Seasons on other planets – Activity
... Seasons on other planets Background information The seasons on the planets of the Solar System are largely a reflection of the size of the difference between the maximum and minimum temperatures on each planet. This difference is caused by the combined influence of a number of factors: 1. The distan ...
... Seasons on other planets Background information The seasons on the planets of the Solar System are largely a reflection of the size of the difference between the maximum and minimum temperatures on each planet. This difference is caused by the combined influence of a number of factors: 1. The distan ...
How to Make a Solar System Necklace
... It is a good idea to review certain measurements which are used throughout this document. A mile (abbreviated: mi) is a unit of length which is well known in the United States. It is also known as a statute mile, and is equivalent to 5280 feet or 1760 yards. The kilometer is not as well understood. ...
... It is a good idea to review certain measurements which are used throughout this document. A mile (abbreviated: mi) is a unit of length which is well known in the United States. It is also known as a statute mile, and is equivalent to 5280 feet or 1760 yards. The kilometer is not as well understood. ...
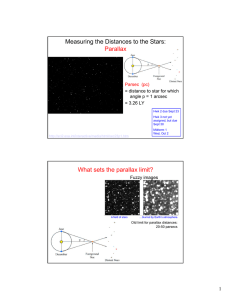
Measuring the Distances to the Stars: Parallax What sets the parallax limit? 1
... • change in temperature • change in luminosity ...
... • change in temperature • change in luminosity ...
The Life Cycles of Stars
... A star’s life cycle is determined by its mass. The larger the mass, the shorter the life cycle. A star’s mass is determined by the amount of matter that is available in its nebula, the giant cloud of gas and dust in which it is born. Over time, gravity pulls the hydrogen gas in the nebula together a ...
... A star’s life cycle is determined by its mass. The larger the mass, the shorter the life cycle. A star’s mass is determined by the amount of matter that is available in its nebula, the giant cloud of gas and dust in which it is born. Over time, gravity pulls the hydrogen gas in the nebula together a ...
Scaling the Universe
... We would like for you to get a “feel” for how far away things in outer space are from the Earth. The distances to these objects are so large that it is hard for us to relate to them as human beings, who are used to dealing with very small distances (relatively speaking). To help us, we will develop ...
... We would like for you to get a “feel” for how far away things in outer space are from the Earth. The distances to these objects are so large that it is hard for us to relate to them as human beings, who are used to dealing with very small distances (relatively speaking). To help us, we will develop ...
The Sun
... A coronal mass ejection (CME) is an ejection of material from the solar corona, usually observed with a white-light coronagraph, such as SOHO’s LASCO instrument. The ejected material is a plasma consisting primarily of electrons and protons (in addition to small quantities of heavier elements such a ...
... A coronal mass ejection (CME) is an ejection of material from the solar corona, usually observed with a white-light coronagraph, such as SOHO’s LASCO instrument. The ejected material is a plasma consisting primarily of electrons and protons (in addition to small quantities of heavier elements such a ...
ES Chapter 30
... – Energy produced in the core of the Sun gets to the surface through two zones in the solar interior. • In the radiative zone, which is above the core, energy is transferred from particle to particle by radiation, as atoms continually absorb energy and then re-emit it. • Above the radiative zone, in ...
... – Energy produced in the core of the Sun gets to the surface through two zones in the solar interior. • In the radiative zone, which is above the core, energy is transferred from particle to particle by radiation, as atoms continually absorb energy and then re-emit it. • Above the radiative zone, in ...
- bYTEBoss
... • The formative and summative assessment will be based on students learning styles. The culminating task will provide students with options so that they can chose how they want to demonstrate their knowledge of the unit. • Specific accommodations and modifications will be given to students as per th ...
... • The formative and summative assessment will be based on students learning styles. The culminating task will provide students with options so that they can chose how they want to demonstrate their knowledge of the unit. • Specific accommodations and modifications will be given to students as per th ...
Document
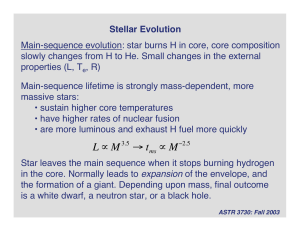
... Radius of the star turning into a red giant is increasing due to the great increase in luminosity being provided by the fusion occurring in a shell around the core. ...
... Radius of the star turning into a red giant is increasing due to the great increase in luminosity being provided by the fusion occurring in a shell around the core. ...
Exercise G1: Our Home Galaxy, the Milky Way
... Question 3: The Sun is moving with a velocity of about 220 km/sec in its orbit about the galactic center. Using your answer from Question 2, what is the approximate time required for the Sun (and the entire Solar System) to complete one orbit of the galactic center? a. 115 million years b. 230 m ...
... Question 3: The Sun is moving with a velocity of about 220 km/sec in its orbit about the galactic center. Using your answer from Question 2, what is the approximate time required for the Sun (and the entire Solar System) to complete one orbit of the galactic center? a. 115 million years b. 230 m ...
Presentation in PDF format.
... Hydrogen-burning is by the CNO-cycle. O stars are always observed close to sites of current or recent star formation. Because of their high luminosities, O stars have very strong stellar winds, observed as asymmetric emission/absorption lines. Material is driven off the star at velocities of several ...
... Hydrogen-burning is by the CNO-cycle. O stars are always observed close to sites of current or recent star formation. Because of their high luminosities, O stars have very strong stellar winds, observed as asymmetric emission/absorption lines. Material is driven off the star at velocities of several ...
Astronomy_in_space_powerpoint Fall 2016
... 2. In what direction does the rim of the bowl push the marble? 3. What force does the rim of the bowl represent? 4. Compare the motion of the marble to that of a satellite around earth. Be sure to include how they are alike and how they are different. ...
... 2. In what direction does the rim of the bowl push the marble? 3. What force does the rim of the bowl represent? 4. Compare the motion of the marble to that of a satellite around earth. Be sure to include how they are alike and how they are different. ...
Notes: Earth`s Atmosphere PowerPoint
... II. Over time, gases were added to the atmosphere by ______________________, and as a result of chemical reactions due to sunlight. III. The ___________ ___________ formed as a result of the chemical reactions. Ozone (O3) is made of three _____________ atoms bonded together. It blocks out __________ ...
... II. Over time, gases were added to the atmosphere by ______________________, and as a result of chemical reactions due to sunlight. III. The ___________ ___________ formed as a result of the chemical reactions. Ozone (O3) is made of three _____________ atoms bonded together. It blocks out __________ ...
Nebular Hypothesis
... Astronomers have only had a good picture of star formation since the advent of infrared astronomy, in the past few decades. They posit the accretion of cold gas onto the star and its disk; so that the gas remains cold unless it is close to the forming Sun. In their model, minerals and ices are inher ...
... Astronomers have only had a good picture of star formation since the advent of infrared astronomy, in the past few decades. They posit the accretion of cold gas onto the star and its disk; so that the gas remains cold unless it is close to the forming Sun. In their model, minerals and ices are inher ...
SES_Book_Interactive 508
... ore than 90% of all the energy that leaves the Sun comes to us in the visible and near-infrared regions of the spectrum, in the form of light and solar heat. Both of these two components vary in step and in phase with changing solar activity: changing by at most a few tenths of a percent in day-to-d ...
... ore than 90% of all the energy that leaves the Sun comes to us in the visible and near-infrared regions of the spectrum, in the form of light and solar heat. Both of these two components vary in step and in phase with changing solar activity: changing by at most a few tenths of a percent in day-to-d ...
Nuclear Reactions Radioactive Decay The stability of an isotope
... U + 1n → 92Kr + 141Ba + 3 1n + energy When U-235 is struck by a neutron, it produces 3 more neutrons which then can react with other uranium atoms creating a chain reaction that can produce massive amounts of energy in under a microsecond. This process is called Nuclear Fission, and is the principle ...
... U + 1n → 92Kr + 141Ba + 3 1n + energy When U-235 is struck by a neutron, it produces 3 more neutrons which then can react with other uranium atoms creating a chain reaction that can produce massive amounts of energy in under a microsecond. This process is called Nuclear Fission, and is the principle ...
1st Year Second Semester Examination - 2013 (EN -1202
... Where the orbits of planets around the Sun are nearly circular, however, the orbits of comets are quite elongated. Nearly 100 known comets have periods (the time it takes them to make one complete trip around the Sun) five to seven Earth years in length. Their farthest point from the Sun ( aphelion ...
... Where the orbits of planets around the Sun are nearly circular, however, the orbits of comets are quite elongated. Nearly 100 known comets have periods (the time it takes them to make one complete trip around the Sun) five to seven Earth years in length. Their farthest point from the Sun ( aphelion ...
3 The detector
... The ANTARES detector, being placed at 43° N in the Mediterranean, observes the sky in the southern hemisphere through the Earth (see Figure 1). It covers a complementary region compared to the South Pole neutrino detector IceCube [1]. In particular it includes the Galactic Centre, a region that rev ...
... The ANTARES detector, being placed at 43° N in the Mediterranean, observes the sky in the southern hemisphere through the Earth (see Figure 1). It covers a complementary region compared to the South Pole neutrino detector IceCube [1]. In particular it includes the Galactic Centre, a region that rev ...
Collapse of the Solar Nebula - Indiana University Astronomy
... from a cloud of gas (from gas to solid or liquid phase) Different kinds of planets and satellites were formed out of ...
... from a cloud of gas (from gas to solid or liquid phase) Different kinds of planets and satellites were formed out of ...
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy - University of Texas Astronomy
... oxygen will be made in its core. But the core will be the left-over white dwarf. The gas put back out into space will come from the red giant’s envelope, which hasn’t been hot enough for fusion to make new elements. Most of the elements in space were put there by supernova explosions. ...
... oxygen will be made in its core. But the core will be the left-over white dwarf. The gas put back out into space will come from the red giant’s envelope, which hasn’t been hot enough for fusion to make new elements. Most of the elements in space were put there by supernova explosions. ...
chap7 (WP)
... established if its surface temperature is known, for example, through the spectrum of its emitted light. Once the luminosity of the star is determined, then the distance to the star can be deduced by measuring the flux from the star. That is, we extract L from the temperature, measure f on Earth, an ...
... established if its surface temperature is known, for example, through the spectrum of its emitted light. Once the luminosity of the star is determined, then the distance to the star can be deduced by measuring the flux from the star. That is, we extract L from the temperature, measure f on Earth, an ...