sun provides light for us to see from ...
... The sky is full of stars from night sky observation The moon is not a star from morning discussion The sun is a star from morning discussion The sun provides light for us to see from ...
Chapter 20
... settled down to a steady and reliable existence on the main sequence. (T Tauri stars always have the word “stars” in their name though technically they haven’t reached the main sequence, so they are not yet fully formed stars.) In astronomical teaching, we have the question of whether to first consi ...
... settled down to a steady and reliable existence on the main sequence. (T Tauri stars always have the word “stars” in their name though technically they haven’t reached the main sequence, so they are not yet fully formed stars.) In astronomical teaching, we have the question of whether to first consi ...
P1 The Earth in the Universe
... Fossils in the layers show which species lived when. Many species have become extinct. Cross-cutting features- if one type of rock cuts across another rock type, it is younger e.g. hot magma can fill cracks in existing rocks and solidify as new rock. These clues only tell us which rocks are older th ...
... Fossils in the layers show which species lived when. Many species have become extinct. Cross-cutting features- if one type of rock cuts across another rock type, it is younger e.g. hot magma can fill cracks in existing rocks and solidify as new rock. These clues only tell us which rocks are older th ...
Lecture 1 - X-ray and Observational Astronomy Group
... Transition region: Separates hot corona from chromosphere. Heat flows from corona into chromosphere, producing thin layer where temperature changes very rapidly (T~106K – 20,000K). Hydrogen is completely ionised, emission dominated by highly ionised lines of C, O and Si (CIV,OIV,SiIV). These are ult ...
... Transition region: Separates hot corona from chromosphere. Heat flows from corona into chromosphere, producing thin layer where temperature changes very rapidly (T~106K – 20,000K). Hydrogen is completely ionised, emission dominated by highly ionised lines of C, O and Si (CIV,OIV,SiIV). These are ult ...
lecture_1_mbu - X-ray and Observational Astronomy Group
... Transition region: Separates hot corona from chromosphere. Heat flows from corona into chromosphere, producing thin layer where temperature changes very rapidly (T~106K – 20,000K). Hydrogen is completely ionised, emission dominated by highly ionised lines of C, O and Si (CIV,OIV,SiIV). These are ult ...
... Transition region: Separates hot corona from chromosphere. Heat flows from corona into chromosphere, producing thin layer where temperature changes very rapidly (T~106K – 20,000K). Hydrogen is completely ionised, emission dominated by highly ionised lines of C, O and Si (CIV,OIV,SiIV). These are ult ...
PYTS/ASTR 206 – The Sun
... Magnetic field lines inhibit convection where they intersect the surface Surface cools off – sunspot forms Sunspots are ~4500K ...
... Magnetic field lines inhibit convection where they intersect the surface Surface cools off – sunspot forms Sunspots are ~4500K ...
Solar System
... Asteroids are very old and exhibit a range of properties not characteristic of either the terrestrial or jovian planets or their moons. Asteroids share, in rough terms, the bulk orbital properties of the planets. However, they appear to be made of primitive, unevolved material. Similarly, meteorites ...
... Asteroids are very old and exhibit a range of properties not characteristic of either the terrestrial or jovian planets or their moons. Asteroids share, in rough terms, the bulk orbital properties of the planets. However, they appear to be made of primitive, unevolved material. Similarly, meteorites ...
Article - Iowa State University
... Dr. Raj Baldev, you are considered one of the authorities on Cosmos and its theories and that’s why you are regarded as ‘Cosmo Theorist’. You have also written a wonderful book “Two Big Bangs Created the Universe” (Formed in Eternal Space) explaining how the Universe was born and developed. Despite ...
... Dr. Raj Baldev, you are considered one of the authorities on Cosmos and its theories and that’s why you are regarded as ‘Cosmo Theorist’. You have also written a wonderful book “Two Big Bangs Created the Universe” (Formed in Eternal Space) explaining how the Universe was born and developed. Despite ...
High School - INFINITY Science Center
... fusion in the sun’s core to release energy that eventually reaches Earth in the form of radiation. HS-ESS1-2. Construct an explanation of the Big Bang theory based on astronomical evidence of light spectra, motion of distant galaxies, and composition of matter in the universe. HS-ESS1-3. Communicate ...
... fusion in the sun’s core to release energy that eventually reaches Earth in the form of radiation. HS-ESS1-2. Construct an explanation of the Big Bang theory based on astronomical evidence of light spectra, motion of distant galaxies, and composition of matter in the universe. HS-ESS1-3. Communicate ...
The science behind our Sun and its interaction with Earth The
... How The Sun affects Life On Earth. Our Sun has lived for approximately 4.6 billion years. It is about halfway through its lifespan (Frank, 2008). The Sun's light and heat are absolutely vital to human existence, yet most of us take them for granted. The Sun is the most important factor in Earth supp ...
... How The Sun affects Life On Earth. Our Sun has lived for approximately 4.6 billion years. It is about halfway through its lifespan (Frank, 2008). The Sun's light and heat are absolutely vital to human existence, yet most of us take them for granted. The Sun is the most important factor in Earth supp ...
School of Physics Multiwavelength Observations of Evolved Stars Research project in Astrophysics
... systems containing evolved giant stars with masses similar to that of our own Sun. Although supernovae are showy objects, stars with mass similar to our Sun are much more plentiful and when they evolve to the red giant stage they begin to lose processed material in the form of a cool wind. These sta ...
... systems containing evolved giant stars with masses similar to that of our own Sun. Although supernovae are showy objects, stars with mass similar to our Sun are much more plentiful and when they evolve to the red giant stage they begin to lose processed material in the form of a cool wind. These sta ...