The Life Cycles of Stars, Part I
... begin to occur, temporarily halting the collapse of the core. However, when the core becomes essentially just iron, it has nothing left to fuse (because of iron's nuclear structure, it does not permit its atoms to fuse into heavier elements) and fusion ceases. In less than a second, the star begins ...
... begin to occur, temporarily halting the collapse of the core. However, when the core becomes essentially just iron, it has nothing left to fuse (because of iron's nuclear structure, it does not permit its atoms to fuse into heavier elements) and fusion ceases. In less than a second, the star begins ...
origin of the solar system - Breakthrough Science Society
... jority of satellites move about the planets that of the orbit nearest to it in the direcin a similar fashion. Even Saturn’s rings tion of the sun. The distances of the planeshare in the common motion. tary orbits are given more accurately by the Next, there had come a new concept, very ‘Bode law’, w ...
... jority of satellites move about the planets that of the orbit nearest to it in the direcin a similar fashion. Even Saturn’s rings tion of the sun. The distances of the planeshare in the common motion. tary orbits are given more accurately by the Next, there had come a new concept, very ‘Bode law’, w ...
v A v A
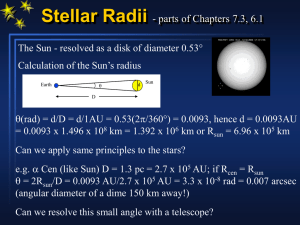
... If aperture > 10 cm, then diffraction = 1 arcsec This is about the limit imposed by the atmosphere ...
... If aperture > 10 cm, then diffraction = 1 arcsec This is about the limit imposed by the atmosphere ...
Midterm Study Game
... system revolve around the sun. Galileo also helped confirm this with his trusty telescope! ...
... system revolve around the sun. Galileo also helped confirm this with his trusty telescope! ...
Mercury
... Earth- 3rd planet from the sun • Average distance from the Sun: 149,597,890 km (called 1 astronomical unit, or AU). • Earth orbits the Sun in 365.26 days, and rotates once on its axis each 23 hours 56 minutes. • Earth is the 5th largest planet in our solar system, and only slightly larger than Venu ...
... Earth- 3rd planet from the sun • Average distance from the Sun: 149,597,890 km (called 1 astronomical unit, or AU). • Earth orbits the Sun in 365.26 days, and rotates once on its axis each 23 hours 56 minutes. • Earth is the 5th largest planet in our solar system, and only slightly larger than Venu ...
Solutions
... Suppose someone claimed to make the discoveries described below. (These are not real discoveries.) Decide whether each discovery should be considered reasonable or surprising. Explain clearly; not all these have definitive answers, so your explanation is more important than your chosen answer. 19. A ...
... Suppose someone claimed to make the discoveries described below. (These are not real discoveries.) Decide whether each discovery should be considered reasonable or surprising. Explain clearly; not all these have definitive answers, so your explanation is more important than your chosen answer. 19. A ...
– 1 – 1. A Gas
... The equation of hydrostatic equilibrium cannot be integrated, even near the surface, as we need an equation of state to specify the relationship between P and T . In some cases we can asssume P ∝ ρm , independent of T , where m = 1 + 1/n, and n is called the polytropic index. The adiabatic case, P V ...
... The equation of hydrostatic equilibrium cannot be integrated, even near the surface, as we need an equation of state to specify the relationship between P and T . In some cases we can asssume P ∝ ρm , independent of T , where m = 1 + 1/n, and n is called the polytropic index. The adiabatic case, P V ...
Lives of the Stars Lecture 3: What makes a star?
... The results of the experiment were astonishing. Davis detected only about a third of the expected number of neutrinos! In his Nobel Prize lecture (2002), Raymond Davis says “The solar neutrino problem lasted from 1967–2001. Over this period neither the measured flux nor the predicted flux changed s ...
... The results of the experiment were astonishing. Davis detected only about a third of the expected number of neutrinos! In his Nobel Prize lecture (2002), Raymond Davis says “The solar neutrino problem lasted from 1967–2001. Over this period neither the measured flux nor the predicted flux changed s ...
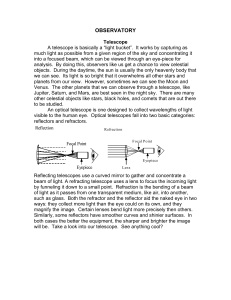
observatory - Science Presenters Central
... Features of the ACTIVE Sun: The Sun’s atmosphere is periodically changed by its magnetic fields, and the most common features of these changes are sunspots. These are areas of the photosphere that appear dark because they are cooler than the rest of the Sun’s lower atmosphere. Most of the time, the ...
... Features of the ACTIVE Sun: The Sun’s atmosphere is periodically changed by its magnetic fields, and the most common features of these changes are sunspots. These are areas of the photosphere that appear dark because they are cooler than the rest of the Sun’s lower atmosphere. Most of the time, the ...
Focus Plan - Texarkana Independent School District
... video at http://www.nasa.gov/ called Mars: a feast for the eyes. Explain to students that Mars may be the next planet for human colonization but that we are looking at many others. During this activity, they will be learning about other planets in our solar system in the hopes of finding one we can ...
... video at http://www.nasa.gov/ called Mars: a feast for the eyes. Explain to students that Mars may be the next planet for human colonization but that we are looking at many others. During this activity, they will be learning about other planets in our solar system in the hopes of finding one we can ...
The Earth – which picture is correct?
... • The Universe is made up of a number of spheres, like the layers of an onion. • The Sun, planets and stars are attached to these spheres and move around the sky as the spheres move around the Earth. • The Sun and Moon always move eastwards on their spheres. • Inferior planets move eastwards then re ...
... • The Universe is made up of a number of spheres, like the layers of an onion. • The Sun, planets and stars are attached to these spheres and move around the sky as the spheres move around the Earth. • The Sun and Moon always move eastwards on their spheres. • Inferior planets move eastwards then re ...
New light on our Sun`s fate - Space Telescope Science Institute
... One of the most remarkable properties of white dwarf stars is their density. The mass of a typical white dwarf is about half that of the Sun, but its size is similar to Earth’s. So, the density of white-dwarf matter can be a million times higher than the Sun’s average. Because white dwarf densities ...
... One of the most remarkable properties of white dwarf stars is their density. The mass of a typical white dwarf is about half that of the Sun, but its size is similar to Earth’s. So, the density of white-dwarf matter can be a million times higher than the Sun’s average. Because white dwarf densities ...
Astronomy 112: The Physics of Stars Class 17 Notes: Core Collapse
... Converting protons to neutrons is via β decays is possible, and in fact it is the first step in the pp-chain. However, as we learned studying that reaction, β decays are slow, and in the few seconds that it takes for the shock to propagate through the star, there is not enough time for them to occur ...
... Converting protons to neutrons is via β decays is possible, and in fact it is the first step in the pp-chain. However, as we learned studying that reaction, β decays are slow, and in the few seconds that it takes for the shock to propagate through the star, there is not enough time for them to occur ...
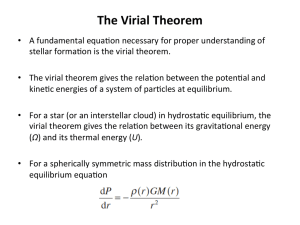
The Virial Theorem
... • During the contrac-on –Ω increases, and so does U. • The virial theorem shows that half of the gravita2onal energy is used to heat the gas (i.e. ΔU=−ΔΩ/2 ). ...
... • During the contrac-on –Ω increases, and so does U. • The virial theorem shows that half of the gravita2onal energy is used to heat the gas (i.e. ΔU=−ΔΩ/2 ). ...
Quiz 3 Feedback Electron Jumps in Atoms Emission and absorption
... • Spectral types are defined by which absorption lines of various elements, ions, and molecules, are seen in a star’s spectrum and the relative strengths of these lines. • Spectral type is not (usually) determined by composition. • Instead, the vast majority of stars have the same surface compositio ...
... • Spectral types are defined by which absorption lines of various elements, ions, and molecules, are seen in a star’s spectrum and the relative strengths of these lines. • Spectral type is not (usually) determined by composition. • Instead, the vast majority of stars have the same surface compositio ...
Astronomy_Stellar_Evolution_and_Type_II_Supernovae_Exam
... indirect detection of gravitational radiation of binary star systems. 5) A remnant produced from a Supernova Explosion, consisting of approximately 3 to 14 solar masses. In this case, the material density has exceeded neutron degeneracy pressure. 6) Spectral class K or M, with luminosities that can ...
... indirect detection of gravitational radiation of binary star systems. 5) A remnant produced from a Supernova Explosion, consisting of approximately 3 to 14 solar masses. In this case, the material density has exceeded neutron degeneracy pressure. 6) Spectral class K or M, with luminosities that can ...