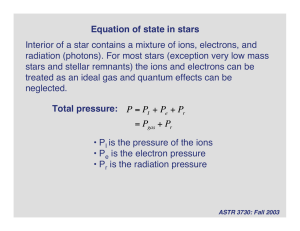
Equation of state in stars Interior of a star contains a mixture of ions
... m will depend upon the composition of the gas and the state of ionization. For example: • Neutral hydrogen: m = 1 • Fully ionized hydrogen: m = 0.5 In the central regions of stars, OK to assume that all the elements are fully ionized. Bookeeping task to determine what m is. Denote abundances of diff ...
... m will depend upon the composition of the gas and the state of ionization. For example: • Neutral hydrogen: m = 1 • Fully ionized hydrogen: m = 0.5 In the central regions of stars, OK to assume that all the elements are fully ionized. Bookeeping task to determine what m is. Denote abundances of diff ...
Section 1 Formation of the Solar System Chapter 27
... information on the distant object delayed a realistic understanding of its characteristics. Pluto is the second largest known dwarf planet and tenth largest orbiting the Sun. From its time of discovery in 1930 to 2006 it was considered to be the ninth planet in the solar system, but because addition ...
... information on the distant object delayed a realistic understanding of its characteristics. Pluto is the second largest known dwarf planet and tenth largest orbiting the Sun. From its time of discovery in 1930 to 2006 it was considered to be the ninth planet in the solar system, but because addition ...
Sun - El Camino College
... seen in front of the Sun. They look bright if seen in front of empty space. 3. Facula – the inverse of sunspots; they look brighter than average on the Sun. Also called “plages.” 4. Spicule – small flame-like, quickly moving prominences (but NOT flares – they don’t leave the Sun’s surface as quickly ...
... seen in front of the Sun. They look bright if seen in front of empty space. 3. Facula – the inverse of sunspots; they look brighter than average on the Sun. Also called “plages.” 4. Spicule – small flame-like, quickly moving prominences (but NOT flares – they don’t leave the Sun’s surface as quickly ...
LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR
... contracts to form a new star. The mass of the new star is about 2x the mass of the Sun – WOW! A star has collapsed under gravity to the point where all the star particles are NEUTRONS. ...
... contracts to form a new star. The mass of the new star is about 2x the mass of the Sun – WOW! A star has collapsed under gravity to the point where all the star particles are NEUTRONS. ...
Document
... around the true value (you’ll get an A for accuracy, because you are on the true value) • Precision – all measurements are clustered but are not centered on true value • Bias – measurements are not centered on true value ...
... around the true value (you’ll get an A for accuracy, because you are on the true value) • Precision – all measurements are clustered but are not centered on true value • Bias – measurements are not centered on true value ...
our brightest star - El Camino College
... seen in front of the Sun. They look bright if seen in front of empty space. 3. Facula – the inverse of sunspots; they look brighter than average on the Sun. Also called “plages.” 4. Spicule – small flame-like, quickly moving prominences (but NOT flares – they don’t leave the Sun’s surface as quickly ...
... seen in front of the Sun. They look bright if seen in front of empty space. 3. Facula – the inverse of sunspots; they look brighter than average on the Sun. Also called “plages.” 4. Spicule – small flame-like, quickly moving prominences (but NOT flares – they don’t leave the Sun’s surface as quickly ...
The Transient Radio Sky Astrophysical and Artificial
... Integration times: hours to days on HLIRGs ...
... Integration times: hours to days on HLIRGs ...
The Case for a Kilometer-Scale High Energy Neutrino Detector
... the GeV-photons detected with space-based instruments. Astronomical instruments have now collected data spanning 60 octaves in photon frequency, an amazing expansion of the power of our eyes which scan the sky over less than a single octave just above 10−7 cm. Doing gamma ray astronomy at TeV energi ...
... the GeV-photons detected with space-based instruments. Astronomical instruments have now collected data spanning 60 octaves in photon frequency, an amazing expansion of the power of our eyes which scan the sky over less than a single octave just above 10−7 cm. Doing gamma ray astronomy at TeV energi ...
10.1 Introduction
... This approach is adequate if, for example, we are interested in reproducing the stellar mass-luminosity relationship (Figure 4.8), or the Main Sequence of hydrogen burning stars in the luminosity-temperature diagram (Figure 3.6). Of course, the implicit assumption in homologous stellar models is tha ...
... This approach is adequate if, for example, we are interested in reproducing the stellar mass-luminosity relationship (Figure 4.8), or the Main Sequence of hydrogen burning stars in the luminosity-temperature diagram (Figure 3.6). Of course, the implicit assumption in homologous stellar models is tha ...
Astronomy Learning Objectives and Study Questions for Chapter 13
... 3. Explain why the Sun will or will not ever become a nova. 4. Describe what spectral observation distinguishes a Type Ia from a Type II supernova, and briefly explain why the spectra of these objects are different. 5. Draw a neat, well labeled sketch of a rotating neutron star and explain how this ...
... 3. Explain why the Sun will or will not ever become a nova. 4. Describe what spectral observation distinguishes a Type Ia from a Type II supernova, and briefly explain why the spectra of these objects are different. 5. Draw a neat, well labeled sketch of a rotating neutron star and explain how this ...
High Energy Observational Astrophysics
... Sun will emit in its entire lifetime) If a main sequence star has a mass of over 8 times the mass of the Sun it is destined to be a type II supernova ...
... Sun will emit in its entire lifetime) If a main sequence star has a mass of over 8 times the mass of the Sun it is destined to be a type II supernova ...
PX269 Galaxies The University of Warwick
... b) Assuming the Galactic disc has a radius of 20 kpc, a thickness of 300 pc, and it contains 1010 solar masses of hydrogen gas, estimate the average number density of hydrogen atoms in the interstellar medium. c) In what forms is this gas found? d) How might each form be detected? ...
... b) Assuming the Galactic disc has a radius of 20 kpc, a thickness of 300 pc, and it contains 1010 solar masses of hydrogen gas, estimate the average number density of hydrogen atoms in the interstellar medium. c) In what forms is this gas found? d) How might each form be detected? ...
13 Formation
... It is generally accepted that the planets accreted from a nebula with a composition similar to that of the sun, i.e., made mostly of hydrogen. The slowly-rotating nebula had a pressure and temperature distribution that decreased radially outward. The density of the nebula was probably not very great ...
... It is generally accepted that the planets accreted from a nebula with a composition similar to that of the sun, i.e., made mostly of hydrogen. The slowly-rotating nebula had a pressure and temperature distribution that decreased radially outward. The density of the nebula was probably not very great ...
The high density QCD phase transition in compact stars
... • The dynamics of the formation of quark matter in compact stars might provide clear signatures in the neutrino signal (measurable in SuperK & IceCube). Possible mechanism for supernova explosions !!! ...
... • The dynamics of the formation of quark matter in compact stars might provide clear signatures in the neutrino signal (measurable in SuperK & IceCube). Possible mechanism for supernova explosions !!! ...
E8A1_CRT_CR_MSTIPS_Final
... for the Northern Hemisphere and away when it is winter. At each of the equinoxes the Earth should not be tilted toward or way from the sun. B. The sun’s rays would be least direct in the winter for the northern hemisphere, and most direct in the southern hemisphere at this same time (The southern he ...
... for the Northern Hemisphere and away when it is winter. At each of the equinoxes the Earth should not be tilted toward or way from the sun. B. The sun’s rays would be least direct in the winter for the northern hemisphere, and most direct in the southern hemisphere at this same time (The southern he ...
Stellar Evolution of a Star like the Sun
... central core. The central temperature need to be hotter and hotter each time a new nuclear fuel is used. Burning H to He requires tens of millions of degrees Kelvin. Burning Helium requires a higher temperature because the repulsion between the He-nuclei is larger (twice as much) than that of the Hn ...
... central core. The central temperature need to be hotter and hotter each time a new nuclear fuel is used. Burning H to He requires tens of millions of degrees Kelvin. Burning Helium requires a higher temperature because the repulsion between the He-nuclei is larger (twice as much) than that of the Hn ...
Asteroseismology with the Whole Earth Telescope
... Asteroseismology with the Whole Earth Telescope (and More!) ...
... Asteroseismology with the Whole Earth Telescope (and More!) ...
honey, i shrunk the solar system
... have each student close their left eye, extend one arm, and cover the X mark with their thumb. Once the X is covered have the students open the left eye and close the right. The thumb will appear to move back and forth due to parallax. Parallax allows the brain to see two slightly different images ( ...
... have each student close their left eye, extend one arm, and cover the X mark with their thumb. Once the X is covered have the students open the left eye and close the right. The thumb will appear to move back and forth due to parallax. Parallax allows the brain to see two slightly different images ( ...