Modern Physics and Subtle Realms: Not Mutually Exclusive
... combinations of the four forces. For example, the electron has electromagnetic, gravitational, and weak coupling, but not strong coupling. Quarks are coupled to all four forces. Neutrinos, because they are massless, or extremely close to massless, have gravitational coupling that is far too small to ...
... combinations of the four forces. For example, the electron has electromagnetic, gravitational, and weak coupling, but not strong coupling. Quarks are coupled to all four forces. Neutrinos, because they are massless, or extremely close to massless, have gravitational coupling that is far too small to ...
eclipse
... with previous observations • Predictions of new phenomena are observed. If the observations agree with the prediction, more predictions can be made. If not, a new theory can be made. ...
... with previous observations • Predictions of new phenomena are observed. If the observations agree with the prediction, more predictions can be made. If not, a new theory can be made. ...
Study Guide for 1ST Astronomy Exam
... o White Dwarf stellar remnant Utilize the HR to identify a star’s luminosity, temperature, radius and mass. Interpret the luminosity class of a star by naming the luminosity class (Table 58.1) and identifying if the star is in the “adult” phase or the “nursing home” phase of its evolution. Unit ...
... o White Dwarf stellar remnant Utilize the HR to identify a star’s luminosity, temperature, radius and mass. Interpret the luminosity class of a star by naming the luminosity class (Table 58.1) and identifying if the star is in the “adult” phase or the “nursing home” phase of its evolution. Unit ...
Transparents
... acceleration and point back to sources Neutrinos from interaction of UHECR: • Guaranteed flux – GZK effect observed, the neutrinos must be there • Flux models depend on UHECR composition, constrained by gamma ray measurements. • At these energies neutrinos are the only messenger particle capable of ...
... acceleration and point back to sources Neutrinos from interaction of UHECR: • Guaranteed flux – GZK effect observed, the neutrinos must be there • Flux models depend on UHECR composition, constrained by gamma ray measurements. • At these energies neutrinos are the only messenger particle capable of ...
It is now well known that the constellations of the Zodiac
... and determining their destinies. Behind the serpent-bodied gods is the figure of Zababa. Very little is known about this ancient god beyond the fact he was a warrior god who was closely associated with the symbol of the eagle. As so little is known about Zababa, the constellation image offered here ...
... and determining their destinies. Behind the serpent-bodied gods is the figure of Zababa. Very little is known about this ancient god beyond the fact he was a warrior god who was closely associated with the symbol of the eagle. As so little is known about Zababa, the constellation image offered here ...
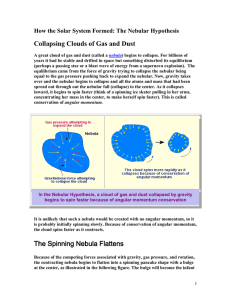
How the Solar System Formed: The Nebular
... Evidence for the Nebular Hypothesis The orbits of the planets lie nearly in a plane with the sun at the center. The planets all revolve in the same direction. All debris (matter) orbits the sun (except moons). The most dense materials are closest to the Sun. All the planets and most of the moons and ...
... Evidence for the Nebular Hypothesis The orbits of the planets lie nearly in a plane with the sun at the center. The planets all revolve in the same direction. All debris (matter) orbits the sun (except moons). The most dense materials are closest to the Sun. All the planets and most of the moons and ...
Name - MIT
... A) The orbit of every planet is a circle with the sun at the center. B) The cube of the orbital period of a planet is directly proportional to the square root of the semi-major axis of its orbit. C) The orbit of every planet is an ellipse with the sun at one focus. D) Planet closer to the Sun move s ...
... A) The orbit of every planet is a circle with the sun at the center. B) The cube of the orbital period of a planet is directly proportional to the square root of the semi-major axis of its orbit. C) The orbit of every planet is an ellipse with the sun at one focus. D) Planet closer to the Sun move s ...
Collapse: Method 2
... importance. Much of what occurs is still theory: Stage 1. The density shields the core from external radiation, allowing the temperature to drop. Dust grains provide efficient cooling. The hydrogen is molecular. Stage 2. An isothermal collapse all the way from densities of 104 cm-3 then proceeds. Th ...
... importance. Much of what occurs is still theory: Stage 1. The density shields the core from external radiation, allowing the temperature to drop. Dust grains provide efficient cooling. The hydrogen is molecular. Stage 2. An isothermal collapse all the way from densities of 104 cm-3 then proceeds. Th ...
Powerpoint Notes
... •Hubble discovered that galaxies are moving away from us and each other. •He discovered the relationship between distance to a galaxy and its speed. ...
... •Hubble discovered that galaxies are moving away from us and each other. •He discovered the relationship between distance to a galaxy and its speed. ...
HEIC0619: EMBARGOED UNTIL: 19:30 (CET)/01:30 PM EST 11
... or maybe even more – tend to be born in multiple systems that can easily disguise themselves as single very heavy stars. Moreover, these stellar heavyweights are so rare that only a few are close enough to the Sun to be examined in detail. One of the top candidates for the title of “Milky Way stella ...
... or maybe even more – tend to be born in multiple systems that can easily disguise themselves as single very heavy stars. Moreover, these stellar heavyweights are so rare that only a few are close enough to the Sun to be examined in detail. One of the top candidates for the title of “Milky Way stella ...
minnesota
... 2) Especially because of their reduced mass loss, low metallicity (very) massive stars have different properties when they die and possibly different nucleosynthesis. They are harder to explode, have more fall back, and rotate more rapidly. 3) Current surveys give good agreement with the abundances ...
... 2) Especially because of their reduced mass loss, low metallicity (very) massive stars have different properties when they die and possibly different nucleosynthesis. They are harder to explode, have more fall back, and rotate more rapidly. 3) Current surveys give good agreement with the abundances ...
B2 Star Formation and Nuclear Fusion
... At increasing density, collapsing protostellar gas becomes optically thick and radiation is no longer able to escape. • During collapse, gravitational potential energy is liberated and radiated away. • Transition to being optically thick prevents further cooling and the temperature begins to rise. I ...
... At increasing density, collapsing protostellar gas becomes optically thick and radiation is no longer able to escape. • During collapse, gravitational potential energy is liberated and radiated away. • Transition to being optically thick prevents further cooling and the temperature begins to rise. I ...
Groupmeeting_shshiu_20090803_nuclearx
... 1) a emitted to reduce mass, only emitted if mass number above 209 2) b- emitted to change neutron into proton, happens when have too many neutrons 3) b emitted (or electron captured) to change proton into neutron, happens when have too few neutrons 4) g emitted to conserve energy in reaction, may ...
... 1) a emitted to reduce mass, only emitted if mass number above 209 2) b- emitted to change neutron into proton, happens when have too many neutrons 3) b emitted (or electron captured) to change proton into neutron, happens when have too few neutrons 4) g emitted to conserve energy in reaction, may ...
The theme “Research of fundamental interactions in nucleus at low
... in the form of WIMPs trapped in the Galactic halo. To reject background caused by cosmic radiation the experiment is located in underground laboratory, Laboratoire Souterrain de Modane (LSM), in the Frejus tunnel between France and Italy. 1800 m rock overburden corresponding to a depth of 4800 mwe r ...
... in the form of WIMPs trapped in the Galactic halo. To reject background caused by cosmic radiation the experiment is located in underground laboratory, Laboratoire Souterrain de Modane (LSM), in the Frejus tunnel between France and Italy. 1800 m rock overburden corresponding to a depth of 4800 mwe r ...
A Possible Effect of Cosmic Rays on Celestial Chemical Composition
... (i) The mtensity of general cosmic rays near the sun is about one order smaller than that gtven in (1), so that the general cosmic rays impinging on the solar surface give a contribution to such nuclear transformations less than the solar ones do. (ii) The same reason applies to the nuclear transfor ...
... (i) The mtensity of general cosmic rays near the sun is about one order smaller than that gtven in (1), so that the general cosmic rays impinging on the solar surface give a contribution to such nuclear transformations less than the solar ones do. (ii) The same reason applies to the nuclear transfor ...
Activity 1 - Wakefield`s Science Classes
... was formed from some of the original energy. Cosmologists (scientists who study the origin and dynamics of the universe) think that most of the matter in the universe was formed within minutes of time zero! The expansion and cooling that started with the Big Bang continues to this day. The galaxies ...
... was formed from some of the original energy. Cosmologists (scientists who study the origin and dynamics of the universe) think that most of the matter in the universe was formed within minutes of time zero! The expansion and cooling that started with the Big Bang continues to this day. The galaxies ...
(the factor f star in the Drake equation. Recall it
... dust clouds (of helium and hydrogen) but as it progressed, the centers of the more massive clouds and the pressure due to the gravitational attraction got larger and larger in them. Eventually, the pressure was so great that the nuclei of the atoms started to get pushed together. To do this requires ...
... dust clouds (of helium and hydrogen) but as it progressed, the centers of the more massive clouds and the pressure due to the gravitational attraction got larger and larger in them. Eventually, the pressure was so great that the nuclei of the atoms started to get pushed together. To do this requires ...
black holes activity
... -Study of the interior of the Sun (has nothing to do with seismic waves and earthquakes) - Using computer models, physics and estimates, scientists have determined the ____________ and temperature of the internal layers of the Sun B.What is convection, how does it work on the Sun? -In the convection ...
... -Study of the interior of the Sun (has nothing to do with seismic waves and earthquakes) - Using computer models, physics and estimates, scientists have determined the ____________ and temperature of the internal layers of the Sun B.What is convection, how does it work on the Sun? -In the convection ...
Soal Short
... If M is mass of black hole, v is the speed of the cloud and R is the orbital radius of cloud, then ...
... If M is mass of black hole, v is the speed of the cloud and R is the orbital radius of cloud, then ...